Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pumping lake water for irrigation
In an era where water scarcity looms large and agricultural sustainability becomes paramount, effectively pumping lake water for irrigation emerges as a strategic solution for many B2B buyers across the globe. However, the challenge lies in navigating the complexities of sourcing, installing, and maintaining these systems in diverse geographical contexts. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process, offering insights into various types of lake irrigation systems, their applications, and best practices for supplier vetting.
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia—will find actionable information tailored to their unique environments and regulatory frameworks. We will delve into the cost considerations associated with different pump systems, the legalities of water usage, and the environmental benefits of utilizing natural water sources for irrigation.
By equipping decision-makers with critical knowledge and resources, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that not only optimize their irrigation efforts but also contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. Whether you are managing a large-scale agricultural operation or a smaller farming venture, understanding the nuances of lake water irrigation can transform your approach to water management and enhance your operational efficiency.
Understanding pumping lake water for irrigation Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pumps | High flow rates, self-priming, durable materials | Large agricultural fields, sports facilities | Pros: Efficient, low maintenance. Cons: Initial cost may be high. |
| Submersible Pumps | Operates underwater, compact design | Residential and small-scale commercial gardens | Pros: Space-saving, quiet operation. Cons: Limited flow rates. |
| Solar-powered Pumps | Utilizes renewable energy, ideal for remote locations | Sustainable farming, eco-friendly projects | Pros: Low operating costs, environmentally friendly. Cons: Dependent on sunlight availability. |
| Diesel-powered Pumps | High power output, suitable for heavy-duty applications | Large-scale irrigation, construction sites | Pros: Strong performance, reliable in remote areas. Cons: Higher fuel costs, environmental concerns. |
| Floating Pumps | Accessible from the water surface, minimal installation | Lakeside parks, golf courses, and waterfront properties | Pros: Easy deployment, versatile use. Cons: Potential for debris clogging. |
What Are the Characteristics of Centrifugal Pumps for Lake Water Irrigation?
Centrifugal pumps are a popular choice for large-scale irrigation due to their ability to handle high flow rates and self-priming capabilities. These pumps are typically constructed from durable materials, ensuring longevity and resistance to corrosion. They are suitable for extensive agricultural fields and sports facilities, where significant water supply is necessary. When considering a centrifugal pump, B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment against the long-term efficiency and low maintenance requirements.
How Do Submersible Pumps Differ in Lake Water Irrigation Applications?
Submersible pumps are designed to operate underwater, making them compact and efficient for smaller applications. Their quiet operation and minimal surface disruption make them ideal for residential gardens and small commercial landscapes. Buyers should consider the flow rate limitations of submersible pumps, as they may not meet the demands of larger irrigation systems, but their space-saving design is a significant advantage for limited areas.
Why Choose Solar-powered Pumps for Sustainable Irrigation Solutions?
Solar-powered pumps harness renewable energy, making them an ideal solution for remote locations where traditional power sources may be unavailable. These systems are particularly beneficial for sustainable farming and eco-friendly projects, reducing operating costs significantly. However, B2B buyers must consider the reliability of sunlight in their region, as cloudy or rainy conditions can impact pump performance.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Diesel-powered Pumps in Irrigation?
Diesel-powered pumps deliver high power output, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications like large-scale irrigation and construction sites. Their reliability in remote areas is a strong selling point, especially when electricity access is limited. However, B2B buyers should be aware of the higher fuel costs and potential environmental concerns associated with diesel use, which may influence long-term sustainability goals.
How Do Floating Pumps Enhance Accessibility and Versatility?
Floating pumps offer the unique advantage of being easily accessible from the water surface, requiring minimal installation effort. They are versatile and can be employed in various settings, such as lakeside parks and golf courses. While floating pumps provide ease of deployment, buyers should consider the potential for debris clogging, which may necessitate regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Key Industrial Applications of pumping lake water for irrigation
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Irrigation for Crop Production | Cost-effective water source with high nutrient content | Pump capacity, energy efficiency, regulatory compliance |
| Landscape Management | Maintenance of Commercial Green Spaces | Enhanced aesthetic value and sustainability | System scalability, ease of installation, maintenance support |
| Golf Course Management | Irrigation of Fairways and Greens | Improved turf quality and reduced operational costs | Pump reliability, water quality management, environmental impact |
| Construction & Development | Dust Suppression and Site Irrigation | Efficient water usage reduces project delays and costs | Water access rights, pump durability, local environmental laws |
| Aquaculture | Water Supply for Fish Farming | Sustainable water source promoting healthy aquatic life | Water quality monitoring, pump specifications, regulatory checks |
How is Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation Used in Agriculture?
