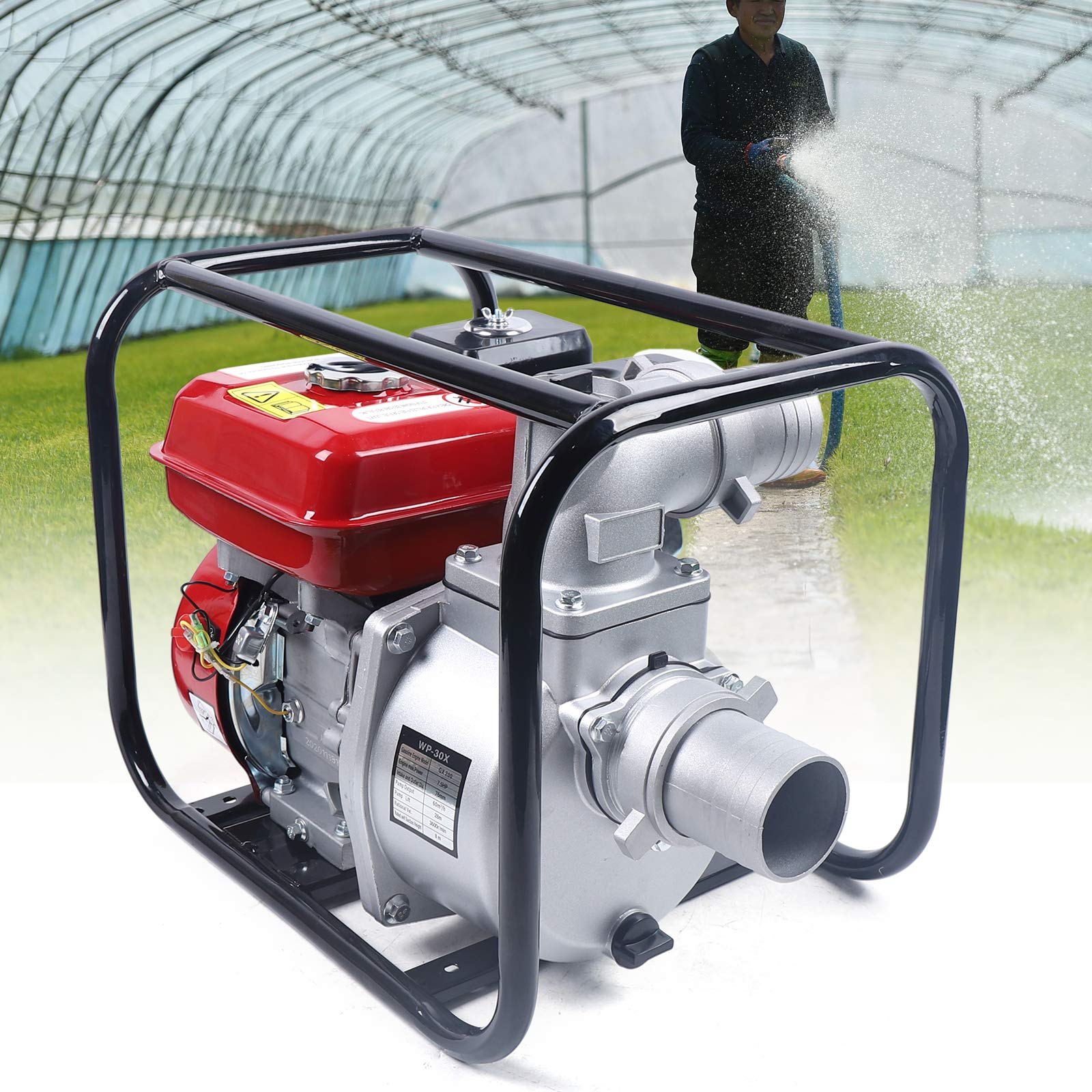
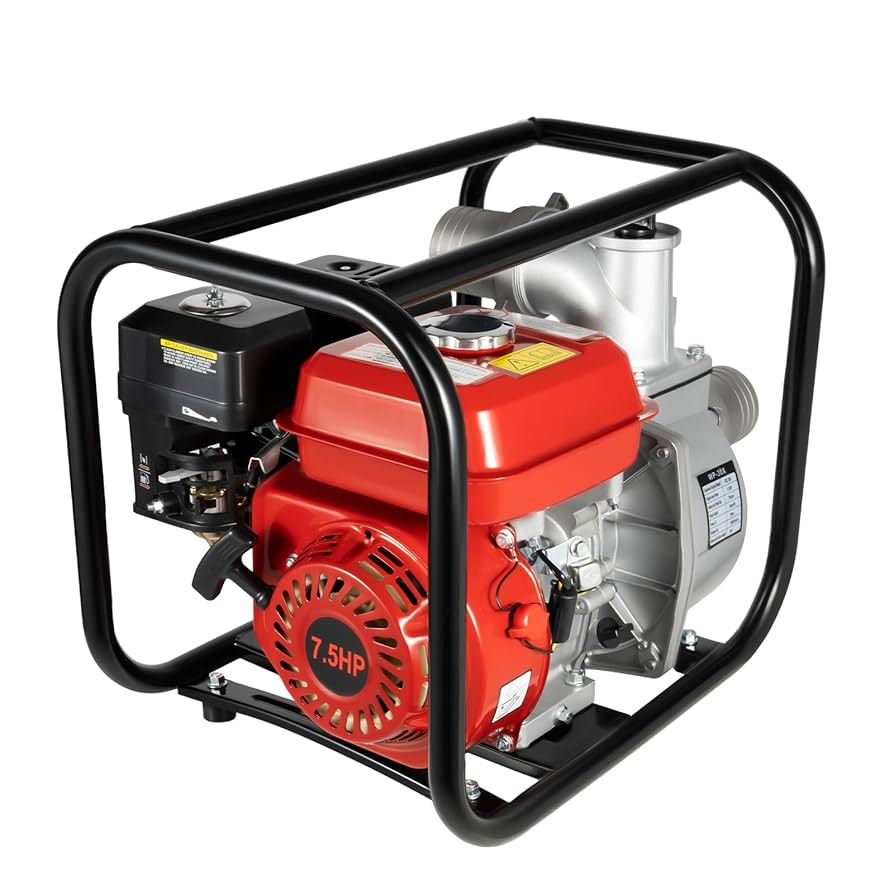
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gasoline irrigation pump
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable gasoline irrigation pumps can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a multitude of options available, decision-makers must navigate through varying types, applications, and specifications to ensure they select the most suitable pump for their irrigation needs. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of gasoline irrigation pumps, including their diverse types—such as high-pressure and self-priming models—and their applications across different sectors, from agriculture to construction.
