Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for irrigation master valve
In today’s global market, sourcing the right irrigation master valve can be a complex and daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The efficient management of water resources is crucial for agricultural success, yet many buyers struggle to identify high-quality valves that meet their specific needs. This comprehensive guide is designed to demystify the intricacies of irrigation master valves, covering essential aspects such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
As you navigate through this guide, you will gain valuable insights into the different types of master valves available, from normally open to normally closed configurations, and their respective benefits and drawbacks. Understanding the unique requirements of your irrigation system and regional challenges will empower you to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we will provide tips on evaluating suppliers to ensure reliability and quality, particularly in markets that require resilience against harsh conditions.
By equipping you with the knowledge to assess features such as pressure regulation, debris tolerance, and flow sensors, this guide aims to enhance your procurement strategy. It will help you select irrigation master valves that not only optimize water usage but also contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. Engage with this resource to ensure your investments yield both immediate and long-term returns in your irrigation systems.
Understanding irrigation master valve Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normally Closed Master Valve (NCMV) | Isolates the mainline until activated; provides disaster protection | Commercial landscaping, agricultural irrigation | Pros: Protects water resources, minimizes leaks; Cons: Requires precise calibration for optimal performance. |
| Normally Open Master Valve (NOMV) | Remains open until activated; allows for quick access to pressurized water | Residential gardens, light commercial use | Pros: Immediate access to water; Cons: Vulnerable to power outages and water surges. |
| Slow-Opening Master Valve | Features gradual opening and closing to prevent water surge | Large-scale irrigation systems | Pros: Reduces risk of pipe damage; Cons: May require more complex installation and maintenance. |
| Anti-Siphon Master Valve | Prevents backflow of contaminated water; typically used in smaller systems | Residential irrigation systems | Pros: Safeguards water quality; Cons: Not suitable for high-pressure applications. |
| Flow-Sensor Integrated Master Valve | Equipped with flow sensors to monitor and manage water flow | Commercial and industrial applications | Pros: Detects leaks and optimizes water usage; Cons: Higher upfront cost and compatibility considerations. |
What Are the Characteristics of Normally Closed Master Valves (NCMV)?
Normally Closed Master Valves are designed to keep the mainline isolated until a signal from the irrigation controller activates the solenoid. This feature is critical in protecting the irrigation system from leaks and potential flooding during emergencies. NCMVs are particularly suitable for commercial landscaping and agricultural applications where water conservation is paramount. Buyers should consider the valve’s compatibility with existing systems, as well as the need for precise calibration to ensure optimal performance.
How Do Normally Open Master Valves (NOMV) Function?
Normally Open Master Valves maintain a constant open state, allowing for immediate access to pressurized water. This design is ideal for residential gardens and light commercial uses where quick access is needed. However, buyers should be aware of the risks associated with power outages, as these valves do not provide protection against water surges, which can lead to system damage. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent sticking and ensure reliability.
What Benefits Do Slow-Opening Master Valves Provide?
Slow-Opening Master Valves are engineered to open and close gradually, minimizing the risk of water surge, which can damage pipes and fittings. These valves are particularly beneficial for large-scale irrigation systems where water management is critical. While they help protect infrastructure, buyers should be prepared for potentially more complex installation and maintenance requirements compared to standard valves.
Why Choose Anti-Siphon Master Valves for Smaller Systems?
Anti-Siphon Master Valves are designed to prevent backflow, protecting the water supply from contamination. They are commonly used in residential irrigation systems where safeguarding water quality is a priority. However, their functionality is limited to lower-pressure applications, making them unsuitable for larger, more demanding systems. Buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their irrigation setup to determine if this type of valve meets their needs.
How Do Flow-Sensor Integrated Master Valves Enhance Irrigation Systems?
Flow-Sensor Integrated Master Valves come equipped with sensors that monitor water flow, allowing for real-time adjustments to optimize water usage and detect leaks. These valves are particularly advantageous in commercial and industrial applications where efficiency is critical. While they provide significant benefits, buyers must consider the higher upfront costs and ensure compatibility with existing irrigation controllers. This investment can lead to long-term savings through improved water management.
Key Industrial Applications of irrigation master valve
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Irrigation Master Valve | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Management of large-scale irrigation systems for crop production | Ensures efficient water usage, reducing waste and operational costs | Durability, size compatibility, and ability to handle reclaimed water |
| Landscape Management | Control of water flow in commercial landscaping projects | Enhances aesthetic quality while conserving water resources | Material resilience, pressure regulation features, and maintenance ease |
| Horticulture | Precision irrigation for nurseries and greenhouses | Optimizes plant health and growth through regulated water supply | Compatibility with flow sensors, size options, and automation capabilities |
| Municipal Water Management | Flood prevention and water supply control in urban areas | Protects infrastructure and manages water resources efficiently | Compliance with local regulations, reliability in emergencies, and ease of installation |
| Sports Facilities | Irrigation control for sports fields and golf courses | Maintains optimal playing conditions while minimizing water usage | Ability to handle varying flow rates, pressure tolerance, and maintenance support |
How is an Irrigation Master Valve Used in Agriculture?