Pumping lake water for irrigation in agriculture enables farmers to utilize a readily available water source for crop production. This method addresses the challenge of water scarcity, particularly in regions where traditional water sources are limited. The nutrient-rich lake water can enhance soil fertility, leading to better crop yields. Buyers in this sector should consider pump capacity and energy efficiency to ensure optimal performance while remaining compliant with local water use regulations.
What Role Does Lake Water Play in Landscape Management?
In landscape management, pumping lake water is essential for maintaining commercial green spaces, parks, and recreational areas. This sustainable irrigation solution not only reduces costs associated with municipal water supply but also enhances the aesthetic appeal of landscaped areas. Buyers should focus on system scalability and ease of installation, ensuring that the irrigation systems can adapt to varying landscape sizes and types while receiving adequate maintenance support.
How is Pumping Lake Water Beneficial for Golf Course Management?
Golf course management relies heavily on consistent irrigation for maintaining the quality of fairways and greens. By utilizing lake water, golf courses can reduce operational costs while ensuring the turf remains healthy and vibrant. The challenge lies in ensuring the reliability of the pumping systems and managing water quality to avoid any detrimental effects on the turf. Buyers must evaluate pump reliability and water quality management practices to maintain the course’s standards while complying with environmental regulations.
In What Ways is Lake Water Used in Construction & Development Projects?
In construction and development, pumping lake water is used for dust suppression and site irrigation. This method promotes efficient water usage, helping to minimize project delays caused by adverse weather conditions. However, securing water access rights and understanding local environmental laws are crucial for compliance. Buyers should prioritize pump durability and regulatory compliance to ensure that their operations are both effective and sustainable.
How Does Pumping Lake Water Support Aquaculture?
Aquaculture operations benefit significantly from pumping lake water as it provides a sustainable water source for fish farming. This practice supports healthy aquatic life by maintaining optimal water conditions. Buyers in this sector need to focus on water quality monitoring and specific pump specifications to ensure the health of the aquatic ecosystem while adhering to regulatory checks. This approach not only promotes sustainability but also enhances the overall productivity of aquaculture operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pumping lake water for irrigation’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Legal Regulations for Water Extraction
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly in regions with strict water regulations like parts of Africa and Europe, often face challenges in understanding the legalities surrounding the extraction of lake water for irrigation. They may be concerned about potential fines, legal disputes, or environmental repercussions if they inadvertently violate local water rights laws or environmental protection guidelines. This uncertainty can lead to hesitance in investing in lake water pumping systems, resulting in lost opportunities for cost-effective irrigation solutions.
The Solution: To navigate these legal complexities, it is crucial to conduct thorough research on local water regulations before proceeding with any lake water extraction. Engage with local authorities such as environmental protection agencies or water resource departments to obtain the necessary permits and understand the specific guidelines for using lake water. Additionally, consider consulting legal experts who specialize in environmental law to ensure compliance. Establishing a clear understanding of riparian rights, water use limitations, and any seasonal restrictions can help create a sustainable irrigation strategy that aligns with legal requirements.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Water Quality for Irrigation
The Problem: Another significant concern for B2B buyers is the quality of lake water used for irrigation. Contaminants, algae blooms, and varying nutrient levels can affect the health of crops and gardens. Buyers may worry about the potential for introducing pathogens or harmful chemicals into their irrigation systems, leading to crop damage or reduced yields. This fear can deter them from utilizing lake water, opting instead for expensive municipal water sources.
The Solution: To ensure high-quality water for irrigation, buyers should invest in comprehensive water testing before implementation. This includes analyzing parameters such as pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and the presence of harmful microorganisms. Collaborate with local agricultural extension services or water quality laboratories to conduct these tests regularly. Furthermore, integrating a filtration system into the pumping setup can help remove debris and contaminants, providing cleaner water for irrigation. Choosing pumps with built-in filtration or easy-to-install external filters can enhance water quality while minimizing maintenance efforts.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Infrastructure Limitations for Pumping Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter logistical challenges related to the infrastructure required for effective lake water pumping systems. Issues such as inadequate power supply, unsuitable terrain, or the absence of existing irrigation frameworks can complicate the installation and operation of these systems. This can lead to increased installation costs and operational inefficiencies, ultimately discouraging businesses from pursuing lake water irrigation.
The Solution: To address these infrastructure limitations, buyers should conduct a comprehensive site assessment before installing a pumping system. This involves evaluating the power availability—whether it can support the required pump specifications—and identifying the most efficient routing for water transport. For sites with challenging terrains, consider using portable or modular pumping solutions that can be easily relocated as necessary. Additionally, investing in solar-powered pumps can mitigate power supply issues while promoting sustainability. Collaborating with experienced irrigation system designers can also provide tailored solutions that enhance efficiency and performance, ensuring that the system is both effective and cost-efficient.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pumping lake water for irrigation
What Are the Key Materials for Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation?