Moreover, we delve into critical aspects such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the importance of maintenance and durability in pump performance. By empowering buyers with actionable insights and practical strategies, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions that align with operational requirements and budget constraints. Whether you’re a buyer in Nigeria seeking effective irrigation solutions or a distributor in Saudi Arabia looking to expand your product offerings, understanding the intricacies of gasoline irrigation pumps is essential. This guide serves as your roadmap to successfully navigate the global market, ensuring you make choices that enhance productivity and operational efficiency in your projects.
Understanding gasoline irrigation pump Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Pressure Pumps | Designed for high flow rates and pressures; self-priming | Irrigation, hydroseeding, fire suppression | Pros: Efficient for large areas; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Medium-Pressure Pumps | Balanced flow rate and pressure; versatile applications | Agricultural irrigation, water transfer | Pros: Suitable for varied tasks; Cons: May not handle extreme conditions. |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Uses a diaphragm for pumping; ideal for viscous fluids | Chemical transfer, dewatering | Pros: Handles sludges and chemicals; Cons: Limited flow rates. |
| Semi-Trash Pumps | Built to handle solids and debris; rugged construction | Construction sites, drainage | Pros: Durable and reliable; Cons: Maintenance can be intensive. |
| Transfer Pumps | Focused on moving water from one location to another | General irrigation, pool filling | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited to clean water applications. |
What are the Characteristics of High-Pressure Pumps?
High-pressure pumps are engineered to deliver substantial flow rates and pressures, making them ideal for demanding applications such as irrigation and hydroseeding. They often feature self-priming capabilities, allowing for quick setup without extensive priming efforts. B2B buyers should consider the pump’s pressure rating and flow capacity to ensure it meets their specific operational needs. While these pumps can be more expensive upfront, their efficiency in large-scale operations often justifies the investment.
How Do Medium-Pressure Pumps Compare?
Medium-pressure pumps strike a balance between flow rate and pressure, making them versatile for various irrigation and water transfer tasks. These pumps are suitable for agricultural applications where both pressure and volume are essential. Buyers should assess the pump’s compatibility with their existing systems and consider factors such as maintenance requirements and energy efficiency. While they are generally more affordable than high-pressure models, they may not perform well in extreme conditions.
What Makes Diaphragm Pumps Unique?
Diaphragm pumps utilize a flexible diaphragm to create a pumping action, making them particularly effective for transferring viscous fluids, sludges, or chemicals. Their design allows for precise control over flow rates, making them suitable for applications in chemical processing and dewatering. B2B buyers should evaluate the materials used in the diaphragm to ensure compatibility with the substances being pumped. While diaphragm pumps excel in specific applications, their flow rates may be lower than other types.
Why Choose Semi-Trash Pumps for Your Projects?
Semi-trash pumps are designed to handle solids and debris, making them ideal for construction sites and drainage applications. Their rugged construction ensures durability in challenging environments. When purchasing, buyers should consider the pump’s ability to handle specific types of debris and the required maintenance. Although these pumps are reliable, they may require more frequent servicing to maintain optimal performance.
What Are the Benefits of Using Transfer Pumps?
Transfer pumps focus on efficiently moving water from one location to another, making them a staple in irrigation and pool filling applications. These pumps are generally more cost-effective and simpler in design compared to other types. B2B buyers should confirm that the pump is suitable for clean water applications, as they may not be designed to handle solid materials. While they offer a budget-friendly option, their limited capabilities may restrict their use in more complex irrigation systems.
