Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to turn off irrigation valve manually
In the dynamic landscape of global agriculture and landscaping, the ability to efficiently manage irrigation systems is paramount. For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—understanding how to turn off an irrigation valve manually can mitigate costly downtime and ensure operational continuity. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of manual valve operation, addressing various types of valves, their applications, and the best practices for maintenance and troubleshooting.
As irrigation systems become increasingly vital for sustainable agriculture and efficient landscaping, knowing how to handle these systems manually empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. In this guide, we will explore essential aspects such as the different types of irrigation valves, practical techniques for manual operation, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations. By equipping international B2B buyers with this knowledge, we aim to foster confidence in sourcing reliable irrigation solutions that enhance efficiency and reduce operational risks.
Whether you are managing a large-scale agricultural operation or a smaller landscaping project, mastering the art of manual irrigation valve control is a crucial skill that can lead to improved system performance and better resource management. Dive into this guide to navigate the complexities of irrigation systems and optimize your purchasing strategy.
Understanding how to turn off irrigation valve manually Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Bleed Screw | Located near the flow control, requires a simple twist. | Landscaping companies, agricultural sectors | Pros: Easy to access, minimal training required. Cons: May cause water leakage during operation. |
| Solenoid Turn | Involves turning the solenoid counter-clockwise. | Irrigation system maintenance and repair | Pros: Less water spillage, quick operation. Cons: Requires manual dexterity, potential for wear over time. |
| Twist Knob Override | Built-in manual activation feature on specific valves. | Residential and commercial landscaping | Pros: User-friendly, immediate control. Cons: Not available on all valve types, may be prone to damage. |
| Inline Valve Shutoff | Manual shutoff for buried inline valves. | Large-scale agricultural operations | Pros: Effective for remote locations, prevents system flooding. Cons: Labor-intensive to access, may require specialized tools. |
| Remote Control Shutoff | Electronic control for turning off valves remotely. | Smart irrigation systems, tech-savvy farms | Pros: Convenient, reduces manual labor. Cons: Higher initial investment, reliant on technology stability. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Manual Bleed Screw Valves?
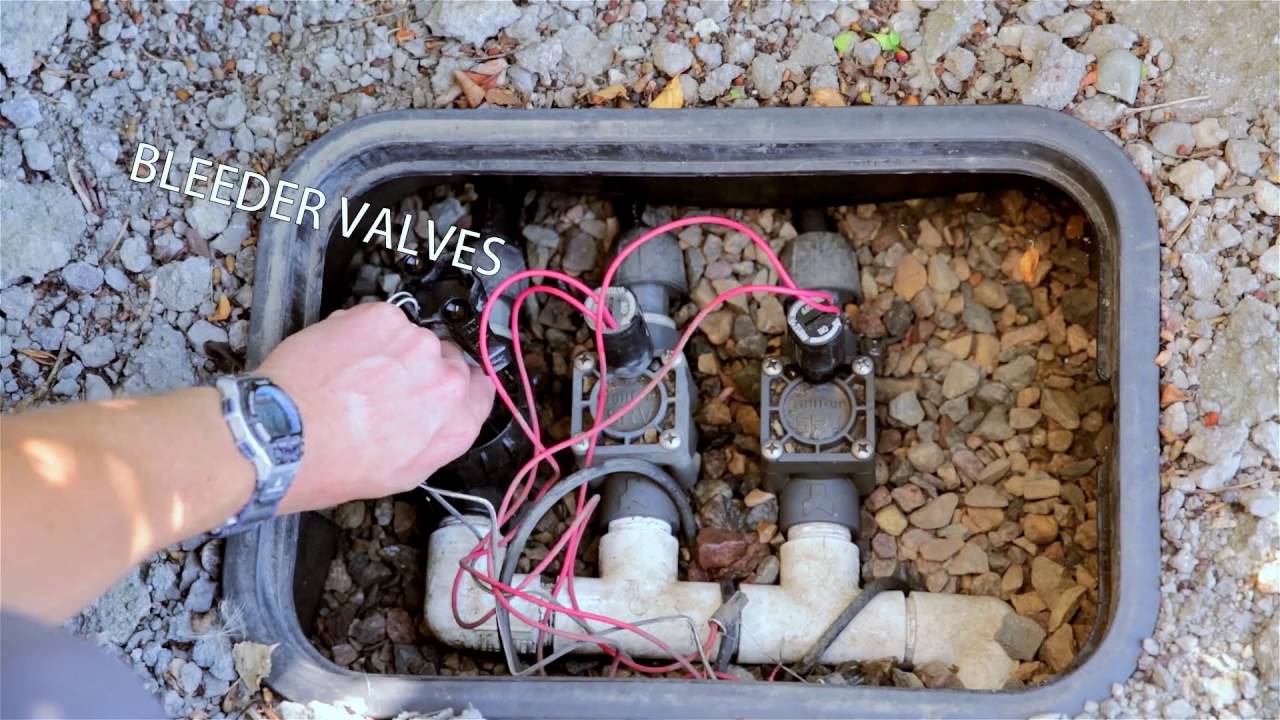
Manual bleed screw valves are typically located near the flow control section of an irrigation valve. These valves allow operators to manually release water pressure and open the valve by simply twisting the screw counter-clockwise. This method is suitable for landscaping companies that require immediate control over their irrigation systems. While it is easy to use and requires minimal training, buyers should be aware that using this method can lead to water leakage, which may necessitate additional cleanup.