When selecting materials for pumping lake water for irrigation, businesses must consider several factors, including durability, compatibility with the environment, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in irrigation pumping systems.
1. Thermoplastic Materials
Key Properties:
Thermoplastics, such as PVC and polyethylene, exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and are lightweight, making them suitable for various irrigation applications. They can typically handle temperatures up to 140°F (60°C) and pressures around 42 PSI.
Pros & Cons:
Thermoplastics are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, allowing for rapid production and installation. However, they may not be as durable as metals under extreme conditions, leading to potential wear and tear over time.
Impact on Application:
These materials are compatible with various media, including lake water, but may require additional filtration to prevent clogging from debris.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding plastic materials. Standards like ASTM for the US and DIN for Europe may apply, influencing material selection.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers exceptional corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and the ability to withstand higher temperatures and pressures compared to thermoplastics.
Pros & Cons:
While stainless steel is highly durable and suitable for long-term use, it comes at a higher cost and can be more complex to manufacture and install. The weight of stainless steel can also be a consideration in transport and installation.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is ideal for pumping systems that require high reliability and longevity, especially in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers must be aware of compliance with standards such as ISO and ASTM for stainless steel components. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are prevalent, the ability to withstand extreme conditions is crucial.
3. Cast Iron
Key Properties:
Cast iron is known for its strength and durability, with excellent pressure ratings and the ability to handle high flow rates.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of cast iron is its longevity and resistance to wear. However, it is heavier and more expensive than thermoplastics, and it may require additional maintenance to prevent rust.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is suitable for larger irrigation systems where high flow rates are necessary, but it may not be ideal for all environments due to its susceptibility to corrosion in saline or acidic waters.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider local environmental conditions and regulations regarding the use of cast iron. Compliance with standards like JIS in Japan or EN in Europe may also affect material selection.
4. Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics (FRP)
Key Properties:
FRP combines the lightweight nature of plastics with the strength of fiberglass, offering high corrosion resistance and the ability to handle a wide range of temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons:
FRP is highly durable and can be molded into complex shapes, making it versatile for various applications. However, it is generally more expensive than traditional plastics and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
FRP is particularly effective in environments where chemical resistance is necessary, such as in areas with high algae growth in lake water.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, understanding compliance with environmental regulations is critical, as well as adhering to standards like ASTM and ISO for FRP materials.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic Materials | Residential and small-scale irrigation systems | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Commercial and large-scale irrigation systems | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex installation | High |
| Cast Iron | High-flow irrigation applications | Longevity and strength | Heavier and requires maintenance | Medium |
| Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics | Specialized applications with chemical resistance | Lightweight and versatile | Higher cost and specialized manufacturing | High |
This guide provides a strategic overview of material selection for pumping lake water for irrigation, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pumping lake water for irrigation
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Irrigation Pumps?
The manufacturing process of irrigation pumps designed for pumping lake water involves several critical stages, each ensuring that the final product meets the necessary performance and quality standards.
Material Preparation: The initial stage involves selecting appropriate materials, such as thermoplastic for pump casings and heavy-duty PVC for hoses. Suppliers typically focus on corrosion-resistant materials to withstand harsh environmental conditions, particularly in regions with varying climates like Africa and the Middle East. The preparation phase also includes sourcing materials that meet international standards, ensuring that they are environmentally friendly and sustainable.
Forming: In this stage, the raw materials are shaped into the required components using techniques such as injection molding for plastic parts and die casting for metal components. Advanced technologies like CNC machining may be employed for precision parts, which is particularly essential in ensuring that pumps operate efficiently under different pressure and flow conditions.
Assembly: The assembly process is critical, as it involves bringing together all individual components, including pumps, filters, and hoses. Automated assembly lines may be used for mass production, while more complex systems may require skilled technicians for hand assembly. This stage often incorporates quality checks to ensure that all components fit correctly and function as intended.
Finishing: After assembly, the products undergo finishing processes, which may include surface treatments to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Painting, coating, or polishing are common techniques used to improve durability and appearance. Additionally, this stage ensures that any potential defects are addressed before the product is packaged for shipment.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Irrigation Pumps?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing process to ensure that irrigation pumps are reliable and perform optimally. Various international and industry-specific standards govern the QA processes.
International Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. This standard emphasizes customer satisfaction, continuous improvement, and a systematic approach to managing processes. Compliance with ISO standards is crucial for manufacturers looking to enter international markets.
Industry-Specific Certifications: In addition to ISO, certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for compliance with European safety standards and API (American Petroleum Institute) for pumps used in oil and gas applications may be relevant. These certifications assure B2B buyers that the products meet specific industry requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints: Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checks are performed to monitor the production process and identify any deviations from quality standards.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, the final products undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they meet performance specifications.Common Testing Methods: Manufacturers utilize several testing methods to validate the quality of irrigation pumps, including:
– Hydraulic Testing: Ensuring that pumps can handle specified pressures without leakage.