Key Industrial Applications of gasoline irrigation pump
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Gasoline Irrigation Pump | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Crop Irrigation | Ensures optimal water supply for increased crop yields | Evaluate pump capacity, fuel efficiency, and durability |
| Construction | Dewatering for Foundations | Maintains dry conditions for safe and efficient construction | Consider pump size, portability, and ease of setup |
| Landscaping | Watering Large Green Spaces | Promotes healthy plant growth in parks and recreational areas | Assess pump adaptability to various terrains and water sources |
| Fire Safety | Emergency Fire Suppression | Provides immediate water access for firefighting efforts | Focus on pump pressure, flow rate, and compatibility with hoses |
| Mining | Water Transfer for Mineral Processing | Facilitates water management in extraction processes | Check for corrosion resistance and pump mobility |
How is a Gasoline Irrigation Pump Used in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, gasoline irrigation pumps are vital for ensuring that crops receive adequate water throughout their growth cycles. These pumps are particularly useful in regions where electricity is unreliable or unavailable. They help solve the problem of inconsistent water supply, which can lead to crop failure. Buyers in this sector should prioritize pumps with high flow rates and self-priming capabilities to ensure efficient operation in diverse field conditions.
What Role Do Gasoline Pumps Play in Construction?
Construction sites often face challenges with water accumulation, especially during heavy rains. Gasoline irrigation pumps are employed for dewatering foundations, ensuring that the ground remains dry for safe construction work. This application is crucial for maintaining timelines and preventing costly delays. Buyers should consider the pump’s portability and the capacity to handle large volumes of water to meet the demands of various project sizes.
How Are Gasoline Pumps Utilized in Landscaping?
In landscaping, gasoline irrigation pumps are used to water expansive green spaces, such as parks and golf courses. These pumps help maintain healthy vegetation, contributing to the aesthetic appeal and ecological balance of urban areas. For international buyers, especially in regions with limited water infrastructure, selecting a pump that can adapt to different terrains and water sources is essential for effective landscaping solutions.
What is the Importance of Gasoline Pumps in Fire Safety?
Gasoline irrigation pumps are crucial in emergency fire suppression scenarios, providing immediate access to water for firefighting efforts. These pumps can quickly transfer water from nearby sources, ensuring rapid response to fire outbreaks. When sourcing pumps for fire safety, businesses should focus on those with high pressure and flow rates, as these factors significantly impact their effectiveness in emergency situations.
How Are Gasoline Pumps Used in Mining Operations?
In the mining industry, gasoline irrigation pumps facilitate water transfer for mineral processing, playing a vital role in managing water resources during extraction operations. These pumps help prevent water accumulation that could hinder mining activities and ensure that processing plants have a steady water supply. Buyers should consider pumps with corrosion-resistant materials and mobility features, as mining sites often require durable equipment that can withstand harsh environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gasoline irrigation pump’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Optimal Water Pressure for Large Fields
The Problem: B2B buyers managing irrigation for large agricultural fields often face challenges with inadequate water pressure when using gasoline irrigation pumps. This can lead to uneven water distribution, affecting crop yields and wasting resources. Many pumps struggle to deliver the necessary pressure, especially over long distances or in challenging terrain. Buyers may find themselves frustrated when pumps fail to meet the specific demands of their irrigation systems, leading to potential losses in productivity.
The Solution: To ensure optimal water pressure, buyers should carefully select gasoline irrigation pumps that offer higher horsepower and pressure ratings. It is essential to evaluate the pump’s specifications, particularly its maximum pressure (PSI) and flow rate (GPM), to match the requirements of the irrigation system. For instance, a pump with a minimum of 2-inch inlet and outlet ports can enhance flow capacity, making it more suitable for larger operations. Additionally, incorporating a pressure regulator can help maintain consistent pressure throughout the irrigation system. Regular maintenance checks, including cleaning filters and inspecting hoses for leaks, can further optimize performance and ensure that the pump operates at its full potential.
Scenario 2: Frequent Pump Failures Leading to Downtime
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience frequent pump failures, leading to significant downtime during critical irrigation periods. This often stems from improper maintenance, lack of understanding of operational limits, or using pumps that are not suited for specific applications. Such failures can disrupt irrigation schedules, jeopardizing crop health and causing financial losses.
The Solution: Buyers should adopt a proactive maintenance schedule to mitigate pump failures. This includes regular inspections and servicing, such as checking for wear and tear on critical components like seals and impellers. Understanding the operational limits of the chosen pump is crucial; using pumps within their specified range of pressure and flow will prolong their lifespan. Additionally, investing in a durable pump designed for specific conditions—such as those featuring heavy-duty roll cages for protection against harsh environments—can minimize the risk of breakdowns. Training staff on proper operational procedures and maintenance techniques can also help reduce downtime and ensure efficient pump performance.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Fuel Efficiency and Operating Costs
The Problem: Operating gasoline irrigation pumps can lead to high fuel consumption and escalating costs, particularly for large-scale operations. Buyers in regions with fluctuating fuel prices, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, may struggle to keep their irrigation costs under control. This situation is compounded when pumps are not optimized for fuel efficiency, leading to unnecessary expenditures that can affect overall profitability.