In agriculture, irrigation master valves are crucial for managing extensive irrigation systems, particularly in regions where water scarcity is a concern. These valves facilitate the controlled flow of water to crops, ensuring that irrigation occurs efficiently and effectively. By optimizing water usage, farmers can significantly reduce operational costs and minimize waste. When sourcing, buyers should consider the valve’s durability, size compatibility with existing systems, and its ability to manage reclaimed water, especially in arid regions of Africa and South America.
What Role Does an Irrigation Master Valve Play in Landscape Management?
For landscape management, irrigation master valves are employed to regulate water flow in commercial projects such as parks and gardens. These valves help maintain the aesthetic quality of landscapes while conserving water resources, addressing the growing demand for sustainable practices. Buyers in this sector should prioritize valves made from resilient materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, as well as those featuring pressure regulation capabilities to ensure consistent performance.
How Does Horticulture Benefit from Using Irrigation Master Valves?
In horticulture, specifically within nurseries and greenhouses, irrigation master valves enable precise control over water delivery to plants. This precision is vital for optimizing plant health and growth, as it allows for tailored irrigation schedules based on specific plant needs. Buyers should seek valves that are compatible with flow sensors and automation systems, ensuring that they can effectively monitor and adjust water supply, particularly in regions with variable climates in Europe and the Middle East.
How Are Irrigation Master Valves Essential for Municipal Water Management?
Municipal water management utilizes irrigation master valves to control water supply and prevent flooding in urban environments. These valves play a critical role in protecting infrastructure and managing water resources efficiently, especially during emergencies. When sourcing for municipal applications, it’s essential to ensure compliance with local regulations, reliability in critical situations, and ease of installation to facilitate quick deployment and maintenance.
What Benefits Do Sports Facilities Gain from Irrigation Master Valves?
Sports facilities, including golf courses and athletic fields, benefit from irrigation master valves by maintaining optimal playing conditions through effective water management. These valves help minimize water usage while ensuring that grass and turf remain healthy and playable. Buyers in this sector should focus on valves that can handle varying flow rates and possess good pressure tolerance, as well as those that offer maintenance support to ensure long-term reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘irrigation master valve’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Water Flow Disrupting Irrigation Efficiency
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter issues with inconsistent water flow in their irrigation systems, often caused by poorly functioning master valves. This inconsistency can lead to under-irrigated areas, causing stress to plants and crops, or over-irrigation, resulting in water wastage and potential flooding. Buyers may struggle to identify whether the problem lies with the master valve itself or with the controller settings, leading to confusion and delays in addressing critical irrigation needs.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality master valves that are compatible with their existing irrigation systems. It’s essential to look for valves with features such as pressure regulation and enhanced debris tolerance. When selecting a master valve, consider investing in a normally closed (NCMV) valve, which isolates the mainline and prevents water from flowing unless the system is actively irrigating. This ensures that the system is only pressurized during operation, thus reducing the chances of inconsistent flow. Additionally, pairing the master valve with a flow sensor can help monitor the flow rates accurately, allowing for real-time adjustments and alerts for any abnormalities. Regular maintenance checks should also be scheduled to ensure all components are functioning optimally, preventing future disruptions.
Scenario 2: Damage from Water Surge During Irrigation Start-Up
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the risk of water surges that can occur when an irrigation system starts up. This often happens when the master valve opens too quickly, causing a sudden influx of water that can damage pipes, fittings, and the plants themselves. Such surges can lead to costly repairs and downtime, ultimately impacting productivity and profitability.
The Solution: To prevent water surge issues, B2B buyers should opt for slow-opening and closing master valves designed to gradually adjust the water flow. These valves help to manage pressure changes and minimize the risk of surges. When specifying a master valve, look for models that include a dual chamber design or those specifically engineered to handle varying flow rates without compromising system integrity. Collaborating with irrigation specialists to analyze the specific needs of the landscape can also provide insights into the best valve size and configuration to use. Additionally, integrating a pressure-regulating device within the system can further stabilize water flow, ensuring that irrigation starts smoothly and efficiently.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Master Valve Maintenance and Longevity
The Problem: Buyers often face challenges related to the maintenance and longevity of their master valves, especially in harsh environments where debris and sediment can clog the system. Regular wear and tear can lead to leaks, reduced performance, and ultimately the failure of the master valve, resulting in unexpected costs and operational disruptions.
The Solution: To address maintenance challenges, buyers should select master valves constructed from durable materials such as brass or glass-filled nylon, which are better suited for handling debris and harsh conditions. Additionally, incorporating a filter assembly within the irrigation system can help trap debris before it reaches the master valve, extending its lifespan and improving performance. Buyers should establish a routine maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections and cleaning of the valve and associated components. Training staff on how to properly maintain and troubleshoot the system can also empower teams to address minor issues before they escalate into major problems. Investing in high-quality, easy-to-maintain valves will not only enhance system performance but also reduce the frequency of repairs and replacements over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for irrigation master valve
What Are the Most Common Materials for Irrigation Master Valves?