– Performance Testing: Measuring flow rates and efficiency under different operational conditions.
– Durability Testing: Simulating long-term usage to identify potential failures.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential. Here are some effective strategies:
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess manufacturing processes, quality control practices, and adherence to international standards. An audit can reveal a supplier’s commitment to quality and help identify any areas for improvement.
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC processes. These reports should outline testing results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies can conduct inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with agreed-upon specifications.
Certification Verification: Buyers should verify the authenticity of certifications claimed by suppliers. This can often be done through official certification bodies or industry associations, ensuring that the supplier meets the necessary quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with suppliers from different regions, international B2B buyers should be aware of specific quality control nuances:
Regional Standards Variability: Different regions may have varying regulations and standards, which can affect product compliance. Buyers must ensure that the products meet the requirements of their own market while also considering the standards of the supplier’s region.
Cultural Differences in Quality Perception: Quality expectations may differ across cultures. Understanding these differences can help buyers communicate their requirements more effectively and establish clearer quality benchmarks.
Logistical Challenges: Importing products from international suppliers can introduce complexities such as customs regulations and transportation issues. Buyers should factor in these elements when evaluating supplier quality control processes.
Long-Term Relationships: Building a long-term relationship with reliable suppliers can lead to better quality assurance over time. Regular communication and collaboration can help ensure that quality standards are consistently met and adapted to evolving market needs.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting irrigation pump suppliers, ensuring that they receive high-quality, reliable products suitable for their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pumping lake water for irrigation’
This guide serves as a practical sourcing checklist for businesses looking to procure solutions for pumping lake water for irrigation. With the increasing demand for sustainable water management solutions, leveraging natural water sources can significantly reduce costs and enhance irrigation efficiency. Follow these steps to ensure a successful procurement process.
Step 1: Assess Your Water Needs and Requirements
Begin by evaluating the specific irrigation needs of your operations. Consider factors such as the volume of water required, the type of crops or landscape being irrigated, and the distance from the lake to the irrigation site. Understanding these requirements will help you determine the capacity and specifications of the pumping system necessary for effective irrigation.
Step 2: Research Local Regulations and Permits
Before proceeding, familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding the extraction of water from lakes. Many regions have specific laws governing water usage, environmental protection, and sustainability practices. Consult with local authorities or environmental agencies to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal complications.
Step 3: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications required for your pumping system. This includes pump capacity (measured in horsepower), the type of pump (centrifugal or submersible), and the necessary accessories such as filters, hoses, and valves. Having detailed specifications will facilitate effective communication with suppliers and help you identify suitable products that meet your operational needs.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reliable suppliers who specialize in irrigation pumping systems. Assess their experience in the industry, product offerings, and customer feedback. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other businesses in similar sectors to validate their capabilities and reputation.
Step 5: Compare Product Features and Costs
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, compare their product features, warranties, and pricing structures. Look for pumps that offer high efficiency, durability, and ease of installation. Ensure that the cost aligns with your budget while also considering the long-term operational savings from using lake water instead of paid water sources.
Step 6: Ensure After-Sales Support and Maintenance Services
Select suppliers that provide comprehensive after-sales support, including installation guidance and maintenance services. A reliable supplier should offer training for your staff on proper operation and maintenance of the pumping system. This support is crucial to ensure longevity and efficiency in your irrigation practices.
Step 7: Negotiate Contracts and Terms
Finally, negotiate the terms of the purchase contract, ensuring clarity on delivery timelines, payment terms, and warranty conditions. Pay attention to the fine print regarding service agreements and replacement parts. A well-negotiated contract will protect your investment and establish a strong relationship with your supplier for future needs.
By following this structured checklist, you can confidently navigate the procurement process for pumping lake water for irrigation, ensuring that you select the best solutions tailored to your business requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pumping lake water for irrigation Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation?
When considering the costs associated with pumping lake water for irrigation, several key components come into play. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The primary materials involved in the irrigation system include pumps, filters, hoses, and connectors. Depending on the specifications and quality, the cost of these materials can vary significantly. For example, durable, high-capacity pumps may range from $1,078 to $1,549, while filters and hoses add to the total expenditure.
Labor: Labor costs encompass installation and maintenance. Skilled technicians are often required for proper installation, which can incur additional charges. The complexity of the irrigation system will also affect labor costs, as larger systems necessitate more manpower.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the production of irrigation components such as factory operations, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Suppliers may pass these costs onto buyers, impacting the overall pricing structure.
Tooling: Customization in irrigation solutions may require specialized tooling, which can increase initial costs. However, such investments can lead to better long-term efficiency and reliability.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that all components meet industry standards is essential for operational efficiency. Quality control processes may add to costs, but they are crucial for preventing future failures that could lead to costly repairs.