How Does the Solenoid Turn Method Work for Valve Operation?
The solenoid turn method involves manually grasping the solenoid and turning it counter-clockwise to open the valve. This approach is favored for its efficiency and reduced water spillage. It is particularly suitable for irrigation system maintenance and repair, allowing technicians to quickly diagnose issues. However, while this method is less messy, it does require a level of manual dexterity, and over time, the solenoid may wear out, necessitating replacement.
What are the Benefits of Using a Twist Knob Override?
Twist knob overrides are built into specific irrigation valves, providing a user-friendly way to manually activate the system. They are particularly beneficial for residential and commercial landscaping applications where quick access is necessary. The ease of use is a significant advantage, but buyers should consider that not all valves come with this feature, and those that do may be more susceptible to physical damage.
Why Choose Inline Valve Shutoff for Buried Systems?
Inline valve shutoff methods are essential for managing buried irrigation systems, especially in large agricultural operations. They enable operators to manually shut off water flow to prevent flooding in remote areas. While effective, accessing these valves can be labor-intensive and may require specialized tools, which could impact operational efficiency.
How Does Remote Control Shutoff Enhance Irrigation Management?
Remote control shutoff systems provide the convenience of turning off irrigation valves from a distance, making them ideal for smart irrigation setups. This technology is increasingly popular among tech-savvy farms and landscaping businesses aiming to streamline operations. Despite the convenience, buyers must consider the higher initial investment and the dependency on technology, which may introduce potential reliability issues.
Key Industrial Applications of how to turn off irrigation valve manually
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to turn off irrigation valve manually | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Manual control of irrigation systems during maintenance or malfunction | Reduces water waste and ensures efficient resource use | Need for durable, weather-resistant components |
| Landscaping Services | Immediate response to irrigation issues in landscaping projects | Enhances service reliability and customer satisfaction | Consideration for compatibility with various valve types |
| Golf Course Management | Quick shutdown of irrigation zones for repairs or emergency situations | Minimizes downtime and protects landscape investment | Sourcing valves that are easy to operate and maintain |
| Municipal Water Management | Control of irrigation in public parks and green spaces | Promotes sustainable water management practices | Compliance with local regulations regarding water usage |
| Horticulture | Manual operation of irrigation for specialized plant care | Supports optimal growth conditions for valuable crops | Need for precision control and adaptability to different systems |
How is Manual Control of Irrigation Valves Applied in Agriculture?
In the agriculture sector, farmers often face irrigation system failures due to equipment malfunction or unexpected weather changes. Manual operation of irrigation valves allows farmers to quickly shut off water flow, preventing overwatering and conserving resources. This capability is especially crucial in regions with limited water supply, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, where efficient water management can significantly impact crop yields. Buyers should consider sourcing robust and reliable valve systems that can withstand harsh outdoor conditions.
What Role Does Manual Valve Control Play in Landscaping Services?
Landscaping professionals frequently encounter issues with irrigation systems that require immediate attention. By being able to manually turn off valves, they can address leaks or system failures without disrupting the entire irrigation schedule. This responsiveness not only saves water but also enhances client satisfaction. For landscaping businesses operating in diverse climates, sourcing valves that are easy to operate and compatible with various irrigation setups is essential for maintaining service quality.
How is Manual Shutoff Used in Golf Course Management?
Golf courses require precise irrigation management to maintain lush greens and fairways. When a valve malfunctions or requires maintenance, being able to manually shut off the irrigation zone minimizes water waste and protects the investment in landscaping. Golf course managers in regions with varying climates, such as Europe and South America, must prioritize sourcing user-friendly valve systems that facilitate quick adjustments and repairs.
What is the Importance of Manual Control in Municipal Water Management?
Municipalities often manage large-scale irrigation systems for public parks and recreational areas. Manual control of irrigation valves is vital for quickly addressing issues that may arise, such as leaks or equipment failures. This capability ensures that water resources are used sustainably, which is increasingly important in regions facing water scarcity. Buyers should look for solutions that comply with local water management regulations and are designed for longevity and ease of maintenance.
