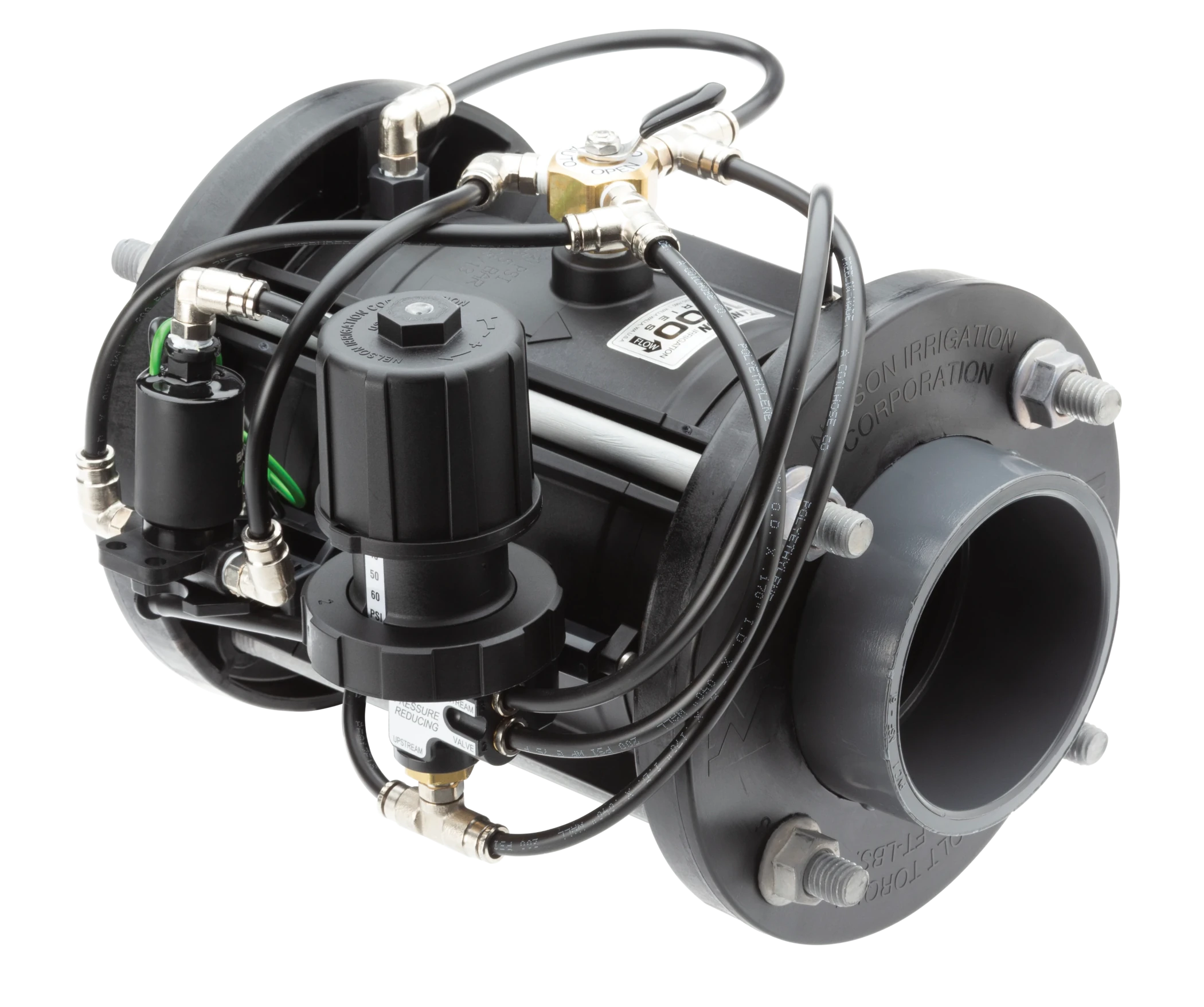
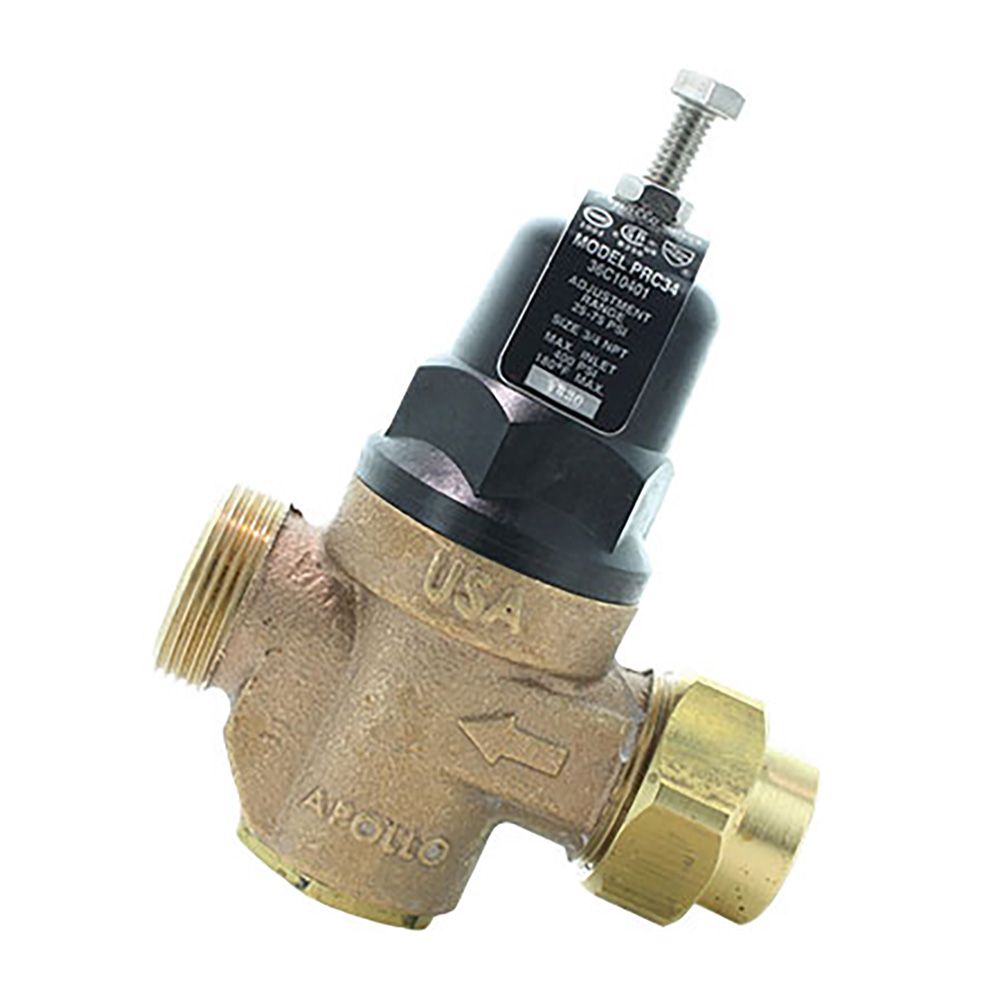
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for irrigation pressure reducing valve
In the dynamic landscape of agricultural innovation, sourcing effective irrigation pressure reducing valves has emerged as a pivotal challenge for international B2B buyers. With the rising demand for efficient water management in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of these valves is essential. Excessive water pressure can lead to system malfunctions, damaging costly drip irrigation setups and impeding agricultural productivity. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of irrigation pressure reducing valves, their applications across diverse agricultural practices, and best practices for supplier vetting.
Our aim is to empower B2B buyers by equipping them with the knowledge necessary for informed purchasing decisions. From exploring the technical specifications that dictate performance to analyzing cost structures and maintenance considerations, this guide covers all critical aspects of irrigation pressure reducing valves. Additionally, we will provide insights into regional market trends, ensuring that buyers from countries like Brazil and Nigeria can navigate their local landscapes effectively. By understanding the right products and suppliers, businesses can enhance their irrigation systems, improve water efficiency, and ultimately drive sustainable agricultural practices.
Understanding irrigation pressure reducing valve Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inline Pressure Regulators | Installed directly in the irrigation line, compact design. | Suitable for large-scale agricultural systems. | Pros: Space-efficient and easy to install. Cons: May require more frequent maintenance. |
| Outlet Pressure Regulators | Attached to the outlet of a water source, adjustable pressure settings. | Ideal for varying flow conditions in drip systems. | Pros: Customizable pressure settings. Cons: Can be more complex to install. |
| Automatic Pressure Regulators | Self-adjusting based on water flow and pressure fluctuations. | Used in dynamic agricultural environments. | Pros: Reduces manual adjustments; maintains efficiency. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Low-Flow Pressure Regulators | Designed for systems with low flow rates, ensuring optimal emitter performance. | Perfect for residential or small-scale irrigation. | Pros: Prevents emitter damage; enhances water savings. Cons: Limited to low-pressure applications. |
| High-Flow Pressure Regulators | Handles larger volumes of water while maintaining consistent pressure. | Suitable for commercial and industrial applications. | Pros: Supports extensive irrigation setups. Cons: Bulkier and potentially more expensive. |
What Are Inline Pressure Regulators and Their Applications?