When selecting an irrigation master valve, the choice of material is critical for ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and compatibility with various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of irrigation master valves: brass, glass-filled nylon, PVC, and stainless steel. Each material has its unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact the decision-making process for international B2B buyers.
How Does Brass Perform in Irrigation Master Valves?
Brass is a traditional choice for irrigation master valves due to its excellent durability and resistance to corrosion. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°F (93°C) and can handle pressures between 20 to 200 PSI, making it suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros: Brass valves are known for their longevity and robustness, making them ideal for demanding environments. They are also resistant to rust and corrosion, which is particularly beneficial in areas with high humidity or saline conditions.
Cons: The primary drawback of brass is its cost, which is generally higher than plastic alternatives. Additionally, brass can be susceptible to dezincification, a process where zinc leaches out, potentially weakening the valve over time.
Impact on Application: Brass valves are compatible with both potable and non-potable water, making them versatile for various irrigation systems. However, they may not be suitable for applications involving aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and ISO is crucial. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, buyers may prefer brass valves for their reliability, while in Africa and South America, cost considerations may lead to alternative materials.
What Are the Benefits of Glass-Filled Nylon in Irrigation Master Valves?
Glass-filled nylon is a composite material that combines nylon with glass fibers to enhance strength and durability. It typically offers a temperature rating of up to 160°F (71°C) and can withstand pressures of up to 150 PSI.
Pros: This material is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and offers excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for various water types, including reclaimed water. Its lower cost compared to brass makes it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers.
Cons: While glass-filled nylon is durable, it may not withstand extreme temperatures as effectively as metal options. Additionally, it can be more susceptible to UV degradation if not properly protected.
Impact on Application: Glass-filled nylon valves are ideal for applications requiring chemical compatibility, such as agricultural irrigation systems using fertilizers. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that glass-filled nylon products meet local standards, such as DIN in Germany or JIS in Japan. In regions with high UV exposure, additional protective measures may be necessary.
How Does PVC Compare for Use in Irrigation Master Valves?
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a widely used plastic in irrigation systems due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. PVC valves typically handle pressures up to 150 PSI and are resistant to a variety of chemicals.
Pros: The primary advantage of PVC is its low cost and lightweight nature, making it easy to transport and install. It is also resistant to corrosion and can last for many years in suitable applications.
Cons: PVC has a lower temperature tolerance, typically around 140°F (60°C), and can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light. Its rigidity may also make it less suitable for applications requiring flexibility.
Impact on Application: PVC valves are ideal for low-pressure irrigation systems and are commonly used in residential and commercial applications. However, they are not recommended for high-temperature or high-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that PVC products comply with local regulations and standards. In regions with extreme temperatures, selecting UV-stabilized PVC is essential to ensure longevity.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Irrigation Master Valves?
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 300°F (149°C) and can handle high pressures.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel makes it an excellent choice for long-term applications. It is also resistant to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for both potable and non-potable water.
Cons: The primary downside is the higher cost compared to other materials. Additionally, stainless steel can be heavy, which may complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are ideal for applications involving aggressive chemicals or high-pressure systems, such as industrial irrigation setups. However, they may not be necessary for low-demand residential systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is essential, especially in Europe, where regulations on water safety are stringent. Buyers in regions with high corrosion risk may prefer stainless steel for its longevity.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Irrigation Master Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for irrigation master valve | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | High-pressure systems | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost, susceptible to dezincification | High |
| Glass-Filled Nylon | Agricultural irrigation systems | Lightweight, chemical resistant | Lower temperature tolerance, UV degradation | Medium |
| PVC | Residential and low-pressure systems | Cost-effective, easy to install | Lower temperature tolerance, rigidity | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial and high-pressure applications | Exceptional strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost, heavier weight | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in diverse regions, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for irrigation master valve
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing an Irrigation Master Valve?
The manufacturing process of an irrigation master valve involves several critical stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets performance and durability standards.
Material Preparation: What Types of Materials Are Used?
The process begins with the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials for irrigation master valves include glass-filled nylon, durable plastics, and metals like brass. Each material has specific properties suited for different environmental conditions and operational demands. For instance, glass-filled nylon offers excellent resistance to corrosion and is lightweight, while brass provides robustness and longevity.
Materials undergo rigorous inspection before being approved for use. This step ensures that only high-quality raw materials are utilized, which significantly affects the valve’s durability and functionality in various irrigation systems.
How Are Irrigation Master Valves Formed?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This typically involves techniques such as injection molding for plastic components and machining for metal parts.
Injection Molding: This technique is used predominantly for creating complex shapes in plastic valves. The process involves melting plastic and injecting it into a mold, allowing for precision and consistency in the valve’s design.