The Solution: To enhance fuel efficiency, buyers should consider investing in modern gasoline pumps that utilize advanced engine technology. Models with eco-friendly engines or those designed for lower fuel consumption can significantly reduce operating costs. Additionally, implementing a fuel management plan—such as regularly monitoring fuel usage and scheduling refueling during off-peak hours—can help control expenses. Buyers should also evaluate their irrigation scheduling; using pumps during cooler parts of the day can reduce evaporation losses, allowing for more efficient water usage and minimizing the need for excessive pumping. Training staff on efficient operational practices, such as avoiding unnecessary idling and ensuring proper pump sizing for specific tasks, will further enhance fuel efficiency and reduce costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gasoline irrigation pump
What Are the Key Materials Used in Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
When selecting materials for gasoline irrigation pumps, it is crucial to consider their properties and how they affect the pump’s performance, durability, and cost. Below are some common materials used in the construction of these pumps, along with their advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
How Do Aluminum Components Benefit Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
Aluminum is a popular choice for various components of gasoline irrigation pumps due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressure levels.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and resistant to rust, making it suitable for outdoor applications where moisture is prevalent. Its lightweight characteristic also facilitates easier handling and installation.
Cons: While aluminum is generally cost-effective, it can be more expensive than plastic alternatives. It is also less durable than steel in high-pressure applications, which may limit its use in heavy-duty scenarios.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with a variety of fluids, including water and mild chemicals, but may not be suitable for aggressive solvents or acids.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum alloys is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that the aluminum used is treated for enhanced corrosion resistance, especially in humid climates.
Why Is Stainless Steel a Preferred Material for Pump Components?
Stainless steel is often utilized for critical components in gasoline irrigation pumps due to its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. It can handle temperatures up to 300°C and high pressure, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel ensures a longer lifespan for pump components, reducing maintenance costs. It is also highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which is generally higher than aluminum and plastic. Additionally, stainless steel components can be heavier, potentially complicating installation.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of fluids, including corrosive substances, making it versatile for various irrigation needs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the stainless steel used meets standards such as ASTM A312 for pipes. In regions with strict quality regulations, such as Europe, compliance with EN standards is also crucial.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
Plastic materials, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene, are increasingly used in gasoline irrigation pumps for non-structural components. These materials typically have a temperature rating of around 80°C and can handle low to moderate pressure.
Pros: Plastic is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern. It is also cost-effective, which can be a significant advantage for budget-conscious buyers.
Cons: The main limitation of plastic is its lower durability compared to metals, especially in high-pressure applications. It can also degrade over time when exposed to UV light unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastic is generally compatible with water and some chemicals, but may not be suitable for high-temperature or aggressive fluids.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with relevant standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties. In regions like South America, where UV exposure is high, selecting UV-stabilized plastics is recommended.
How Does Cast Iron Compare as a Material for Pumps?
Cast iron is often used for the housing and structural components of gasoline irrigation pumps due to its strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: Cast iron is highly durable and provides excellent vibration dampening, which can enhance pump performance. Its strength makes it ideal for high-pressure applications.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is its weight, which can complicate transportation and installation. Additionally, cast iron is prone to rust if not properly coated or maintained.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with water and many other fluids but may not be suitable for corrosive environments unless treated.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A48 for gray iron is essential. Buyers in regions with high humidity, like Nigeria, should consider protective coatings to prevent rust.
Summary of Material Selection for Gasoline Irrigation Pumps
| Material | Typical Use Case for gasoline irrigation pump | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Pump casing and impellers | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under high pressure | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Critical components | High strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and heavier weight | High |
| Plastic | Non-structural components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower durability and UV sensitivity | Low |
| Cast Iron | Housing and structural components | Excellent durability and vibration dampening | Heavy and prone to rust without treatment | Medium |
This guide provides essential insights into material selection for gasoline irrigation pumps, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gasoline irrigation pump
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
The manufacturing process of gasoline irrigation pumps involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing pumps for agricultural or industrial applications.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation, where high-quality raw materials are sourced. Common materials include aluminum for the pump casing and impeller, which provide lightweight yet durable properties, and various grades of steel for the engine components. Additionally, rubber is often used for seals and foot mountings to minimize vibration and enhance stability during operation. Suppliers should ideally provide certifications for their raw materials, ensuring they meet industry standards for durability and performance.
How Are Gasoline Irrigation Pumps Formed?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into pump components. Techniques such as die casting for aluminum parts and precision machining for engine components are commonly used. Die casting allows for intricate designs and is particularly effective for producing lightweight yet strong pump casings. Machining processes such as milling and turning ensure that critical dimensions are maintained to high tolerances, which is essential for the pump’s efficiency and longevity.
What Is Involved in the Assembly Process of Gasoline Pumps?
Once the individual components are ready, the assembly stage begins. This process typically involves several sub-steps:
- Component Integration: Various parts, including the engine, impeller, and casing, are assembled using bolts and seals.
- Installation of Electrical Systems: For self-priming pumps, electrical components such as ignition systems are integrated.
- Quality Checks: During assembly, initial quality checks are performed to ensure that parts fit correctly and function as intended.
Effective assembly requires skilled labor and often benefits from the use of jigs and fixtures to maintain alignment and reduce assembly time.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the pump’s durability and appearance. Common techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing or powder coating protect aluminum components from corrosion while providing a visually appealing finish.
- Testing for Seals: After assembly, pumps undergo tests to ensure that seals are properly fitted and leak-free.