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs must also be factored in, especially for international buyers. These can vary based on the distance from the supplier, shipping method, and any tariffs that may apply.
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on the market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation?
Several factors influence the pricing of irrigation systems for lake water, particularly for international buyers:
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often have tiered pricing structures, so understanding MOQs can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions tailored to specific irrigation needs may incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the additional expense.
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. High-quality, corrosion-resistant materials may cost more upfront but can lead to lower maintenance costs over time.
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or have certifications may come at a premium but can provide peace of mind regarding reliability and efficiency.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency in Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency:
Negotiation: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing with suppliers. Many are open to discussions, especially for larger orders.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Factor in installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs to make a more informed decision.
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Get quotes from multiple suppliers to compare prices and services. This can also provide leverage in negotiations.
Research Local Regulations: Understanding the legalities of water usage for irrigation in your region can prevent costly penalties and help in negotiating with suppliers.
Plan for Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new technologies.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier changes, and specific project requirements. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pumping lake water for irrigation With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives for Irrigation Solutions
When considering irrigation methods, it’s vital to evaluate various alternatives to pumping lake water. Each solution presents unique advantages and challenges, making it essential for B2B buyers to analyze their specific needs in terms of performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases. Below is a comparative analysis of pumping lake water against two viable alternatives: groundwater pumping and rainwater harvesting systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Pumping Lake Water For Irrigation | Groundwater Pumping | Rainwater Harvesting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High nutrient content; reliable supply from self-sustaining lakes | Consistent water supply; varies based on aquifer recharge | Variable based on rainfall; effective in rainy seasons |
| Cost | Lower operational costs; initial setup costs can be moderate | Higher energy costs for pumping; potential licensing fees | Low operational costs; initial setup can be high |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires infrastructure for pumping; relatively easy to set up | Requires drilling and installation of pumps; complex permitting | Requires installation of collection systems; moderate complexity |
| Maintenance | Moderate; pumps and filters need regular checks | High; pumps and filtration systems require ongoing maintenance | Low; minimal maintenance after initial setup |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for areas with accessible lakes and high water demands | Best for regions with reliable groundwater sources | Suitable for areas with seasonal rainfall and water conservation goals |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Groundwater Pumping
Groundwater pumping involves extracting water from underground aquifers using pumps. This method can provide a consistent water supply, especially in regions where surface water is scarce. However, the costs associated with drilling, pumping, and maintaining the system can be high. Additionally, over-extraction can lead to depletion of aquifers, making it less sustainable in the long term. Regulatory requirements can also complicate implementation, particularly in areas with strict water management policies.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for irrigation and other uses. This approach can significantly reduce dependency on traditional water sources and lower operational costs. The initial investment for the collection and storage infrastructure can be high, but the long-term savings on water bills can be substantial. However, the effectiveness of rainwater harvesting largely depends on the local climate and seasonal rainfall patterns, which may limit its applicability in arid regions.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Irrigation Needs
Selecting the most suitable irrigation solution requires a careful assessment of your specific circumstances, including geographical location, climate, available resources, and budget constraints. Pumping lake water presents a cost-effective and nutrient-rich option in areas with accessible lakes, while groundwater pumping offers reliability in drier regions. Rainwater harvesting stands out as an eco-friendly solution for areas with sufficient rainfall. Ultimately, B2B buyers must weigh these factors to determine the best irrigation method that aligns with their operational goals and environmental considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pumping lake water for irrigation
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation?