Machining: For metal parts, machining processes like turning, milling, and drilling are employed. This method allows for tight tolerances and the ability to create intricate features essential for valve functionality.
The forming stage is crucial as it directly influences the valve’s operational efficiency, sealing capability, and resistance to pressure fluctuations.
What Is Involved in the Assembly of Irrigation Master Valves?
After forming, components are assembled. This stage requires skilled labor and adherence to strict protocols to ensure that each valve functions as intended.
During assembly, various parts such as solenoids, diaphragms, and valve bodies are combined. The assembly process may vary depending on whether the valve is normally open or normally closed. For example, normally closed valves must be calibrated to ensure they only open when the system requires water flow.
Quality checks are integrated into this stage to prevent defects. Assembled valves undergo functional tests to verify that they open and close correctly and maintain pressure without leaks.
What Finishing Processes Are Required for Irrigation Master Valves?
The finishing stage involves treatments that enhance the valve’s durability and aesthetic appeal. Common processes include surface treatments like coating or painting to improve corrosion resistance and prevent wear from environmental factors.
Additionally, final inspections are conducted to ensure all components are free from defects and meet specified standards. This may include pressure testing to verify that the valve can withstand operational pressures without failure.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Irrigation Master Valves?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that irrigation master valves meet international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance for Irrigation Valves?
Manufacturers often adhere to internationally recognized quality management standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with these standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe and API standards in North America provide frameworks for quality assurance. These certifications ensure that products meet safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are performed to catch defects early, ensuring that any deviations from standards are addressed immediately.
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection checks the complete product against the specifications. It often includes performance testing under simulated operating conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Conducting audits of manufacturing facilities is one of the most effective methods. These audits can evaluate the supplier’s adherence to quality management systems and international standards.
Buyers should also request quality assurance reports and documentation that outline the QC processes and test results for the valves. Third-party inspections can provide an additional layer of verification, ensuring that the products meet the required specifications before shipment.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various certification requirements. Understanding local regulations and standards is crucial, as they can vary significantly between regions.
For example, European buyers must ensure compliance with CE marking, which is mandatory for many products sold within the EU. In contrast, buyers in the Middle East may focus on local standards set by national authorities.
Buyers should also be aware of potential language barriers and cultural differences that may affect communication with suppliers. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication can help mitigate these challenges.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing and QC Important for B2B Buyers?
A comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with irrigation master valves is essential for B2B buyers. This knowledge not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also ensures that the products meet the specific needs of their irrigation systems. By prioritizing quality and compliance with international standards, buyers can significantly enhance the efficiency and longevity of their irrigation solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘irrigation master valve’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure irrigation master valves. Understanding the critical features and supplier qualifications will ensure that you select a reliable, efficient valve that meets the specific needs of your irrigation system.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s essential to outline your technical requirements. Identify the size, type (normally open or normally closed), and material (plastic, metal, or glass-filled nylon) suited for your application. This clarity will help streamline the selection process and ensure compatibility with your existing irrigation setup.
- Size Range: Master valves typically range from 1 to 8 inches. Choose a size that aligns with your system’s flow requirements.
- Material Considerations: Depending on your water quality (clean, reclaimed, or dirty), select a material that can withstand potential contaminants.
Step 2: Assess System Compatibility
Evaluate how the master valve will integrate with your existing irrigation system. Compatibility with controllers, flow sensors, and other components is crucial for seamless operation.
- Controller Compatibility: Ensure your irrigation controller can interface with the master valve, particularly if you plan to use flow sensors for leak detection.
- Flow Rates: Match the valve’s flow capacity to your system’s requirements to prevent underperformance or damage.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
It’s vital to verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and standards compliance. This ensures that the products meet quality and safety benchmarks, which is especially important in international markets.
- Quality Assurance: Look for ISO certifications or industry-specific standards that guarantee product reliability.
- Regional Compliance: Be aware of any regional regulations regarding water use and irrigation equipment that your suppliers must adhere to.
Step 4: Compare Features and Benefits
Take the time to compare the features of different master valves. Focus on aspects like pressure regulation, debris tolerance, and maintenance accessibility.
- Pressure Regulation: Valves with built-in pressure regulation can help manage fluctuations, protecting your irrigation system from damage.
- Maintenance Needs: Opt for valves designed for easy maintenance, such as those with external plumbing for filter assembly access.
Step 5: Request Samples and Technical Documentation
Before finalizing your purchase, request samples and detailed technical documentation from suppliers. This allows you to verify product quality and understand installation requirements.
- Technical Specs: Ensure you have access to installation guides, maintenance instructions, and warranty details.
- Sample Testing: If feasible, conduct a test run of the valve to assess performance under your specific conditions.
Step 6: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Analyze pricing structures from different suppliers, ensuring you’re getting value for your investment. Pay attention to payment terms and conditions, including warranties and return policies.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the initial purchase price but also long-term maintenance costs and potential savings from efficiency gains.