- Painting and Branding: Final touches include applying paint for branding and aesthetic appeal, ensuring that the product meets customer specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Gasoline Irrigation Pump Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a pivotal aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that pumps meet international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in establishing a quality management system (QMS) that governs the production processes. Compliance with these standards assures buyers that the manufacturer adheres to consistent quality practices. Additionally, certifications like CE mark and API standards for pumps indicate compliance with European safety regulations and American Petroleum Institute requirements, respectively.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify their quality and compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, regular inspections ensure that processes are performed correctly and that components meet quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed pumps are subjected to rigorous testing, including pressure tests, performance evaluations, and durability assessments.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used?
Common testing methods for gasoline irrigation pumps include:
- Hydraulic Testing: Pumps are tested under pressure to ensure they can handle the specified operational loads without failure.
- Performance Testing: This involves running the pump to measure flow rates, pressure levels, and operational noise to confirm they meet manufacturer specifications.
- Vibration Analysis: Ensures that the pump operates smoothly, reducing wear and extending its operational life.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Here are actionable strategies:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of manufacturing facilities help ensure compliance with quality standards and manufacturing processes.
- Request Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality assurance reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC tests.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an objective evaluation of manufacturing practices and product quality, especially important for international transactions where buyers may not have direct access to manufacturing sites.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific nuances to consider:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the products comply with local regulations and standards, which may differ significantly from the supplier’s country.
- Cultural and Language Barriers: Effective communication is crucial. Employing local representatives or consultants can facilitate better understanding and negotiations.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Understand the logistics involved in shipping, including customs regulations, which can impact delivery timelines and costs.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in the production of gasoline irrigation pumps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gasoline irrigation pump’
Introduction
Procuring a gasoline irrigation pump requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to assist international B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions. By following these steps, you can ensure that your investment meets your agricultural or industrial irrigation needs effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for selecting the right gasoline irrigation pump. Consider factors such as flow rate (GPM), pressure (PSI), and the type of irrigation system you will be using. This clarity will help you narrow down your options and communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
- Flow Rate: Determine the volume of water you need to move and at what speed.
- Pressure Requirements: Assess the pressure needed to deliver water through your irrigation system efficiently.
Step 2: Assess Your Budget Constraints
Understanding your budget is essential in the procurement process. Gasoline irrigation pumps come in a range of prices, influenced by their specifications and brand reputation. Allocate a budget that not only covers the initial purchase but also considers maintenance, operational costs, and potential upgrades.
- Initial Costs: Research average market prices for the specifications you require.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in fuel consumption and maintenance costs over the pump’s lifespan.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This due diligence helps ensure that you partner with a reputable supplier who can deliver quality products and reliable service.
- Supplier Reputation: Investigate online reviews and testimonials to gauge customer satisfaction.
- Industry Experience: Look for suppliers with a strong track record in providing irrigation solutions.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the gasoline irrigation pumps you consider meet local and international standards. Certifications not only indicate product quality but also compliance with safety and environmental regulations. This step is particularly important in regions with strict import laws.
- Quality Standards: Check for ISO certifications or other relevant quality assurance marks.
- Environmental Compliance: Verify that the pumps meet local emissions standards.
Step 5: Request Samples or Demonstrations
Whenever possible, request samples or demonstrations of the gasoline irrigation pumps you are considering. This hands-on experience allows you to evaluate the pump’s performance and suitability for your specific needs. It also provides an opportunity to assess the supplier’s responsiveness and support.
- Performance Testing: Observe how the pump operates under different conditions.
- Supplier Engagement: Gauge the supplier’s willingness to provide support and information during the demonstration.
Step 6: Review Warranty and Service Agreements
Before finalizing your purchase, carefully review the warranty and service agreements provided by the supplier. A comprehensive warranty can protect your investment and provide peace of mind regarding future maintenance and repairs.
- Warranty Coverage: Look for warranties that cover both parts and labor.
- Service Availability: Ensure that the supplier offers accessible service options in your region for ongoing support.
Step 7: Finalize Payment and Delivery Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate and finalize payment and delivery terms. Clear agreements on payment schedules, delivery timelines, and shipping costs are essential to avoid potential disputes later on.
- Payment Options: Discuss various payment methods and any financing options available.
- Delivery Logistics: Confirm the estimated delivery date and shipping arrangements, ensuring they align with your operational needs.
Following this checklist will help streamline your procurement process and ensure that you select the best gasoline irrigation pump for your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gasoline irrigation pump Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
When sourcing gasoline irrigation pumps, understanding the cost structure is vital for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
Materials: The quality of materials directly influences the pump’s durability and efficiency. Common materials include high-grade aluminum for the pump case, robust impellers, and durable engine components. The choice of materials can significantly affect the overall cost.
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the final price of the pump. Skilled labor is often required for assembly and quality control processes, especially in manufacturers that emphasize high-quality outputs.
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and salaries of non-production staff. Efficient manufacturing processes can help in keeping these costs down.
Tooling: Specialized tools and molds for producing specific pump designs can add to the initial investment. These costs are often amortized over production runs, impacting unit pricing.
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control processes ensure that pumps meet specified standards, which is critical for reliability. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the level of scrutiny and testing required.
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping, customs, and handling, play a crucial role in the final price, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and urgency can lead to significant variations in logistics costs.
Margin: Suppliers will typically apply a margin based on their operational costs and desired profit levels. This margin can vary widely depending on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Gasoline Irrigation Pump Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of gasoline irrigation pumps, particularly for B2B transactions:
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in larger volumes often results in lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for minimum order quantities (MOQ), which can be beneficial for buyers looking to make significant purchases.