When considering pumping lake water for irrigation, understanding the technical specifications of the pumps and associated equipment is essential for ensuring efficient and reliable operation. Here are some critical properties to evaluate:
Horsepower (HP)
Horsepower indicates the pump’s power and ability to move water. A higher HP generally correlates with greater flow rates. For example, 1 HP pumps may handle up to 55 gallons per minute (GPM), while 2 HP models can manage larger volumes. B2B buyers should assess their specific irrigation needs to select an appropriately powered pump, balancing cost with performance.Maximum Capacity and Flow Rate
This specification measures the volume of water a pump can deliver over a specific period, usually expressed in GPM. For instance, a pump with a max capacity of 80 GPM is suitable for larger irrigation areas. Understanding flow rates helps buyers determine how many sprinklers or hoses can be operated simultaneously, impacting overall irrigation efficiency.Suction Lift
The suction lift is the maximum vertical distance a pump can draw water from a source, typically measured in feet. A pump with a 25-foot suction lift can access deeper water sources more effectively. Knowing this specification is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure that the pump can efficiently draw water from their specific lake or pond.Material Construction
The materials used in pump construction, such as thermoplastic or fiberglass-reinforced thermoplastic, influence durability and resistance to corrosion. Pumps exposed to harsh environmental conditions must be made from high-quality materials to ensure longevity and reduce maintenance costs. B2B buyers should prioritize pumps that offer robust material construction to minimize downtime.Voltage and Electrical Requirements
Pumps are typically rated for specific voltage requirements (e.g., 110V or 220V). Understanding the electrical needs is vital for ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure. Buyers must assess their power supply capabilities to avoid operational issues or the need for additional electrical work.Temperature Rating
This indicates the maximum temperature at which the pump can operate effectively, usually measured in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius. For instance, a pump rated for 140°F (60°C) is suitable for warmer climates. Knowing the temperature limits helps buyers select pumps that will perform reliably under their local conditions.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some essential trade terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of irrigation pumps, working with an OEM can ensure that you receive high-quality components tailored to your specifications.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier requires a buyer to purchase. Understanding MOQs is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure they meet the supplier’s conditions without overcommitting.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where buyers invite suppliers to submit price offers for specific products or services. For irrigation systems, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers efficiently.Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping, costs, and risk management associated with purchasing pumps from overseas suppliers.Lead Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead times is vital for B2B buyers to plan their irrigation projects and ensure that equipment is available when needed.Warranty Period
This is the timeframe during which a manufacturer will repair or replace defective products. Knowing the warranty terms can provide peace of mind and help buyers assess the reliability of the equipment they are purchasing.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their irrigation systems, ensuring efficiency and sustainability in their agricultural practices.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pumping lake water for irrigation Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation?
The demand for sustainable irrigation solutions is accelerating globally, driven by factors such as climate change, population growth, and increasing agricultural needs. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, pumping lake water for irrigation presents a viable solution to mitigate water scarcity. Emerging technologies in the sector, such as advanced pump systems and smart irrigation controllers, are enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring and management of water resources, ensuring optimal use of lake water while minimizing waste.
Additionally, the trend towards automation and IoT integration in irrigation systems is reshaping sourcing strategies. For instance, systems that can be controlled remotely via smartphone applications enable farmers to manage irrigation schedules more effectively. This shift not only improves water conservation but also reduces labor costs, making it attractive for large-scale agricultural operations. As the market evolves, suppliers that offer customizable and scalable solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge, appealing to diverse buyer needs.
Another critical aspect is the growing importance of regulatory compliance and sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can demonstrate adherence to environmental regulations and provide transparent information about their sourcing methods. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions where water rights and conservation policies are strictly enforced.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation Sector?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the pumping lake water irrigation sector, as environmental concerns and resource management become paramount. The ecological impact of utilizing lake water for irrigation is generally positive, provided that water extraction is managed responsibly. Sustainable practices involve ensuring that the water levels in lakes are maintained, preventing over-extraction that could disrupt local ecosystems. Buyers must prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainable water management.
Ethical sourcing has also gained traction among B2B buyers, with a focus on transparent supply chains and the environmental certifications of products. Certification schemes such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Water Stewardship certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Buyers should look for partners who not only provide reliable pumping solutions but also engage in practices that protect water quality and promote biodiversity in surrounding areas.
Moreover, as consumer awareness about environmental issues rises, companies involved in the irrigation sector are increasingly required to adopt green practices. This includes using recyclable materials in their products, offering energy-efficient systems, and engaging in community initiatives that support sustainable water use. Suppliers that align with these values will be better positioned to meet the expectations of conscious buyers.
How Has the Pumping Lake Water for Irrigation Sector Evolved Over Time?
The practice of utilizing lake water for irrigation has evolved significantly, especially with advancements in technology and changing agricultural practices. Historically, irrigation methods relied heavily on surface water and manual labor, often leading to inefficient water use. However, the introduction of mechanized pumping systems in the mid-20th century revolutionized the sector, allowing for more precise water management.
As awareness of environmental sustainability grew in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the focus shifted towards responsible water use and conservation. Innovations such as variable speed pumps and automated irrigation systems have emerged, enabling users to optimize water usage and reduce waste. Furthermore, the regulatory landscape has become more complex, with increased scrutiny on water rights and environmental impact assessments, necessitating that buyers remain informed about compliance requirements.
In conclusion, the pumping lake water for irrigation sector is on a trajectory towards sustainability and technological advancement, driven by the need for efficient water management solutions in the face of global challenges. B2B buyers must navigate these dynamics carefully, ensuring they partner with suppliers who align with their sustainability goals and offer innovative solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pumping lake water for irrigation
How do I solve water quality issues when pumping lake water for irrigation?
To address water quality concerns, it’s crucial to conduct a comprehensive water analysis before implementation. Testing for contaminants such as pathogens, heavy metals, and nutrient levels is essential. Depending on the results, consider integrating filtration systems and treatment options to ensure the water is suitable for irrigation. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the pumping system will also help in maintaining water quality over time, ensuring that your crops receive the necessary nutrients without harmful substances.What is the best type of pump for lake water irrigation systems?