- Flexible Payment Options: Look for suppliers offering favorable payment terms that align with your budgetary constraints.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Establish Communication
Once you’ve selected a supplier, finalize your order and establish clear lines of communication for ongoing support. This ensures you can address any issues that may arise post-purchase.
- Contact Points: Identify key contacts for customer service and technical support.
- Follow-Up Procedures: Establish a timeline for delivery and installation, along with procedures for addressing potential problems.
Following this checklist will facilitate a structured and informed procurement process, ultimately leading to a successful acquisition of irrigation master valves that enhance your irrigation system’s efficiency and reliability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for irrigation master valve Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Irrigation Master Valves?
When sourcing irrigation master valves, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s profit margin.
Materials: The choice of materials—such as glass-filled nylon, plastic, or metal—directly impacts the cost. For instance, brass valves may be more expensive due to their durability and performance in harsh conditions, especially in regions with extreme climates.
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the manufacturing location and the complexity of the valve design. Regions with higher labor costs may increase the overall price, making it essential for buyers to consider where the valves are produced.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and equipment used in production. Efficient manufacturers often have lower overheads, which can lead to competitive pricing.
Tooling: Custom designs may require specialized tooling, which can add to the initial cost. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the upfront investment.
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality control measures ensures reliable product performance, which is particularly critical for irrigation systems. Valves that pass stringent QC processes may carry a higher price tag, reflecting their quality assurance.
Logistics: Shipping costs, including tariffs and duties for international shipments, can significantly affect the total cost. Understanding the logistics involved, especially when sourcing from different continents, is crucial.
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin is also a factor. Buyers should inquire about the margin and assess whether it aligns with the expected value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Irrigation Master Valves?
Several factors influence the pricing of irrigation master valves, particularly for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to reduced unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it advantageous for businesses to consolidate their purchasing.
Specifications/Customization: Custom valves tailored to specific applications or local regulations may incur additional costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
Materials and Quality Certifications: Valves made from high-grade materials or those that comply with international quality certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) typically command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits of investing in certified products versus cheaper alternatives.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for calculating total costs. Terms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) will determine who bears the shipping costs and risks, influencing the final price.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Master Valves?
To maximize cost-efficiency and ensure a favorable deal when sourcing irrigation master valves, consider the following tips:
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Establishing a good relationship can lead to better terms and conditions.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the upfront cost. Factors such as maintenance, longevity, and efficiency can significantly affect the overall expense of using the valves over time.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of the currency fluctuations and economic conditions in the supplier’s country, which may affect pricing. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local regulations that could impact the importation of valves.
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide insight into market rates and help identify the best value.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific order requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to determine the most accurate pricing for your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing irrigation master valve With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Irrigation Master Valves
In the quest for efficient irrigation solutions, businesses often evaluate various technologies and methods to optimize water management. While irrigation master valves (MVs) are widely recognized for their ability to regulate water flow and protect irrigation systems, several alternative solutions also exist. This analysis compares irrigation master valves against flow control devices and pressure regulators, highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| Comparison Aspect | Irrigation Master Valve | Flow Control Device | Pressure Regulator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent at managing water flow and preventing backflow. | Good for regulating flow rates but may not prevent backflow. | Maintains consistent pressure, ensuring efficient water distribution. |
| Cost | Medium to high initial investment; longevity reduces overall cost. | Low to medium; depends on complexity and brand. | Medium cost; can vary based on pressure requirements and features. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation, especially for larger systems. | Generally easier to install; suitable for DIY projects. | Moderate complexity; requires knowledge of system pressure settings. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks to ensure proper operation; can be labor-intensive. | Low maintenance; occasional checks needed. | Minimal maintenance; periodic pressure checks recommended. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large, complex irrigation systems needing high control. | Best for residential or small-scale applications where flow regulation is needed. | Suitable for varied agricultural applications requiring stable pressure. |
What Are Flow Control Devices and Their Benefits?
Flow control devices are designed to manage the rate of water flow in irrigation systems. They can be as simple as manual valves or more complex automated systems.
Pros: These devices offer flexibility in managing water supply and can be easily installed in various irrigation setups. They are often more affordable than master valves, making them a popular choice for smaller operations or residential use.
Cons: Flow control devices typically do not offer the same level of protection against backflow or system surges as master valves. This makes them less suitable for larger systems that require stringent safety measures.
How Do Pressure Regulators Function and What Are Their Advantages?
Pressure regulators are essential components that maintain consistent water pressure throughout an irrigation system. They are particularly important in areas with fluctuating water pressure.
Pros: By ensuring a stable pressure, these regulators can enhance the efficiency of water usage, reduce waste, and protect irrigation equipment from damage caused by high pressure. They are often easier to maintain than master valves.
Cons: However, pressure regulators do not control flow rates directly and may require additional devices to achieve optimal system performance. Their effectiveness can also be limited in systems with significant elevation changes or varied water sources.