How Does Manual Operation Benefit Horticulture?
In horticulture, where specific water needs are critical for plant health, the ability to manually control irrigation valves is invaluable. Growers can adjust water flow based on plant requirements or environmental conditions, ensuring optimal growth. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in regions like Brazil, where diverse crops may have varying irrigation needs. Buyers should focus on sourcing precise and adaptable valve systems that support specialized horticultural practices.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to turn off irrigation valve manually’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Accessing Buried Valves
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those managing large agricultural or landscaping operations, face the challenge of accessing buried irrigation valves. These valves can often be located deep underground, making manual operation cumbersome. If a valve needs to be turned off manually due to a malfunction in the automated system, the labor-intensive process of digging them out can lead to delays in irrigation management. This is especially problematic in regions where time-sensitive agricultural practices are crucial, such as during planting or harvesting seasons.
The Solution: To effectively manage this issue, buyers should consider investing in valve box risers or extension kits that elevate valve access points above ground level. This proactive approach allows for easier manual operation without the need for extensive excavation. Additionally, they should implement a regular maintenance schedule that includes checking and marking the locations of all irrigation valves. By keeping these areas clear and accessible, users can save time and labor costs when they need to operate valves manually. Furthermore, training staff on the specific location and operation of these valves will ensure that they can respond quickly in emergencies.
Scenario 2: Lack of Knowledge on Manual Operation Methods
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers, especially those new to irrigation systems, is the lack of knowledge regarding the specific methods for manually turning off valves. Misunderstanding the mechanics can lead to improper handling, resulting in further system damage or inefficient water use. This is particularly concerning in regions with water scarcity, where every drop counts.
The Solution: To address this knowledge gap, organizations should provide comprehensive training sessions for all personnel involved in the irrigation process. This training should cover the different types of valves used in their systems, such as solenoid-operated and manual bleed valves, and demonstrate the proper techniques for manual operation. Creating easy-to-follow instructional materials, such as step-by-step guides or video tutorials, can also enhance understanding. Additionally, B2B buyers can establish a network of suppliers who offer technical support and resources, ensuring that they have access to expert advice when needed.
Scenario 3: Emergency Situations Requiring Immediate Action
The Problem: In situations where an irrigation valve fails unexpectedly, such as during peak growing seasons, the inability to turn it off manually can lead to significant water waste or even crop damage. For B2B buyers managing large-scale agricultural operations, the stakes are high, as prolonged water flow can disrupt irrigation schedules and lead to financial losses.
The Solution: To mitigate the risks associated with valve failures, buyers should implement a robust emergency response plan that includes contingency protocols for manual valve operation. This plan should involve equipping teams with the right tools, such as adjustable wrenches or screwdrivers, specifically designed for their irrigation systems. Additionally, regular drills can prepare staff to act swiftly and effectively in emergencies. Investing in smart irrigation systems with fail-safe features can also provide real-time alerts to any malfunctions, allowing for quicker manual intervention. By prioritizing preparedness and equipping teams with the necessary tools and knowledge, organizations can minimize the impact of unexpected irrigation challenges.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to turn off irrigation valve manually
What are the Common Materials Used for Irrigation Valve Components?
When selecting materials for irrigation valve components, particularly for manual operation, several options are prevalent. Each material offers unique properties that can affect performance, durability, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of irrigation valves, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties:
PVC is known for its excellent chemical resistance, lightweight nature, and ability to withstand moderate pressure and temperature variations. It is typically rated for pressures up to 150 psi and can handle temperatures up to 140°F (60°C).
Pros & Cons:
PVC is durable and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for irrigation systems. However, it can become brittle over time, especially when exposed to UV light, which may limit its lifespan in outdoor applications. Additionally, while it is relatively easy to manufacture, the joints require careful sealing to prevent leaks.
Impact on Application:
PVC is compatible with water and many fertilizers, making it suitable for various irrigation applications. However, it is not recommended for hot water or steam applications due to its lower temperature tolerance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or ISO. In areas with high UV exposure, UV-resistant grades of PVC should be considered.
2. Brass
Key Properties:
Brass offers excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and durability, withstanding high pressures (up to 300 psi) and temperatures (up to 200°F/93°C).
Pros & Cons:
Brass is robust and provides a long service life, making it ideal for high-performance applications. However, it is more expensive than plastic alternatives and can be susceptible to dezincification in certain water conditions, which may compromise its integrity.
Impact on Application:
Brass valves are highly effective for controlling water flow and are compatible with various media, including potable water. Their durability makes them suitable for high-pressure systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like the Middle East, where water quality can vary, buyers should ensure that the brass used is of high quality to prevent corrosion. Compliance with standards like JIS or DIN may also be necessary.
3. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures (up to 500 psi and 1000°F/538°C).