The optimal pump for lake water irrigation typically depends on your specific needs, including the required flow rate, lift height, and the size of the area to be irrigated. Centrifugal pumps are popular due to their efficiency and ability to handle varying water levels. For larger operations, submersible pumps may be more suitable, as they can operate submerged and reduce the risk of air lock. It’s advisable to consult with a pumping systems expert to determine the best solution tailored to your irrigation requirements.What are the legal considerations for pumping water from lakes for irrigation?
Legal regulations surrounding water extraction vary significantly by region and country. Generally, users must adhere to local water rights laws, which may dictate how much water can be extracted and for what purposes. It’s essential to consult with local authorities or environmental protection agencies to understand the specific legal framework in your area. Obtaining necessary permits can help avoid potential legal issues and ensure sustainable water use practices.How can I vet suppliers for lake water pumping systems?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation in the industry. Look for client testimonials, case studies, and certifications that demonstrate expertise in pumping systems. Assess their product quality and warranty options, and inquire about their experience with international shipping and compliance with local regulations. Engaging in discussions about their support services and after-sales assistance can provide insights into their reliability as a long-term partner.What customization options are available for irrigation pumping systems?
Many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific irrigation needs. This may include adjustments in pump capacity, filtration systems, and additional accessories such as timers and controllers. When discussing your requirements with potential suppliers, specify the size of your irrigation area, the type of crops, and any unique environmental conditions. This will allow them to propose tailored solutions that enhance efficiency and effectiveness in your irrigation practices.What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pumping systems?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may have flexible MOQs for custom projects, while others may require larger orders to optimize production and shipping costs. It’s advisable to communicate your needs upfront and negotiate terms that work for both parties. If you’re starting with a smaller scale operation, inquire about trial units or pilot projects to assess system effectiveness before committing to larger orders.What payment terms should I expect when sourcing pumping systems internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on supplier policies and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include partial upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s vital to discuss and agree upon terms that protect both parties, considering factors such as currency fluctuations and international transaction fees. Establishing clear payment timelines and conditions will help build trust and facilitate smoother transactions.How do logistics and shipping impact the sourcing of irrigation systems?
Logistics play a critical role in the sourcing process, particularly for international buyers. Factors to consider include shipping methods, lead times, customs clearance, and potential tariffs. Partnering with suppliers who have experience in international shipping can streamline the process. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides comprehensive documentation for customs to prevent delays and complications upon arrival. Understanding these logistics will help in planning your project timelines effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Pumping Lake Water For Irrigation Manufacturers & Suppliers List