Making the Right Choice for Your Irrigation Needs
When considering alternatives to irrigation master valves, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, including system size, water source characteristics, and budget constraints. For large agricultural operations in regions like Africa and South America, where water conservation is critical, an irrigation master valve may be the best choice due to its robust performance and protective features. Conversely, for smaller-scale applications or less demanding environments, flow control devices or pressure regulators can provide sufficient functionality at a lower cost and with easier implementation.
Ultimately, the decision should align with the overall goals of water management, operational efficiency, and sustainability, ensuring that the chosen solution meets both immediate and long-term irrigation objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for irrigation master valve
What Are the Key Technical Properties of an Irrigation Master Valve?
Understanding the essential technical properties of irrigation master valves is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Composition
Irrigation master valves are commonly made from materials such as glass-filled nylon, plastic, or metal. The choice of material impacts durability, resistance to corrosion, and overall longevity. For instance, metal valves are preferred in high-pressure applications due to their strength, while plastic valves are lighter and often more cost-effective. Selecting the right material is essential for ensuring the valve meets the demands of specific irrigation environments, particularly in regions with varying climates and water qualities.
2. Size and Flow Rate
Master valves typically range from 1 to 8 inches (25 to 200 mm) in diameter, with flow rates varying significantly. Understanding the required flow rate—measured in gallons per minute (GPM)—is vital for ensuring the valve can handle the system’s demands without causing pressure drops or inefficiencies. For large-scale agricultural applications, opting for a valve that can accommodate higher flow rates is critical to maintaining optimal irrigation performance.
3. Pressure Rating
Pressure ratings for irrigation master valves generally range from 20 to 200 PSI. This specification indicates the maximum pressure the valve can withstand without failing. Choosing a valve with an appropriate pressure rating is essential for preventing leaks and ensuring system reliability, especially in high-pressure irrigation setups.
4. Valve Type: Normally Open vs. Normally Closed
Master valves come in two primary configurations: normally open (NOMV) and normally closed (NCMV). NOMVs remain open until a signal from the controller directs them to close, providing flexibility for additional water access. In contrast, NCMVs keep the system isolated until activated, offering enhanced protection against leaks and water contamination. Understanding these configurations is crucial for selecting a valve that aligns with the specific operational needs of an irrigation system.
5. Debris Tolerance and Maintenance Features
Many modern master valves incorporate features that enhance debris tolerance and ease of maintenance. Valves with dual chamber designs or external plumbing for filter assembly maintenance can reduce clogging issues and prolong the valve’s lifespan. Selecting a valve with these features can minimize downtime and maintenance costs, making it a wise investment for B2B buyers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Irrigation Master Valves?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several common trade terms related to irrigation master valves:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of irrigation systems, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources of master valves and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budget planning, especially for large-scale projects, as it can significantly affect procurement costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request for pricing from suppliers, often including specifications and quantities of the desired products. Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from multiple vendors, ensuring they secure the best price and terms for their irrigation master valves.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers, as they influence shipping costs, risk management, and delivery timelines.
5. Flow Sensor Integration
Flow sensors are devices used to monitor the flow of water through the irrigation system. Understanding how to integrate flow sensors with master valves can optimize system performance, detect leaks, and minimize water waste, which is particularly important in water-scarce regions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding irrigation master valves, ensuring they select the right products for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the irrigation master valve Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Irrigation Master Valve Sector?
The global market for irrigation master valves is experiencing notable growth, driven by increasing agricultural productivity demands and the need for efficient water management systems. As the agriculture sector faces challenges such as water scarcity and climate change, the role of master valves becomes critical in optimizing irrigation practices. Particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where water resources are limited, the adoption of advanced irrigation technologies is crucial for sustainable agricultural practices.
Emerging trends include the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology into irrigation systems, enabling real-time monitoring and control of water flow. This technology not only enhances efficiency but also helps in early detection of leaks or malfunctions, thereby minimizing water wastage. Additionally, the shift towards automation in irrigation systems is leading to increased demand for normally closed master valves, which provide better protection against water loss during power outages or system failures.
International B2B buyers are also influenced by regional sourcing trends. For instance, European markets are increasingly favoring environmentally friendly products, such as valves made from recycled materials or those that comply with stringent EU regulations. In contrast, buyers from South America may prioritize cost-effective solutions that still meet their agricultural needs. This divergence in preferences highlights the importance of understanding local market dynamics when sourcing irrigation master valves.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Irrigation Master Valve Market?
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of sourcing in the irrigation master valve sector. The environmental impact of irrigation systems is significant, particularly concerning water usage and resource management. Buyers are increasingly aware of the necessity to choose products that minimize ecological footprints. This has led to a growing preference for valves constructed from sustainable materials, such as glass-filled nylon or recycled metals, which not only reduce waste but also enhance the longevity of the products.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, as buyers seek transparency in sourcing practices. Companies that adhere to ethical standards often leverage this in their marketing, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other ‘green’ certifications serve as indicators of a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainable practices. For international buyers, especially in regions like Europe, these certifications are often prerequisites for procurement.