Pros & Cons:
While stainless steel is highly durable and suitable for a wide range of applications, it is also one of the more expensive materials. Its manufacturing process is complex, which can lead to higher costs.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel valves are ideal for harsh environments, including those with high salinity or chemical exposure. They maintain integrity and performance over time, making them a reliable choice for irrigation systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider the grade of stainless steel (e.g., 304 or 316) based on environmental conditions. Compliance with local standards is essential, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
4. Polypropylene
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is a lightweight, chemical-resistant thermoplastic that can handle pressures up to 100 psi and temperatures up to 180°F (82°C).
Pros & Cons:
It is cost-effective and offers good resistance to chemicals and UV light. However, it may not be as durable as PVC or metal options and can become brittle over time under certain conditions.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene valves are suitable for various irrigation applications, especially in environments where chemical exposure is a concern. However, they may not be ideal for high-pressure systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In regions like Brazil, where agricultural chemicals are commonly used, polypropylene’s chemical resistance can be a significant advantage. Buyers should verify compliance with local standards to ensure product suitability.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to turn off irrigation valve manually | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Residential and light commercial irrigation systems | Cost-effective and lightweight | Brittle over time, UV exposure | Low |
| Brass | High-performance irrigation systems | Excellent durability | Higher cost, dezincification risk | High |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environments with high salinity or chemicals | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Expensive, complex manufacturing | High |
| Polypropylene | Chemical exposure environments in agriculture | Good chemical resistance | Less durable than metals | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with valuable insights into material selection for irrigation valves, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to turn off irrigation valve manually
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Irrigation Valves?
The manufacturing process for irrigation valves involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, such as durable plastics or metals like brass and stainless steel. These materials are typically subjected to rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet the necessary specifications for strength, corrosion resistance, and durability.
Forming: During the forming stage, the selected materials are shaped into the components of the irrigation valve. This can involve various techniques such as injection molding for plastics or machining for metals. Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining are often utilized to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances, which are critical for the valve’s functionality.
Assembly: Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This stage often includes the integration of solenoids, which are essential for the automatic operation of the valves. Automated assembly lines may be employed to enhance efficiency, but manual assembly techniques are also common to ensure quality control at each step.
Finishing: The final stage involves finishing processes that improve the valve’s appearance and enhance its resistance to environmental factors. This may include surface treatments like anodizing or coating to prevent corrosion and increase longevity. The finishing touches not only contribute to the aesthetic appeal but also play a crucial role in the valve’s overall performance.
Which Key Techniques Are Used in Manufacturing Irrigation Valves?
Several techniques are pivotal in the manufacturing of irrigation valves, each contributing to the reliability and efficiency of the final product.
Injection Molding: This technique is widely used for creating plastic components of the valves. It allows for complex shapes and designs, which can enhance functionality and reduce material waste.
CNC Machining: CNC technology is critical for producing precise metal components. It offers high accuracy and repeatability, ensuring that each valve meets stringent specifications.
Leak Testing: After assembly, valves undergo leak testing, which is vital for ensuring that they perform effectively under pressure. This testing can be done using water or air pressure to identify any potential weaknesses.
Electromagnetic Testing: For solenoid valves, electromagnetic testing is utilized to ensure that the solenoids function correctly. This includes checking for electrical integrity and operational reliability.
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for Irrigation Valves?
Quality control is paramount in the manufacturing of irrigation valves, ensuring that products are reliable and safe for use. Several international standards and industry-specific certifications guide this process.
ISO 9001: This internationally recognized standard focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements, which is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking demonstrates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. This certification is vital for ensuring that irrigation valves meet EU regulations.
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) has developed standards for valves used in various industries, including agriculture. Adhering to these standards can enhance the credibility of manufacturers, particularly in regions with stringent regulatory frameworks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
The quality control process in the manufacturing of irrigation valves includes several checkpoints that help maintain high standards.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards before they enter the production process is crucial for preventing defects.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, IPQC involves regular inspections at various stages of production. This includes monitoring machine settings, tolerances, and assembly procedures to identify and rectify issues early.
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the valves are shipped, they undergo final inspections, including functional testing and performance checks. This stage ensures that the valves operate as intended and meet all relevant standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for mitigating risk.
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers allows buyers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with relevant standards. This firsthand examination can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s capabilities.
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers can help buyers understand the QC measures in place. These reports should outline testing methods, failure rates, and corrective actions taken.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can verify compliance with international standards and provide an additional layer of assurance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with suppliers from different regions, international B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control.
Regulatory Differences: Different countries have varying regulations and standards for irrigation products. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements to ensure compliance.
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and reliability can impact supplier relationships. In some regions, there may be a stronger emphasis on personal relationships, while in others, formal agreements and documentation are prioritized.