Inline pressure regulators are installed directly within the irrigation line, making them a compact option for managing water pressure in large-scale agricultural systems. They are designed to reduce incoming water pressure to a level suitable for drip emitters, ensuring efficient water distribution. Buyers should consider the specific flow rate requirements of their irrigation system, as inline models may require more frequent maintenance due to their continuous exposure to water flow.
How Do Outlet Pressure Regulators Work in Drip Systems?
Outlet pressure regulators attach to the outlet of a water source and provide adjustable pressure settings, making them ideal for systems where flow conditions can vary. These regulators allow users to customize the pressure based on the specific needs of their irrigation setup, which is crucial for optimizing water use and emitter performance. When purchasing outlet regulators, buyers should evaluate their system’s pressure requirements and consider the complexity of installation.
What Are the Advantages of Automatic Pressure Regulators?
Automatic pressure regulators are designed to self-adjust based on fluctuations in water flow and pressure. This feature makes them particularly beneficial in dynamic agricultural environments where water supply conditions can change frequently. They minimize the need for manual adjustments, thereby enhancing operational efficiency. However, the initial investment for these regulators can be higher, so buyers should assess their long-term water management needs against the upfront costs.
Why Choose Low-Flow Pressure Regulators?
Low-flow pressure regulators are specifically engineered for irrigation systems with lower flow rates, ensuring optimal performance of drip emitters. These regulators are perfect for residential or small-scale irrigation applications, as they prevent emitter damage and promote water savings. Buyers should consider the specific pressure requirements of their systems to ensure compatibility, as low-flow models are limited to lower pressure applications.
What Are High-Flow Pressure Regulators Best Suited For?
High-flow pressure regulators are designed to manage larger volumes of water while maintaining consistent pressure levels. They are particularly suitable for commercial and industrial irrigation applications, where extensive setups demand reliable performance. While these regulators support larger irrigation systems, they can be bulkier and more expensive. Buyers should evaluate their irrigation scale and budget when considering high-flow options.
Key Industrial Applications of irrigation pressure reducing valve
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valve | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Drip Irrigation Systems | Ensures optimal water delivery, reducing waste | Compatibility with existing systems and local water pressure |
| Landscaping & Horticulture | Sprinkler Systems | Protects systems from high pressure damage | Flow rate specifications and pressure settings |
| Golf Course Management | Irrigation Management for Greens and Fairways | Maintains healthy turf while conserving water | Durability under varying environmental conditions |
| Municipal Water Management | Urban Green Spaces and Parks | Enhances sustainability and reduces maintenance | Compliance with local regulations and pressure requirements |
| Greenhouse Operations | Controlled Environment Agriculture | Optimizes water usage for plant health | Precision in pressure regulation to meet specific crop needs |
How is the Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valve Used in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, irrigation pressure reducing valves are crucial for drip irrigation systems. They regulate high incoming water pressure to ensure that emitters deliver water at the optimal pressure, typically between 10 to 30 PSI. This prevents damage to the system, such as burst lines or blown emitters, which can lead to costly repairs and water wastage. Buyers should consider compatibility with existing irrigation infrastructure and the local water supply characteristics, particularly in regions like Brazil and Nigeria, where water pressure can vary significantly.
What Role Do Pressure Reducing Valves Play in Landscaping & Horticulture?
In landscaping and horticulture, pressure reducing valves are used to maintain the integrity of sprinkler systems. High water pressure can lead to over-spraying and inefficient water distribution, harming plants and wasting resources. These valves ensure that the water delivered is at a safe pressure, enhancing the efficiency of irrigation systems. For international buyers, sourcing valves that match the flow rate and pressure requirements of their specific applications is essential, especially in diverse climates across South America and Africa.
How Do Golf Course Managers Benefit from Using Pressure Reducing Valves?