Moreover, the use of reclaimed water in irrigation systems is gaining traction, making it essential for master valves to be compatible with non-potable water. This trend aligns with global initiatives aimed at promoting water recycling and conservation, further emphasizing the need for sustainable sourcing practices.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Irrigation Master Valve Industry?
The irrigation master valve industry has evolved significantly over the last few decades. Initially, irrigation systems relied heavily on manual controls, which were labor-intensive and prone to inefficiencies. The introduction of automatic solenoid valves revolutionized the sector by allowing for precise control of water flow, leading to improved water conservation practices.
As technology advanced, the integration of electronic controls and sensors into irrigation systems became commonplace. This evolution has been further accelerated by the rise of smart agriculture, where data-driven decisions enhance operational efficiency. Today’s master valves are designed not only for durability but also for compatibility with advanced irrigation technologies, such as flow sensors and automated controllers.
In summary, the evolution of the irrigation master valve industry reflects broader trends in agricultural technology, sustainability, and the necessity for efficient water management. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to make informed sourcing decisions in this rapidly changing market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of irrigation master valve
How do I solve issues with irrigation master valve performance?
To resolve performance issues with an irrigation master valve, first, check for debris or blockages that may be obstructing the valve’s operation. Ensure that the solenoid is functioning correctly by testing it with a multimeter. If the valve is not responding, inspect the electrical connections for any loose wires. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and periodic checks, can prevent many common problems. If issues persist, consider consulting with your supplier for troubleshooting support or possibly replacing the valve with a more reliable model.What is the best material for an irrigation master valve?
The ideal material for an irrigation master valve depends on your specific application and environmental conditions. For most commercial applications, brass or stainless steel valves are preferred due to their durability and corrosion resistance. Plastic valves can be suitable for smaller systems or areas with less exposure to harsh conditions. Ensure that the valve material aligns with the water quality being used, particularly if recycled or non-potable water is involved, as this can impact the valve’s longevity and performance.How can I assess the quality of an irrigation master valve supplier?
To evaluate the quality of a supplier for irrigation master valves, start by reviewing their reputation in the industry through customer testimonials and case studies. Check if they provide certifications or compliance with international standards relevant to your region. It’s also beneficial to inquire about their manufacturing processes, material sourcing, and warranty policies. Engaging in direct communication with the supplier can give you insights into their customer service and responsiveness, which are crucial for long-term partnerships.What are the common customization options available for irrigation master valves?
Customization options for irrigation master valves often include size, flow rate, and material selection tailored to specific project requirements. Some suppliers offer features like pressure regulation, enhanced debris tolerance, and the ability to handle reclaimed water. Additionally, you may request specific configurations such as globe or angle design based on your installation needs. Always communicate your requirements clearly to the supplier to ensure they can accommodate your customization requests.What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for irrigation master valves?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for irrigation master valves can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, MOQs range from 10 to 100 units, depending on the supplier’s manufacturing processes and inventory policies. For larger projects, suppliers may be willing to negotiate lower MOQs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with the supplier, as they may offer flexibility based on your long-term purchasing intentions or project size.What payment terms should I expect when purchasing irrigation master valves internationally?
When sourcing irrigation master valves internationally, payment terms can vary widely. Common options include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may also offer credit terms for established customers or larger orders. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement and consider using secure payment methods to protect your transaction.How do I ensure timely logistics and shipping of irrigation master valves?
To ensure timely logistics and shipping, work closely with your supplier to establish clear timelines for production and delivery. Inquire about their shipping methods and any potential customs requirements specific to your region. It’s advisable to choose a supplier with experience in international shipping and logistics. Additionally, consider using a freight forwarder to help navigate the complexities of cross-border shipping and ensure that your order arrives on time.What are the best practices for installing an irrigation master valve?