Communication Barriers: Language differences can pose challenges in understanding quality control processes. Establishing clear communication channels and using straightforward documentation can help mitigate these issues.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with irrigation valves, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. This knowledge not only fosters better supplier relationships but also ensures the procurement of reliable, high-quality irrigation solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to turn off irrigation valve manually’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring the necessary knowledge and tools for manually turning off irrigation valves, this guide provides a structured checklist. This is essential for ensuring that irrigation systems operate efficiently, especially in regions where reliable water management is crucial for agricultural and landscaping success.
Step 1: Understand Your System Type
Before taking any action, identify the type of irrigation system and valves in use. Different systems, such as drip or sprinkler irrigation, may have unique valve designs and operation methods. Knowing the specifics helps in selecting the right tools and techniques for manual operation.
Step 2: Assess Valve Accessibility
Evaluate the physical accessibility of your irrigation valves. Some valves may be buried underground or positioned in hard-to-reach areas, making manual operation challenging. Ensure that you have the necessary equipment, like a shovel or proper tools, to reach the valves safely and efficiently.
Step 3: Gather Required Tools
Collect all necessary tools for manually operating the valves. Common tools include:
– Screwdrivers for turning manual bleed screws.
– Wrenches for adjusting solenoid valves.
– Protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, to ensure safety while working in potentially muddy or wet conditions.
Having these tools on hand streamlines the process and minimizes downtime.
Step 4: Follow Manufacturer Instructions
Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for your specific valve model. This is crucial as different brands may have distinct mechanisms for manual operation. Look for:
– Manuals or product guides that detail the operation process.
– Online resources or customer support for additional clarification if the manuals are unavailable.
Step 5: Test Valve Functionality
Once you have manually turned off the valve, it’s essential to test its functionality. Check for leaks or signs of malfunction to ensure the valve is working correctly.
– Observe the valve box for any water accumulation, which may indicate a problem.
– Perform a thorough inspection to confirm that all parts are intact and operational.
Step 6: Document Your Findings
Maintain a record of your manual operations and any issues encountered. This documentation is valuable for future reference and can aid in troubleshooting.
– Note specific valve models and any repairs or adjustments made.
– Keep a log of operational times and conditions to identify patterns that may require attention.
Step 7: Consider Professional Assistance
If manual operation proves too complex or if issues persist, consider engaging a professional. This can save time and ensure that the irrigation system is correctly set up for optimal performance.
– Evaluate local service providers who specialize in irrigation systems.
– Request quotes and service details to compare options effectively.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can ensure their irrigation systems function reliably and efficiently, ultimately supporting their agricultural or landscaping goals in diverse environments.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to turn off irrigation valve manually Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Irrigation Valve Manual Shut-off Solutions?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing solutions to manually turn off irrigation valves, several critical components contribute to the overall pricing. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The type of materials used in the manufacturing of manual shut-off devices significantly affects pricing. Common materials include durable plastics, metals, and rubber, which contribute to the valve’s longevity and functionality. Buyers should consider the cost differences between standard materials and those that offer higher resistance to corrosion or wear, especially in regions with harsh climates.
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to workers during the manufacturing process. This can vary significantly based on the region and skill level required. For instance, countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to ensure that quality is not compromised.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which may be passed on to buyers in the form of lower prices.
Tooling: The investment in tooling—such as molds and dies used in the production of valves—can impact pricing. Custom tooling for specialized valves may increase initial costs but can lead to cost savings in large volume orders due to economies of scale.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet quality standards is vital, particularly in B2B transactions. Rigorous QC processes might add to the cost but are essential for maintaining reliability and customer satisfaction.
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. Import duties and tariffs are additional costs that can significantly affect pricing, especially for international buyers.
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a profit margin that reflects their business model and market conditions. This margin can vary based on competition and the unique value proposition offered.
What Price Influencers Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Several factors influence the pricing of manual irrigation valve solutions:
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases generally lead to lower per-unit costs. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQs) can help buyers negotiate better pricing structures.
Specifications and Customization: Custom solutions tailored to specific irrigation needs may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against standard options.
Quality and Certifications: Valves that meet international quality standards or have specific certifications may be priced higher. Buyers should assess the importance of these certifications in their local market.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a role in pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge a premium but often deliver better quality and service.
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) can aid buyers in calculating total landed costs, including shipping and insurance, which are crucial for accurate budgeting.
What Are Some Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Tips for International Buyers?
B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies to optimize their procurement process:
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders or early payments.
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not only the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, replacement, and operational efficiency of the valves.
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of local market conditions and currency fluctuations that can affect pricing. This is particularly relevant for international transactions where exchange rates can impact costs.