Golf course management relies heavily on maintaining lush greens and fairways, which requires precise irrigation control. Pressure reducing valves play a vital role by ensuring that the irrigation systems operate within the correct pressure range, preventing damage and ensuring uniform water distribution. This not only promotes healthy turf growth but also conserves water, aligning with sustainability goals. Buyers should prioritize sourcing durable valves that can withstand varying environmental conditions, particularly in the Middle East, where heat and dryness can impact irrigation efficiency.
Why Are Pressure Reducing Valves Important for Municipal Water Management?
Municipal water management systems utilize pressure reducing valves in urban parks and green spaces to promote sustainable irrigation practices. By controlling water pressure, these valves help maintain plant health while minimizing water usage, which is critical in areas facing water scarcity. Compliance with local regulations regarding water usage and pressure specifications is a key consideration for municipalities when sourcing these valves, especially in European markets where environmental standards are stringent.
How Do Greenhouse Operations Optimize Water Usage with Pressure Reducing Valves?
In controlled environment agriculture, such as greenhouses, pressure reducing valves are integral for optimizing water usage. They ensure that water is delivered at the precise pressure required for different crops, promoting healthy growth and maximizing yield. This precision is particularly important for international buyers who may deal with varying crop types and local water conditions. When sourcing, it is crucial to consider valves that provide consistent performance and are adaptable to specific greenhouse conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘irrigation pressure reducing valve’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Water Pressure Causing System Damage
The Problem: Many agricultural businesses and landscaping companies face the challenge of high incoming water pressure that can lead to serious damage within drip irrigation systems. Excessive pressure can result in burst lines, blown emitters, and overall inefficiency in water distribution. This not only jeopardizes crop health but also increases maintenance costs and downtime, leading to potential financial losses.
The Solution: To effectively manage high water pressure, it is crucial for buyers to source and install an appropriate irrigation pressure reducing valve (PRV). When selecting a PRV, ensure that it is rated for the specific pressure range of your system, typically between 10 to 30 PSI for drip irrigation. Additionally, it’s essential to place the PRV downstream of the main water source and after any filtration systems to prevent debris from damaging the regulator. Regular maintenance checks should also be scheduled to ensure the regulator remains functional over time, with replacements made as necessary to prevent system failures.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Water Flow and Distribution Issues
The Problem: Inconsistent water flow is a common issue faced by businesses operating irrigation systems. This inconsistency can stem from fluctuations in incoming water pressure, leading to uneven watering across fields or landscapes. Such variability can hinder plant growth and lead to patchy results, affecting overall crop yields and quality.
The Solution: To tackle this problem, B2B buyers should consider investing in high-quality pressure reducing valves that feature adjustable settings. By selecting a model that allows for fine-tuning of the output pressure, users can ensure a consistent flow rate that aligns with the requirements of their irrigation system. Additionally, implementing a network of pressure sensors along with the PRVs can provide real-time data, allowing for immediate adjustments and improving overall system reliability. Buyers should also ensure that the PRVs are properly calibrated according to the specific needs of their irrigation setup for optimal performance.
Scenario 3: Maintenance and Longevity of Pressure Regulators
The Problem: Buyers often encounter issues with the longevity and effectiveness of pressure reducing valves due to wear and tear, debris accumulation, or poor installation. A malfunctioning PRV can lead to inadequate pressure regulation, resulting in system inefficiencies and potentially costly repairs. This problem is particularly relevant in regions with high sediment levels in the water supply, where debris can quickly clog regulators.
The Solution: To extend the lifespan of pressure reducing valves and ensure their reliability, buyers should prioritize regular maintenance practices. This includes routine inspections for signs of wear, cleaning or replacing filters to prevent clogging, and verifying that the PRV is positioned correctly within the irrigation system. It is also advisable to select PRVs with robust construction materials that can withstand local environmental conditions. Additionally, investing in high-quality, reliable products from reputable manufacturers can significantly reduce the frequency of replacements and maintenance needs, ultimately leading to cost savings and enhanced operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for irrigation pressure reducing valve
When selecting materials for irrigation pressure reducing valves, it is essential to consider properties that directly affect performance, durability, and compatibility with various irrigation systems. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of these valves, highlighting their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Brass for Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves?
Brass is a popular choice for irrigation pressure reducing valves due to its excellent mechanical properties and resistance to corrosion. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and can handle pressures exceeding 150 PSI. Brass is also resistant to rust and oxidation, making it suitable for various water sources.
Pros: Brass valves are durable and have a long lifespan, often exceeding 20 years with proper maintenance. They are also relatively easy to manufacture and can be machined to precise specifications.