Specifications and Customization: Customizing pumps to meet specific operational needs can lead to higher prices. Buyers should balance their requirements against budget constraints and consider off-the-shelf options when possible.
Materials and Quality Certifications: Pumps made with higher-quality materials or those that meet specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) typically come at a premium. Buyers should assess the trade-off between price and the expected performance/durability of the pump.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established manufacturers with a proven track record may charge more due to their perceived value and lower risk of product failure.
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can affect the total landed cost of the pumps. Understanding whether the price includes shipping, insurance, and duties is crucial for accurate cost assessment.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable tips to enhance cost-efficiency:
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage volume purchases and long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Building a relationship with suppliers can also facilitate more favorable terms.
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, evaluate ongoing maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. A higher-quality pump may have a higher upfront cost but can save money over its lifespan.
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of local market conditions, tariffs, and currency fluctuations that may affect pricing. Familiarizing yourself with local suppliers can also provide alternatives that may offer better pricing or support.
Evaluate Supplier Capabilities: Assess the supplier’s ability to deliver quality products on time. A cheaper option may lead to higher costs if the supplier fails to meet delivery deadlines or product specifications.
In summary, thorough research and understanding of the cost structure, pricing influencers, and strategic negotiation can significantly benefit B2B buyers in sourcing gasoline irrigation pumps effectively. Always remember that indicative prices can vary widely based on the factors discussed, and it is advisable to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers for a comprehensive comparison.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gasoline irrigation pump With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Gasoline Irrigation Pumps
When considering irrigation solutions, it’s essential to evaluate various technologies and methods that can meet agricultural needs effectively. Gasoline irrigation pumps are popular for their portability and power, but alternatives exist that may suit specific operational contexts better. Below, we compare gasoline irrigation pumps with two viable alternatives: electric irrigation pumps and solar-powered irrigation systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Gasoline Irrigation Pump | Electric Irrigation Pump | Solar-Powered Irrigation System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High pressure and flow rates, ideal for large-scale irrigation | Moderate pressure; may require more time for large areas | Variable performance based on sunlight; best for small to medium areas |
| Cost | Initial cost ranges from $1,025 to $10,585; higher fuel costs | Lower initial cost, typically $500 – $3,000; lower operational costs | Higher initial investment (solar panels, batteries); low operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires fuel supply and regular transportation | Easy to set up with minimal infrastructure | Requires sun exposure and installation of solar panels |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for engine and fuel system | Generally low maintenance, with occasional electrical checks | Minimal maintenance; battery replacement every few years |
| Best Use Case | Suitable for remote areas without electricity; high-demand irrigation needs | Ideal for regions with reliable electricity access; consistent irrigation | Best for areas with abundant sunlight and low water demand; eco-friendly projects |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Electric Irrigation Pumps
Electric irrigation pumps provide a reliable alternative to gasoline-powered options, particularly in regions with stable electrical infrastructure. These pumps are quieter and produce no emissions, making them environmentally friendly. While they may not achieve the same high-pressure outputs as gasoline pumps, they are sufficient for many irrigation tasks. The primary downside is their dependence on a consistent power supply, which may not be available in rural or remote areas.
Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems
Solar-powered irrigation systems represent a sustainable and increasingly popular choice, especially in regions with abundant sunlight. These systems harness solar energy to power pumps, leading to low operational costs after the initial investment. They are particularly advantageous for environmentally conscious businesses and can be deployed in areas with limited access to conventional power sources. However, their performance can fluctuate based on weather conditions, and the upfront cost for installation can be significantly higher than other solutions.