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Loyalty can often translate into favorable terms and access to exclusive deals.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for irrigation valve manual shut-off solutions can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they receive competitive pricing that aligns with their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to turn off irrigation valve manually With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives for Turning Off Irrigation Valves
In the realm of irrigation management, effective control of water flow is essential for both resource conservation and system efficiency. While manually turning off irrigation valves is a common practice, several alternative methods offer unique benefits and drawbacks. This analysis compares the manual method with automated systems and remote control technologies, providing B2B buyers with actionable insights into the best solution for their needs.
| Comparison Aspect | How To Turn Off Irrigation Valve Manually | Automated Irrigation System | Remote Control Irrigation System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for immediate control | Consistent, programmable | Flexible, can be adjusted remotely |
| Cost | Low (requires no additional investment) | Medium to High (installation costs) | Medium (requires devices and setup) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple, no tools needed | Requires professional installation | Moderate, needs initial setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, basic checks needed | Regular maintenance required | Moderate, depends on technology used |
| Best Use Case | Small-scale operations, quick fixes | Large farms or extensive systems | Areas with variable needs, remote locations |
Understanding the Alternatives
Automated Irrigation System
Automated irrigation systems are designed to control water flow based on pre-set schedules or environmental conditions. These systems utilize timers and sensors to ensure optimal watering without manual intervention.
Pros:
– Increased efficiency and conservation of water.
– Reduces labor costs as manual checks are minimized.
– Can be programmed for different zones based on plant needs.
Cons:
– Higher initial investment and installation costs.
– Requires ongoing maintenance and potential repairs.
– Complexity may lead to user errors if not properly configured.
Remote Control Irrigation System
Remote control irrigation systems allow users to manage their irrigation from a distance via smartphone apps or web interfaces. This technology often integrates with weather forecasts to optimize watering schedules.
Pros:
– Flexibility to adjust watering schedules in real-time, based on weather conditions or immediate needs.
– Ideal for managing multiple zones or large properties without physical presence.
– Can enhance system efficiency by minimizing overwatering.
Cons:
– Dependence on technology, which can fail or require updates.
– Initial setup can be complex and may necessitate technical expertise.
– Potentially higher operational costs due to technology investment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers, the decision between manually turning off irrigation valves and adopting alternative technologies hinges on specific operational needs, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Manual control is best suited for smaller operations or situations requiring immediate action. In contrast, automated and remote control systems provide efficiency and convenience for larger-scale agricultural settings or businesses aiming to optimize water usage over extensive areas. By carefully assessing these factors, buyers can select the irrigation control method that aligns best with their operational goals and resource management strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to turn off irrigation valve manually
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Irrigation Valves?
Understanding the technical specifications of irrigation valves is critical for B2B buyers, especially when it comes to ensuring reliability and efficiency in agricultural and landscaping applications. Here are some essential properties:
Material Grade
The material grade of an irrigation valve often dictates its durability and resistance to corrosion. Common materials include PVC, brass, and stainless steel. For instance, brass valves are favored for their longevity and resistance to harsh weather conditions, making them ideal for diverse climates, including those found in Africa and the Middle East.Pressure Rating
This specification indicates the maximum pressure the valve can withstand. It is crucial for ensuring that the valve operates efficiently under varying water pressures. Typically, irrigation valves are rated between 150 to 300 psi (pounds per square inch). Selecting the correct pressure rating is vital to prevent valve failure, especially in high-pressure systems common in larger agricultural setups.Flow Rate
The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM), defines how much water can pass through the valve. This specification is critical for matching the valve to the system’s needs, ensuring that crops receive adequate water without overloading the system. Buyers should assess their irrigation needs to select valves that optimize water distribution effectively.Temperature Tolerance
Valves must be rated for specific temperature ranges to prevent material degradation. This is particularly important in regions with extreme weather conditions. For example, some valves are designed to operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -20°F to 150°F. Understanding temperature tolerance helps buyers avoid premature failures and extend the lifespan of their irrigation systems.Actuation Type
Irrigation valves can be either manual or automated. Manual valves require physical intervention to open or close, which may be suitable for smaller systems. In contrast, automated valves are controlled electronically and can be programmed for efficiency. Understanding the actuation type helps buyers determine the level of labor and automation needed for their irrigation projects.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Irrigation Systems?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation between B2B buyers and suppliers. Here are several important terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly when dealing with large-scale irrigation systems.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. This process is crucial for procurement teams to gather competitive pricing and make informed purchasing decisions.Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities.Hydraulic Performance
This term describes how well a valve operates under hydraulic conditions, including flow rates and pressures. Understanding hydraulic performance is vital for ensuring that the irrigation system functions efficiently and meets agricultural demands.Valve Configuration
This refers to the design and layout of the valve within the irrigation system, which can affect performance. Common configurations include inline and angle valves, each suited for different applications. Understanding valve configuration aids in system design and troubleshooting.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their irrigation systems’ effectiveness, efficiency, and longevity.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to turn off irrigation valve manually Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics for Turning Off Irrigation Valves Manually?