Cons: The primary drawback of brass is its cost, which is generally higher than plastic alternatives. Additionally, brass can be susceptible to dezincification in certain water conditions, leading to premature failure.
Impact on Application: Brass valves are compatible with a wide range of media, including potable water and irrigation systems. However, care must be taken in areas with aggressive water chemistry.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe may prefer brass due to its robustness, while those in Africa and South America may weigh cost more heavily.
How Does PVC Perform as a Material for Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is another common material used for irrigation pressure reducing valves. It is lightweight, has a temperature rating of up to 60°C, and can handle pressures up to 100 PSI.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for agricultural applications where soil and water conditions can vary significantly. Its low weight simplifies installation.
Cons: PVC is less durable than metals and may become brittle over time, especially when exposed to UV light. It also has a lower temperature tolerance, limiting its use in hot climates.
Impact on Application: PVC valves are suitable for non-potable water applications, including irrigation systems that utilize surface water. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards is essential, especially in regions like the Middle East, where temperature extremes can affect material performance. Buyers should ensure that the PVC used meets the necessary certifications.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves?
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength and resistance to corrosion, making it an excellent choice for irrigation pressure reducing valves. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 400°C) and pressures (over 300 PSI).
Pros: Stainless steel valves are highly durable and can last for decades, even in harsh environments. They are also resistant to chemical corrosion, making them suitable for various irrigation applications.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of stainless steel is its cost, which is significantly higher than both brass and PVC. Additionally, manufacturing stainless steel components can be more complex, leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are ideal for high-pressure systems and applications involving aggressive chemicals. They are compatible with both potable and non-potable water.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with international standards such as JIS and ASTM. In Europe, the preference for stainless steel is often driven by its longevity and performance in diverse conditions.
How Does Polypropylene Compare for Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves?
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer that is becoming increasingly popular for irrigation pressure reducing valves. It has a temperature rating of up to 90°C and can handle pressures around 80 PSI.
Pros: Polypropylene is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to a wide range of chemicals. It is also less prone to cracking compared to PVC, making it a reliable choice for irrigation applications.
Cons: While polypropylene is durable, it may not perform as well under high pressures or extreme temperatures compared to metals. Its mechanical strength is lower than that of brass or stainless steel.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene valves are suitable for agricultural irrigation systems, especially in regions with moderate climate conditions. They are not recommended for high-pressure or high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that polypropylene valves comply with local regulations. In regions like Africa and South America, where cost is a significant factor, polypropylene may be favored for its affordability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for irrigation pressure reducing valve | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | General irrigation systems, potable water applications | Durable and long-lasting | Higher cost, dezincification risk | High |
| PVC | Non-potable irrigation, low-pressure systems | Cost-effective and lightweight | Brittle over time, lower pressure tolerance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure and chemical-resistant applications | Extremely durable and corrosion-resistant | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Polypropylene | Agricultural irrigation in moderate climates | Lightweight and chemical resistant | Lower strength under pressure/temperature | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their irrigation pressure reducing valve choices based on regional conditions and application requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for irrigation pressure reducing valve
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves?
The manufacturing process of irrigation pressure reducing valves involves several critical stages designed to ensure durability, functionality, and compliance with international standards. These stages can be summarized as follows:
Material Preparation: Selecting the Right Components
The first step in manufacturing irrigation pressure reducing valves is the selection of high-quality materials. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and durable plastics. The choice of material is crucial, as it affects the valve’s resistance to corrosion, pressure handling capabilities, and overall lifespan. Suppliers often conduct material testing to verify the quality and suitability of the selected materials before proceeding.
Forming: Crafting the Valve Body
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves various techniques such as machining, forging, or molding, depending on the design specifications of the valve. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is commonly used for precision parts, ensuring that each valve body is manufactured to exact dimensions. Forging processes are preferred for metal components, as they enhance strength and structural integrity.
Assembly: Bringing Components Together
After forming, the assembly stage takes place. This involves the integration of various components such as the diaphragm, spring, and valve seat. Each component must be installed with precision to ensure proper functioning. Automated assembly lines may be employed for efficiency, but manual assembly is often utilized for more complex designs. During this stage, attention to detail is paramount, as any misalignment can lead to performance issues.