How to Choose the Right Irrigation Solution for Your Needs
When selecting an irrigation solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, including the scale of irrigation, location, budget, and environmental impact. Gasoline pumps are robust and effective for high-demand scenarios, particularly in remote locations. Conversely, electric pumps are best for operations with reliable electricity, while solar solutions cater to sustainability-focused initiatives. By evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their agricultural goals and operational capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gasoline irrigation pump
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
Understanding the technical specifications of gasoline irrigation pumps is crucial for B2B buyers in agriculture and water management sectors. Here are some essential properties to consider:
Power Output (HP)
The horsepower (HP) rating indicates the pump’s capacity to handle various irrigation tasks. Common ratings range from 5.5 HP to 23 HP. Higher HP ratings typically allow for greater water flow and pressure, making it essential for large-scale irrigation projects. Buyers should assess the power requirements based on the area to be irrigated and the type of crops being grown.Flow Rate (GPM)
Flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM), indicates how much water the pump can move within a specific timeframe. Typical flow rates for gasoline irrigation pumps can vary significantly, from 126 GPM to over 300 GPM. Understanding the flow rate is vital for ensuring that the pump can meet the irrigation demands of the intended application, especially in regions with high agricultural output.Self-Priming Capability
A self-priming pump can draw water from a source without needing manual priming. This feature is especially beneficial in remote areas where access to water may be limited. Self-priming pumps reduce setup time and labor costs, making them a preferred choice for B2B buyers focusing on efficiency.Material Construction
The materials used in the pump, such as aluminum or stainless steel, affect durability and corrosion resistance. Aluminum pumps are lightweight and often more affordable, while stainless steel models offer superior durability, especially in harsh environments. Buyers should consider the local climate and water quality when choosing the material grade, as this impacts the pump’s longevity and performance.Suction and Discharge Size
The diameter of the suction and discharge ports determines the volume of water that can be moved. Common sizes include 2”, 3”, and 4”. Selecting the right sizes based on the irrigation layout and equipment compatibility is crucial for optimal performance. Mismatched sizes can lead to inefficiencies and increased wear on the pump.Maximum Pressure (PSI)
Maximum pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), is essential for determining how far water can be pushed and the types of irrigation systems the pump can effectively support. For example, higher PSI ratings are necessary for systems that require water to be transported over long distances or to elevated areas.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
Familiarity with industry jargon is key to effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are several essential terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of gasoline irrigation pumps, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can impact product reliability and warranty considerations.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for budget-conscious buyers, as purchasing below the MOQ may result in higher per-unit costs or the inability to place an order.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers solicit price quotes from suppliers. This document outlines specific requirements, such as technical specifications and quantities, allowing buyers to compare offers effectively.Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps mitigate risks associated with shipping, insurance, and customs clearance.Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order until delivery. Knowing the lead time is essential for planning irrigation schedules, especially in regions where timely water application is critical for crop health.Warranty Period
The warranty period specifies the duration that a product is guaranteed against defects. For gasoline irrigation pumps, a longer warranty can indicate higher confidence in product quality and durability, providing peace of mind for buyers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their irrigation systems’ efficiency and effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gasoline irrigation pump Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Gasoline Irrigation Pump Sector?
The gasoline irrigation pump market is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. Increasing agricultural productivity demands, especially in regions like Africa and South America, are pushing for efficient irrigation solutions. The rise in smallholder farming and the need for cost-effective irrigation methods further fuel this demand. Additionally, urbanization and climate change are leading to more erratic weather patterns, prompting farmers to adopt irrigation systems that can quickly adapt to varying water availability.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends in this sector. For instance, the integration of IoT devices in gasoline pumps is enhancing monitoring capabilities, allowing users to track performance metrics in real-time. This not only improves operational efficiency but also aids in predictive maintenance, reducing downtime. Furthermore, manufacturers are increasingly offering customizable solutions, such as different horsepower options and pump configurations, catering to the diverse needs of international buyers.
International B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape characterized by fluctuating fuel prices and varying regulatory environments across regions. In markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, where irrigation is critical due to arid conditions, understanding local regulations and sourcing from reliable suppliers can significantly impact operational success.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Addressed in the Gasoline Irrigation Pump Market?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies within the gasoline irrigation pump sector. The environmental impact of gasoline-powered pumps, particularly concerning emissions and resource consumption, has prompted stakeholders to seek solutions that minimize ecological footprints. Manufacturers are increasingly pursuing ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are looking for suppliers who prioritize fair labor practices and environmentally friendly materials. This trend is particularly evident in regions where consumers are becoming more conscious of the origins of their products. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers that provide transparency in their supply chains and adhere to ethical sourcing standards.
Moreover, advancements in technology are leading to the development of hybrid and alternative fuel options for irrigation pumps, reducing reliance on gasoline. Buyers should consider these options not only for their lower environmental impact but also for potential cost savings in the long term.
What Is the Evolution of the Gasoline Irrigation Pump Industry?
The gasoline irrigation pump industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by manual and less efficient systems, the market has seen a shift towards more advanced, engine-driven pumps that offer improved performance and reliability. The introduction of self-priming features and durable materials has enhanced the usability and lifespan of these pumps.
In recent years, the emphasis on technology and efficiency has driven the development of high-pressure pumps capable of meeting the needs of modern agriculture. This evolution reflects a broader trend in the agricultural sector, where innovation and efficiency are critical to addressing the challenges posed by climate change and global food demands. As the industry continues to adapt, international B2B buyers must stay informed about these advancements to make strategic sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gasoline irrigation pump
How do I choose the right gasoline irrigation pump for my needs?
Selecting the appropriate gasoline irrigation pump requires assessing your specific irrigation needs, including the required flow rate (GPM), pressure (PSI), and the type of water being pumped (clean, semi-trash, or chemical). Consider the pump’s size and portability, particularly if you operate in varied terrains. Additionally, evaluate the pump’s self-priming capabilities and ease of maintenance. Engage with suppliers to understand the features of their models and request demonstrations if possible.What specifications should I look for in a high-pressure gasoline irrigation pump?
When sourcing a high-pressure gasoline irrigation pump, focus on its maximum pressure rating, which is crucial for effective irrigation. Look for specifications such as flow rate (GPM), inlet and outlet sizes, and whether it has self-priming capabilities. Assess the pump’s durability and materials, especially if it will be used in harsh environments. It’s also essential to verify compliance with local regulations regarding emissions and safety standards.What are the typical payment terms for international purchases of gasoline irrigation pumps?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary significantly between suppliers. Common terms include a percentage upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or escrow services to secure the transaction. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring adequate protection against risks. Always clarify any additional fees, such as currency conversion or bank transfer charges.What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for gasoline irrigation pumps?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for gasoline irrigation pumps typically depend on the supplier and the specific model. Some manufacturers may have an MOQ of one unit for standard models, while others may require a larger order to justify production or shipping costs. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about flexibility in MOQs, especially if you are testing the market or establishing a new relationship.How can I ensure the quality of gasoline irrigation pumps before purchasing?