The global market for irrigation systems, including the manual operation of irrigation valves, is witnessing significant growth due to increased agricultural demands and water scarcity concerns. Key drivers include the rising need for efficient water management in regions facing drought, particularly in parts of Africa and the Middle East, where agricultural practices are heavily reliant on irrigation systems. Furthermore, as urbanization expands, countries in South America and Europe are increasingly investing in advanced irrigation technologies that allow for manual overrides, such as turning off valves without electronic systems.
Emerging trends in B2B technology highlight the integration of smart irrigation systems with manual functionalities, enabling operators to efficiently manage water resources while also having the capability to intervene manually when necessary. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, the emphasis is on sourcing durable, easy-to-operate manual systems that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. The market is also seeing a shift towards modular systems that can be tailored to specific agricultural needs, allowing businesses to optimize their irrigation processes while maintaining flexibility.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Irrigation Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing practices in the irrigation sector. With global awareness surrounding environmental impacts, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to ethical sourcing standards and utilize eco-friendly materials. For example, manufacturers that offer irrigation valves made from recycled plastics or sustainably sourced metals are gaining traction among international buyers.
In addition, certifications related to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ labels, are becoming essential in the decision-making process. Buyers are not just looking for products that perform well but also for those that minimize environmental impact over their lifecycle. This trend is particularly pronounced in European markets, where regulatory frameworks encourage sustainable practices. By aligning with suppliers that prioritize sustainability, businesses can enhance their brand reputation while contributing to global efforts in conservation and responsible resource management.
What Is the Historical Context of Manual Irrigation Valve Operation?
The operation of irrigation valves has evolved significantly over the decades. Initially, irrigation systems were purely mechanical, relying heavily on manual intervention to control water flow. As technology advanced, automated systems emerged, allowing for timed irrigation based on pre-set schedules. However, the need for manual overrides has remained crucial, especially in regions with unreliable electricity supply or where systems may fail due to wear and tear.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards creating more user-friendly manual options that can easily integrate with automated systems, ensuring that operators can quickly address any issues without needing specialized training. This evolution reflects a broader trend in the irrigation industry towards creating systems that are not only efficient but also adaptable to varying operational contexts and challenges faced by international B2B buyers.
By understanding these dynamics, businesses can make informed sourcing decisions that align with both current market trends and future sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to turn off irrigation valve manually
How do I manually turn off my irrigation valve?
To manually turn off an irrigation valve, locate the solenoid (a cylindrical component with wires attached) at the valve’s top. Turn the solenoid clockwise approximately one-quarter turn to close the valve. Alternatively, if your valve has a manual bleed screw, twist it clockwise until the water flow stops. Be cautious, as some water may leak out during this process, particularly if the system was under pressure. This method is essential for immediate control, especially when the automatic timer is malfunctioning.What are the common issues that prevent irrigation valves from closing?
Irrigation valves may fail to close due to debris buildup, mechanical failure, or electrical issues. Sediment can clog the valve, preventing it from sealing properly. Additionally, a faulty solenoid may not activate or deactivate the valve as required. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspecting the components, can help mitigate these issues and ensure the system operates efficiently.What is the best type of irrigation valve for manual operation?
The best type of irrigation valve for manual operation is typically a solenoid valve with a manual override feature. This allows users to engage or disengage the valve manually without relying on an electronic timer. Look for models that offer easy access to the solenoid or have a manual bleed screw for quick adjustments. Brands like Rain Bird and Hunter are well-regarded in the industry for their reliability and ease of use.How can I ensure my irrigation system is suitable for different climates?
To ensure your irrigation system is suitable for various climates, consider the local weather patterns, soil types, and plant requirements in your region. In arid areas, a drip irrigation system may be more efficient, while regions with high rainfall may benefit from a more traditional sprinkler system. Additionally, sourcing systems designed to withstand extreme temperatures and conditions is crucial for longevity and performance.What customization options are available for irrigation valves?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for irrigation valves, including size, pressure ratings, and flow control features. You can often select materials that are resistant to corrosion or UV damage, especially important for harsh climates. When sourcing valves, discuss your specific requirements with suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs, whether for residential or commercial applications.What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for irrigation valves?
Minimum order quantities for irrigation valves can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of valve. Generally, MOQs range from a few units to several hundred for bulk purchases. For international buyers, it’s essential to confirm MOQs during the negotiation process to ensure they align with your project needs and budget.What payment terms should I expect when purchasing irrigation valves internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of irrigation valves typically include options like upfront payment, net 30/60/90 days, or letter of credit. It’s crucial to discuss these terms with your supplier upfront to avoid any misunderstandings. Be aware that different regions may have varying standards, so ensure compliance with local financial regulations.How can I verify the quality of irrigation valves before purchasing?