Finishing: Ensuring a High-Quality Surface
The final manufacturing stage is finishing, which includes surface treatments like polishing, coating, or painting. These treatments not only enhance aesthetics but also improve corrosion resistance and durability. For instance, anodizing is often applied to aluminum components to protect against oxidation. Quality control checks are performed at this stage to ensure that all finished products meet the required specifications and standards.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Pressure Reducing Valves?
Quality assurance is a fundamental aspect of manufacturing irrigation pressure reducing valves, ensuring that the final products meet both customer expectations and regulatory requirements. Various international and industry-specific standards guide this process.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
The most recognized international quality standard is ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to consistent quality and continuous improvement. In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for the European market and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications may also apply, depending on the intended use and market of the valves.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process. These checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various checks are conducted to ensure that each stage adheres to quality standards. This may include monitoring dimensions and tolerances during machining and assembly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the valves are assembled and finished, a final inspection is performed. This includes functional testing to verify performance under specified pressure conditions.
What Common Testing Methods Are Utilized?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the functionality and safety of irrigation pressure reducing valves:
- Hydraulic Testing: This method checks the valve’s ability to withstand pressure without leaking.
- Flow Testing: Ensures that the valve regulates water flow as intended, maintaining the appropriate pressure levels.
- Durability Testing: Simulates long-term use to assess wear and tear over time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensuring reliable products.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Ensure Quality?
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help assess a supplier’s adherence to quality standards. Buyers should request documentation of past audits and certifications.
Request Quality Control Reports: Suppliers should provide comprehensive QC reports detailing inspection results, testing methods used, and any corrective actions taken.
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Independent inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process and product quality. This can be particularly beneficial for buyers unfamiliar with local suppliers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate several nuances when it comes to quality control:
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying standards and regulations. Buyers should be familiar with the specific requirements of their target markets, such as CE compliance in Europe or NSF certification for potable water applications.
Cultural and Language Barriers: Communication issues may arise when working with suppliers in different countries. It’s essential to establish clear lines of communication and confirm that all parties understand quality expectations.
Lead Times and Logistics: International shipping can introduce delays, affecting the timely delivery of products. Buyers should consider lead times in their procurement strategies and communicate with suppliers to manage expectations.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for irrigation pressure reducing valves are intricate and multifaceted. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, recognizing the importance of quality control, and taking proactive steps to verify supplier practices, B2B buyers can ensure they are sourcing reliable and high-quality products. This diligence not only enhances operational efficiency but also builds long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers across the globe.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘irrigation pressure reducing valve’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure irrigation pressure reducing valves. These essential components play a critical role in maintaining optimal pressure levels within irrigation systems, ensuring efficient water distribution and protecting against damage caused by excessive pressure. By following this checklist, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for selecting the right pressure reducing valve. Consider the specific flow rates, pressure ranges (typically between 10 to 30 PSI for drip systems), and connection sizes required for your irrigation system. This step ensures that the valve you select will integrate seamlessly into your existing infrastructure.
- Flow Rate: Determine the maximum and minimum flow rates your system will experience.
- Pressure Requirements: Assess the incoming pressure and identify the reduction needed for optimal performance.
Step 2: Assess Environmental Conditions
Understanding the environmental conditions where the valve will be installed is crucial. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can influence the valve’s performance and longevity.
- Material Selection: Choose valves made from durable materials that can withstand your local conditions, such as UV-resistant plastics or corrosion-resistant metals.
- Installation Location: Consider whether the valve will be exposed to the elements or installed in a protected environment.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions to gauge reliability and product quality.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for established suppliers with a proven track record in the irrigation industry.
- Customer Reviews: Check online reviews and testimonials to understand other buyers’ experiences.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Standards
Ensure that the pressure reducing valves meet local and international quality and safety standards. Compliance with standards can significantly reduce the risk of operational failures and legal issues.
- Certifications: Look for products certified by recognized organizations (e.g., ISO, NSF) that ensure adherence to quality protocols.
- Testing Procedures: Inquire about the testing processes the manufacturer employs to ensure product reliability.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing your purchase, request samples of the pressure reducing valves to conduct compatibility and performance testing. Testing allows you to assess the valve’s efficiency and identify any potential issues before a bulk order.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate the valve under various pressure and flow conditions to ensure it meets your specifications.
- Installation Trials: Test the ease of installation and integration with your existing systems.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and product, engage in negotiations to secure the best pricing and terms. Understanding market rates and supplier constraints can help you achieve favorable outcomes.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about bulk purchase discounts or loyalty programs.