To ensure quality, request product certifications and compliance documents, such as ISO or CE certifications. Conduct due diligence on the supplier by reviewing customer testimonials, checking their manufacturing processes, and understanding their quality assurance protocols. If possible, arrange for product samples or visits to the manufacturing site. Engaging third-party inspection services can provide additional assurance of product quality before shipment.What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing gasoline irrigation pumps?
Logistics play a critical role in the timely delivery of gasoline irrigation pumps. Consider factors such as shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs clearance requirements, and local regulations regarding the import of gasoline-powered equipment. Work closely with your supplier to ensure they provide the necessary shipping documentation. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to customs or shipping congestion, especially during peak seasons.Are there customization options available for gasoline irrigation pumps?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor gasoline irrigation pumps to specific needs. Customizations may include modifications to flow rates, sizes, or the addition of specialized features like enhanced filtration systems. Discuss your requirements with the supplier to explore available options. Keep in mind that customized products may involve longer lead times and higher costs, so factor these into your planning.What after-sales support should I expect from suppliers of gasoline irrigation pumps?
After-sales support varies by supplier, but you should expect assistance with installation, maintenance guidance, and warranty services. Inquire about the availability of spare parts and the supplier’s response time for repairs or replacements. Reliable suppliers often provide training for your staff on proper operation and maintenance practices. Establishing a clear communication channel for ongoing support can greatly enhance your operational efficiency.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Gasoline Irrigation Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
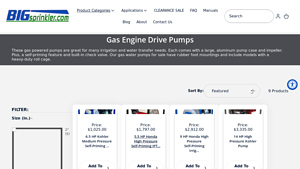
1. Big Sprinkler – Gas Engine Drive Pumps
Domain: bigsprinkler.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Gas Engine Drive Pumps are designed for various irrigation and water transfer needs. Key features include:
– Large aluminum pump case and impeller
– Self-priming feature
– Built-in check valve
– Rubber foot mountings
– Models available with heavy-duty roll cage
Available sizes:
– 2″ (5 products)
– 2-1/2″ (1 product)
– 2.5″ (2 products)
– 3″ (1 product)
Max Flow Range (GPM):
– 100 (1 product)
– 1…
2. Honda – Water Pumps
Domain: powerequipment.honda.com
Registered: 1989 (36 years)
Introduction: Honda offers a complete line-up of water pumps including centrifugal, submersible, and diaphragm pumps. These gas-powered pumps are driven by Honda GX Series commercial-grade engines known for quick starts, reliability, impressive performance, and fuel efficiency. Honda pumps are designed to move liquids quickly, safely, quietly, and easily, making them suitable for tough tasks. The pumps feature …
3. Rainflo – 6 HP Portable Water Pump
Domain: rainfloirrigation.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Portable Water Pumps:
1. 6 HP Portable Water Pumps:
– Engine: Honda
– Features: Direct mounted to an AMT aluminum pump, made in the USA, excellent for sprinklers, drip irrigation, small guns, filling tanks.
– Operation: Runs 2.5 hours on a tank of gas; approx. 12 hours with larger tank.
– Item #2P5XHR: 2″ Pressure Pump W/ Roll Cage – Price: $865.00
– Item #2S5XHR: 2″ Trash Pump W/ …
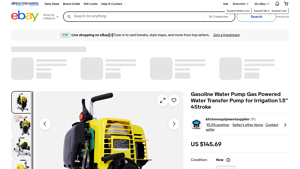
4. Gasoline – Water Transfer Pump
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“title”: “Gasoline Water Pump Gas Powered Water Transfer Pump for Irrigation 1.5” 4Stroke”, “condition”: “New”, “price”: “$145.69”, “monthly_payment”: “As low as $49.70/mo with Klarna”, “shipping”: “Free shipping”, “estimated_delivery”: “Tue, Sep 9 – Sat, Sep 13”, “quantity_available”: “More than 10 available”, “item_number”: “286684849378”, “main_color”: “Yellow”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gasoline irrigation pump
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
In the competitive landscape of agricultural equipment, strategic sourcing of gasoline irrigation pumps is essential for maximizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. B2B buyers should prioritize pumps that feature robust construction, such as aluminum pump cases and self-priming capabilities, to ensure reliability in diverse conditions. Additionally, understanding the variety of options available—ranging from high-pressure models to specialized pumps for chemical transfer—can significantly enhance irrigation strategies.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Agricultural Operations?
Employing strategic sourcing not only lowers procurement costs but also ensures access to high-quality products that meet specific agricultural needs. By fostering relationships with reputable suppliers, buyers can benefit from better pricing, improved after-sales support, and timely delivery, which are critical in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Does the Future Hold for International B2B Buyers of Gasoline Irrigation Pumps?
As global agricultural demands increase, the market for gasoline irrigation pumps is poised for growth. International buyers are encouraged to stay informed about technological advancements and to explore partnerships that can enhance their sourcing strategies. Investing in quality pumps today will yield sustainable benefits, ensuring agricultural productivity and resilience for the future.