To verify the quality of irrigation valves before purchasing, request samples from suppliers and conduct a thorough inspection. Check for certifications, such as ISO or ASTM, that indicate compliance with industry standards. Additionally, seek references or reviews from previous clients to gauge the supplier’s reputation and the durability of their products. Engaging in quality assurance practices upfront can save significant costs in repairs and replacements later.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 How To Turn Off Irrigation Valve Manually Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Backflow Prevention – Essential Components and Tools
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Double-check (backflow prevention device), isolation valve (likely buried, possibly a gate valve), ball valve, DCVA (double check valve assembly), wye strainer. Tools mentioned: crescent wrench, channel locks. Replacement parts: spare ball valve handles (available on eBay or specialist irrigation/plumbing shops).
2. Sprinkler Supply Store – Manual Bleed Screw & Solenoid
Domain: sprinklersupplystore.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Manual Bleed Screw: Located towards the back of the valve near the flow control; twist counter-clockwise to open (usually no more than half a turn) and clockwise to close. Solenoid: A black cylinder with wires attached; turn approximately one-quarter turn counter-clockwise to open and clockwise to close. Note: Opening the manual bleed screw causes water to leak out, which is normal.
3. Rain Bird – Inline Sprinkler Valves
Domain: houzz.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Old Rain Bird inline sprinkler valves, 1″ sprinkler lines, buried 18″ in the ground, manual shut-off capability via small knob on top of the valve.
4. Irrigation Solutions – Key Components
Domain: diy.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Irrigation system components including popup sprinklers, drip sprinklers, zone valves, and a controller. The valves have a black plastic turn screw head for manual operation. A 24 VAC power supply can be used for testing the solenoid of the valves.
5. Quality Irrigation – Sprinkler System Services
Domain: quality-irrigation.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Emergency Sprinkler System Shutdown Instructions, Professional Shutdown & Winterization, Backflow Preventer Testing, Residential Sprinkler Systems, Commercial Outdoor Lighting Systems, WiFi Controlled Lawn Sprinkler Systems, Affordable Financing Options, Service Area: Omaha, NE and surrounding areas.
6. JustAnswer – Sprinkler Valve Troubleshooting Guide
Domain: justanswer.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Sprinkler valve troubleshooting guide; common issues include solenoid malfunctions and valve diaphragm wear; recommended actions: check solenoid for debris, clean solenoid filter screen, test solenoid coil with multimeter, inspect valve diaphragm, manually close valve, regularly flush valve to remove sediment, replace worn parts to restore operation.
7. Terry Love – Electric Anti-Siphon Valve
Domain: terrylove.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Electric anti-siphon valve, appears to be old, has a solenoid for manual operation, may have a stuck diaphragm or plunger.
8. Hunter – Pro-C Sprinkler System
Domain: lawnsite.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Hunter Pro-C sprinkler system; includes 5 solenoid valves; each valve has 1/4 turn mechanism for manual operation; main brass valve connected to water line.
9. Hydro-Rain – Pop-Up Rotor 4 in. & K-Rain – MiniPro Rotor 12 in.
Domain: school.sprinklerwarehouse.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Hydro-Rain Pop-Up Rotor 4 in. | HRX-075, K-Rain MiniPro Rotor 12 in. | 13012
10. Horizon – Checkmate 3
Domain: horizononline.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Horizon offers troubleshooting guidance for irrigation valves, including steps for electrical and mechanical checks. Key products mentioned include the Checkmate 3, Checker Plus, and Checker Jr., which are devices for verifying solenoid operation. The troubleshooting process involves checking water supply, controller programming, solenoid functionality, and cleaning or replacing valve components. …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to turn off irrigation valve manually
In conclusion, mastering the manual operation of irrigation valves is not only a practical skill but also a critical component of effective irrigation management for B2B buyers in diverse agricultural markets. By understanding the mechanics of your irrigation systems, including how to manually turn off valves, you can ensure continuous operation and prevent costly water wastage. This knowledge is particularly vital for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where water resources may be limited and agricultural efficiency is paramount.
Strategic sourcing of high-quality irrigation components can further enhance system reliability. Investing in durable valves and reliable controllers can minimize maintenance costs and downtime, ultimately leading to a more sustainable operation. As you navigate the complexities of irrigation management, consider partnerships with suppliers who understand local needs and offer tailored solutions.
Looking ahead, prioritize the integration of innovative irrigation technologies that enhance efficiency and adaptability in your operations. By proactively addressing the challenges of manual valve control and seeking out strategic suppliers, you can position your business for long-term success in an increasingly competitive landscape.