- Payment Terms: Discuss payment options that align with your budget and cash flow management.
Step 7: Establish a Maintenance Plan
Finally, develop a maintenance plan to ensure the longevity and reliability of the pressure reducing valves. Regular maintenance can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the lifespan of your irrigation system.
- Routine Checks: Schedule regular inspections to monitor performance and identify wear.
- Replacement Parts: Ensure that replacement parts are readily available to minimize downtime in case of failure.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing irrigation pressure reducing valves effectively, leading to improved irrigation efficiency and system longevity.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for irrigation pressure reducing valve Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves?
When sourcing irrigation pressure reducing valves, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials include brass, plastic, and stainless steel, each with varying costs. High-quality materials may lead to higher upfront costs but offer better durability and longevity.
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality control processes. Skilled labor may be necessary for high-precision valves, especially those requiring customization.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs of utilities, rent, and equipment used in production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, impacting the final price.
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom designs. These costs are typically spread across larger production runs, making bulk orders more cost-effective.
Quality Control (QC): Investing in stringent QC processes ensures product reliability and compliance with industry standards. This can add to the initial cost but may save buyers from future expenses related to failures.
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, are critical, especially for international orders. Factors like distance, shipping method, and freight terms (Incoterms) can significantly influence logistics costs.
Margin: Suppliers will typically mark up prices to ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market positioning and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Irrigation Valve Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of irrigation pressure reducing valves:
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for minimum order quantities (MOQs), making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their purchases.
Specifications and Customization: Custom valves tailored to specific requirements can incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of custom features against their budget.
Materials and Quality Certifications: The selection of premium materials and certifications (such as ISO or NSF) can raise costs. However, these investments may be justified by the enhanced performance and reliability of the product.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record, while new entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) will affect shipping costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better deals and manage total costs effectively.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Their Sourcing Process?
To enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing irrigation pressure reducing valves, buyers should consider the following strategies:
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leverage bulk purchasing and long-term relationships to negotiate better rates.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential replacement costs. Investing in higher-quality valves may reduce long-term expenses related to repairs and replacements.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, fluctuations in currency and international trade tariffs can affect pricing. Staying informed about these factors can aid in budget planning.
Regular Market Research: Continuously monitor market trends and competitor pricing. This can provide leverage during negotiations and help identify the best sourcing opportunities.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific order requirements. Always consult with multiple suppliers to get accurate quotes tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing irrigation pressure reducing valve With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves
When considering effective irrigation solutions, it’s crucial to evaluate not only the primary technology, such as irrigation pressure reducing valves (PRVs), but also alternative methods that can achieve similar objectives. This analysis will provide insight into viable alternatives, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their unique agricultural needs.
Comparison Table of Irrigation Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valve | Drip Irrigation Systems | Smart Irrigation Controllers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficiently regulates pressure to protect emitters | Delivers water directly to plant roots | Optimizes watering based on real-time data |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; long-term savings | Variable costs depending on complexity | Higher upfront costs; potential long-term savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires minimal adjustment | More complex setup; requires planning | Requires integration with sensors and software |
| Maintenance | Periodic checks needed; can wear over time | Regular maintenance to prevent clogging | Software updates and occasional sensor maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for systems with fluctuating water pressure | Best for water conservation in gardens and farms | Optimal for large-scale operations needing precision |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation is a method that delivers water directly to the roots of plants through a network of tubing and emitters. This system is particularly advantageous for water conservation, as it minimizes evaporation and runoff. However, the initial setup can be more complex and costly compared to PRVs. Regular maintenance is required to prevent clogging, which can lead to inefficiencies if not properly managed. Drip systems are best suited for small to medium-sized agricultural operations focused on maximizing water efficiency.
2. Smart Irrigation Controllers
Smart irrigation controllers utilize advanced technology, such as weather data and soil moisture sensors, to optimize watering schedules. This method can significantly reduce water usage and increase crop yield through precise irrigation practices. Although the upfront investment is higher due to the need for technology integration, the long-term savings and efficiency gains can justify the costs. These controllers are ideal for larger agricultural operations where precise water management is critical. However, they require regular software updates and sensor maintenance to ensure optimal functionality.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Irrigation Solution
Selecting the right irrigation solution involves assessing various factors, including performance needs, budget constraints, and the specific agricultural context. While irrigation pressure reducing valves offer a reliable method for managing water pressure, alternatives like drip irrigation systems and smart irrigation controllers may provide enhanced efficiency and savings over time. B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their operational requirements, long-term goals, and available resources to determine the most suitable solution for their irrigation needs. By doing so, they can ensure optimal performance and sustainability in their agricultural practices.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for irrigation pressure reducing valve
What Are the Key Technical Properties of an Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valve?