Best practices for installing an irrigation master valve include selecting an appropriate location that allows easy access for maintenance and monitoring. Ensure that the valve is installed according to the manufacturer’s specifications, paying attention to the orientation and alignment. Use proper fittings and ensure all connections are secure to prevent leaks. It’s also beneficial to incorporate a flow sensor for real-time monitoring, which can help detect issues early and minimize water loss. Regularly inspect the valve post-installation to confirm its performance and functionality.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Irrigation Master Valve Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sprinkler Warehouse – Irrigation Master Valve
Domain: school.sprinklerwarehouse.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
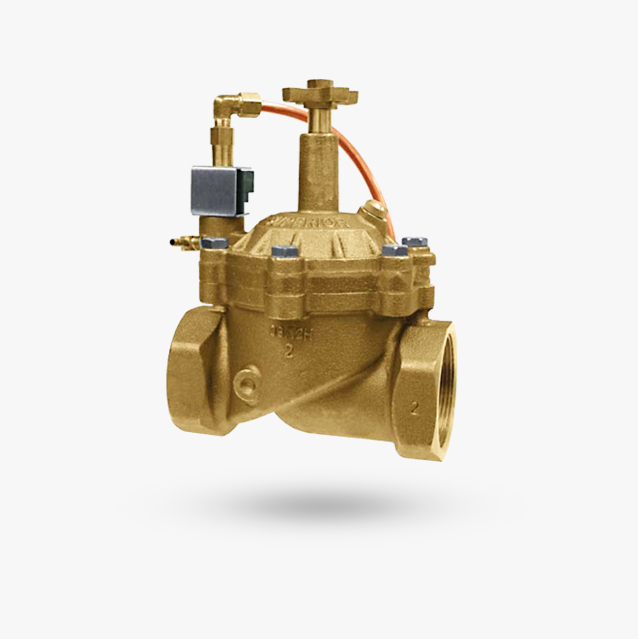
Introduction: An irrigation master valve is an electric valve installed at the supply point of an irrigation system, controlling water flow into the main piping system. It prevents water supply when closed, reducing water loss from leaky station valves and allowing for repairs to the mainline without shutting off the water supply. The master valve is typically the same type as station valves but is installed up…
2. Reddit – Master Valves
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Master valves are used in irrigation systems to help manage water flow and prevent leaks. They can be beneficial in preventing extensive damage from mainline leaks, especially in high-end properties. However, they may also cause issues by masking smaller leaks that could go unnoticed for extended periods. The necessity of a master valve often depends on the specific irrigation setup and whether a …
3. Sprinkler Supply Store – 24 VAC Sprinkler System
Domain: sprinklersupplystore.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: This company, Sprinkler Supply Store – 24 VAC Sprinkler System, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. U.S. Solid – Motorized Brass Ball Valve 1
Domain: community.rachio.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Motorized Ball Valve- 1″ Brass Ball Valve with Standard Port, 9-24V DC and 2 Wire Reverse Polarity by U.S. Solid
5. Superior – SPVLF Valve
Domain: getsuperior.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Superior offers a range of irrigation products including valves (In-Line, Master, Manual, Hydraulic, Reverse Flow), accessories (Control Zone Kits, Quick Couplers, Low Profile, Traditional), sprinklers (Impact, Pop-Up & Nozzles, Bases), adaptors, and controllers. The SPVLF valve is highlighted as an affordable and reliable option, built on the popular 3200 master valve and operable regardless of f…
6. Seattle Landscapes – Master Valve
Domain: seattlelandscapes.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: A Master Valve is an automatic valve installed on the main line of an irrigation system, usually just after the backflow preventer. It opens only when an irrigation zone is actively running and closes when the system is off, minimizing the risk of leaks and water waste. Key benefits include preventing water waste, protecting property from unnoticed irrigation leaks, adding a layer of system contro…
7. Hunter – Master Valve & HC 24 Controller
Domain: thelawnforum.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Master Valve, Hunter HC 24 controller, Hunter flow meter, Hydrawise system, 1″ flow meter, 1.5″ ICV Filter Sentry, custom shielded wire for flow meter installation.
8. Rain Bird – Durable Valves for All Water Types
Domain: store.rainbird.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Rain Bird – Durable Valves for All Water Types, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
9. Irrigation Tutorials – Master Valve
Domain: irrigationtutorials.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: A master valve is an automatic electric solenoid valve installed at the connection point of the irrigation system to the water supply. It is wired to a master valve circuit on the irrigation controller, which turns the valve on and off. The master valve acts as a fail-safe, shutting off water when no zone valves are operating. Benefits include minimizing water loss from leaks and damage from mainl…
10. Hunter Irrigation – Master Valve
Domain: hunterirrigation.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: A master valve is an automatic valve installed at the point where the irrigation system connects to the water supply, functioning as a backup or fail-safe valve. It is controlled by a Hydrawise controller, which supports 6 or 12 zone valves depending on the model. The master valve shuts off water to the irrigation system when no zone valves are operating. Configuration of the master valve can be d…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for irrigation master valve
The strategic sourcing of irrigation master valves is pivotal for optimizing water management systems, particularly in regions where water conservation is paramount. By selecting high-quality valves, businesses can ensure efficient water flow control, reduce wastage, and protect infrastructure from potential damage. The choice between normally closed and normally open valves should align with specific operational needs, emphasizing features such as debris tolerance and compatibility with flow sensors to enhance system reliability.
Moreover, investing in durable materials, like brass or reinforced nylon, can lead to long-term savings and reduce maintenance costs, particularly in challenging environments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As global demand for efficient irrigation solutions grows, so does the importance of sourcing valves that not only meet technical specifications but also offer robust performance in diverse climatic conditions.
International buyers are encouraged to leverage strategic sourcing practices to identify suppliers that prioritize innovation and sustainability. By doing so, they will not only enhance their operational efficiencies but also contribute to a more sustainable future in agricultural practices. As we look ahead, the integration of advanced technologies in irrigation systems will be critical. Take action now to secure partnerships that will help you stay ahead in this evolving market.