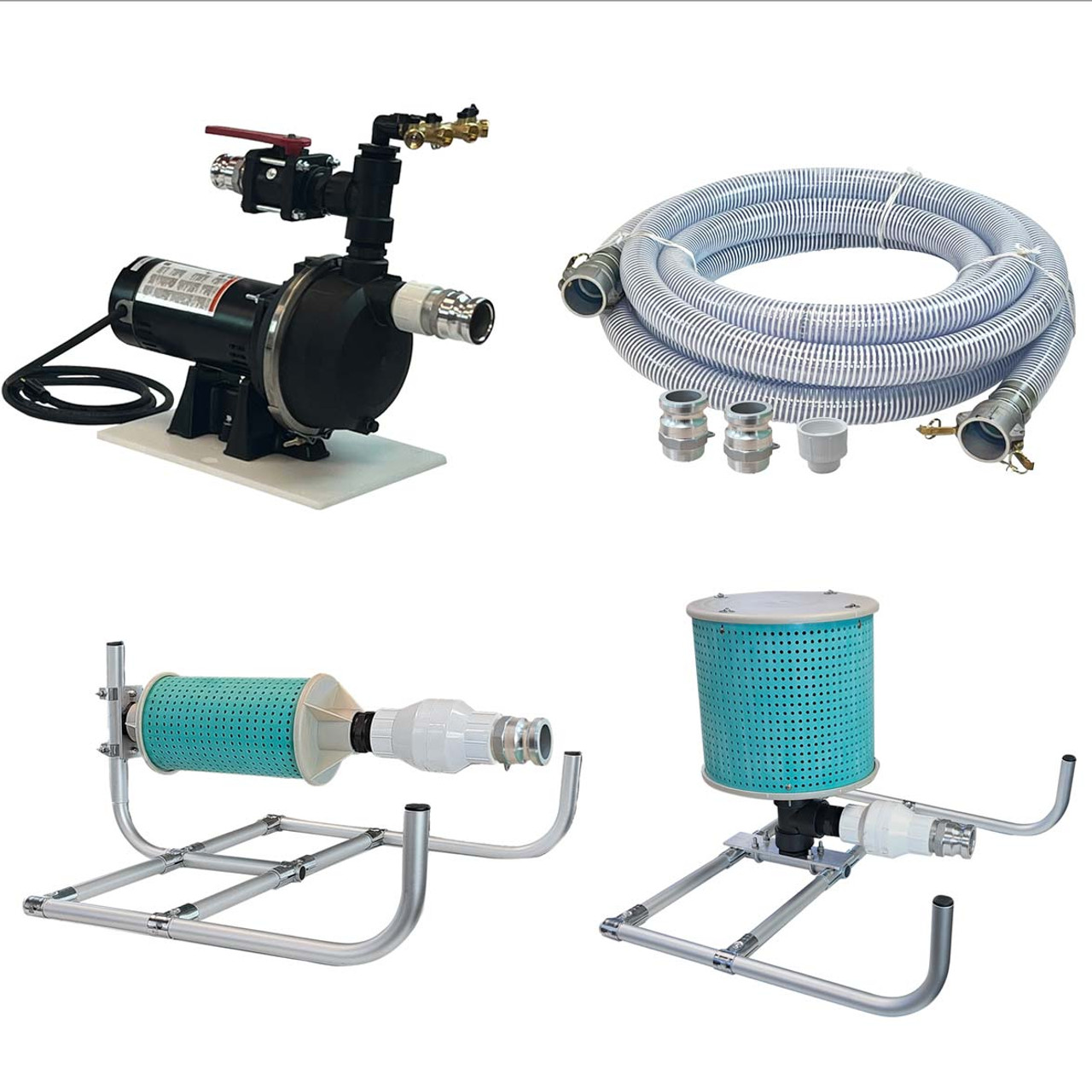
1. Wayne – 1-1/2 HP Cast Iron Quick-Prime Lawn-Sprinkler Pump
Domain: diy.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Pump: Wayne 1-1/2 HP Cast Iron Quick-Prime Lawn-Sprinkler Pump; Intake size: 2 inch; Discharge size: 1 1/2 inch.
2. Lawn Forum – Irrigation System Solutions
Domain: thelawnforum.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 1. Irrigation System: Aiming to install a 16 zone controller with pop-up sprinklers. 2. Sprinkler Type: Currently using pulsating sprinklers that require low pressure and have large ports to allow debris passage. 3. Water Source: Drawing water from a 2-acre spring-fed pond. 4. Pump Requirements: Need a pump with sufficient GPM, PSI, and lift to overcome a 45-foot elevation change. 5. Automation: D…
3. LawnSite – Pumps and Equipment
Domain: lawnsite.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1. Pump Types: Shallow-well jet pump, submersible pump, cast-iron Goulds J10S shallow-well jet pump. 2. Horsepower: 1 HP, 3/4 HP, 1 1/2 HP. 3. Flow Rate: 12 GPM desired, standard setup flows 20-25 GPM at 50 PSI. 4. Pressure: 50 PSI with an estimated 4 PSI loss for elevation. 5. Additional Equipment: Rainbird 5004 sprinkler heads, Rainbird flow control valves. 6. Installation Considerations: Need f…
4. World Water Reserve – Ultimate Guide to Pumping Water
Domain: worldwaterreserve.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Ultimate Guide to Pumping Water from a River, Lake, or Creek provides comprehensive information on pumping water from surface water sources for domestic purposes. Key topics include: 1. Water rights and legal considerations for pumping water. 2. Types of water sources and their suitability for different pumping systems (e.g., submersible pumps for lakes vs. hydraulic ram pumps for streams). 3. Ide…
5. Red Lion – Sprinkler Pumps
Domain: redlionproducts.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Lawn & Irrigation Overview: Red Lion offers sprinkler pumps designed to transport water from lakes or ponds for irrigation purposes. These pumps are suitable for high-volume applications, including filling pools and boosting household water pressure. Key considerations for selecting a sprinkler pump include suction lift and the number of sprinkler heads in operation. To determine the required pump…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pumping lake water for irrigation
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of lake water for irrigation presents a sustainable, cost-effective solution for agricultural and landscaping needs across diverse global markets. By harnessing local water resources, businesses can significantly reduce reliance on paid water sources and energy costs, while also benefiting from the high nutrient content of lake water. This approach not only fosters environmental stewardship but also aligns with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly practices.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in advanced irrigation systems that utilize lake water can lead to enhanced operational efficiency and long-term sustainability. Companies should prioritize partnerships with reliable suppliers who offer comprehensive solutions, including high-quality pumps and tailored irrigation packages.
As the global emphasis on resource conservation continues to rise, now is the time to explore innovative irrigation strategies. Engage with experienced providers in the market to customize a lake water pumping system that meets your specific irrigation needs. Together, we can cultivate a greener future while optimizing water use for agriculture and landscaping.