Understanding the technical specifications of irrigation pressure reducing valves is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their irrigation systems. Here are some essential properties to consider:
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of pressure reducing valves typically includes brass, stainless steel, or durable plastics. Brass and stainless steel offer superior durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for long-term use in various environmental conditions. For buyers, selecting the right material is vital for ensuring longevity and reducing maintenance costs.Pressure Rating
This specification indicates the maximum pressure the valve can handle, usually measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). Most irrigation pressure reducing valves operate effectively within a range of 10 to 30 PSI. It’s essential for buyers to match the pressure rating with their irrigation system’s requirements to avoid damage from excessive pressure.Flow Rate
The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM), specifies how much water can pass through the valve at a given pressure. Choosing a valve with the appropriate flow rate is critical for maintaining efficient water distribution across the irrigation system. A mismatch can lead to inadequate watering or system failure.Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the acceptable limits of variation in the valve’s dimensions or performance specifications. Tight tolerances ensure precise control over water pressure and flow, which is particularly important in drip irrigation systems. For buyers, understanding tolerance levels can aid in the selection of valves that provide consistent and reliable performance.Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the ambient temperatures within which the valve can function optimally. Different materials may have varying temperature tolerances, impacting their performance in hot or cold climates. Buyers should consider local climate conditions when selecting valves to ensure optimal functionality.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Related to Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valves?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some commonly used terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, sourcing irrigation pressure reducing valves from reputable OEMs can ensure product quality and compatibility with existing systems.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers as it can impact inventory costs and supply chain management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price and availability information from suppliers. It typically includes specific requirements, quantities, and delivery timelines. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ helps ensure competitive pricing and informed decision-making.Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and obligations, which is vital for international transactions.Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to plan their irrigation projects effectively and ensure timely implementation.Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the performance of the valve. Buyers should consider warranty terms as they reflect the manufacturer’s confidence in the product and can influence long-term maintenance costs.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing irrigation pressure reducing valves, ultimately enhancing their irrigation system’s efficiency and reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the irrigation pressure reducing valve Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valve Sector?
The irrigation pressure reducing valve (PRV) sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by global agricultural demands and technological advancements. One of the primary market drivers is the increasing emphasis on efficient water usage due to climate change and water scarcity issues, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East. Countries like Brazil and Nigeria are heavily investing in advanced irrigation systems to enhance crop yields while minimizing water waste.
Emerging B2B technology trends such as smart irrigation systems, which integrate IoT devices and sensors, are reshaping how pressure regulators are utilized. These systems allow for real-time monitoring and adjustments to pressure levels, improving the overall efficiency of irrigation setups. Furthermore, the rise of precision agriculture is pushing manufacturers to develop PRVs that can cater to specific crop needs and environmental conditions, thus providing tailored solutions for international buyers.
Market dynamics are also influenced by the growing demand for durable and high-performance materials that can withstand varying environmental conditions. As competition intensifies, B2B buyers should focus on sourcing suppliers that offer innovative products with extended warranties and robust customer support. Adopting a proactive approach in understanding local market regulations and certifications can also aid in making informed sourcing decisions.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valve Market?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the irrigation pressure reducing valve sector. The environmental impact of traditional irrigation practices has led to a shift towards more sustainable technologies. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and ensuring that their manufacturing processes are energy-efficient.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with a growing demand for transparency in supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to evaluate suppliers based on their adherence to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and sustainability-focused labels can serve as benchmarks for responsible sourcing decisions.
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ materials in the production of PRVs is not only beneficial for the environment but can also enhance the product’s marketability. As consumers and businesses alike become more eco-conscious, offering products that meet these sustainability standards can provide a competitive edge in the market. B2B buyers should consider partnering with manufacturers who are committed to sustainability and ethical sourcing to align with the evolving expectations of their customers.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valve Sector?
The evolution of irrigation pressure reducing valves can be traced back to the early days of agricultural irrigation when the focus was primarily on basic water flow management. As agricultural practices evolved, so did the technology behind irrigation systems. The introduction of drip irrigation in the 1960s marked a pivotal moment, highlighting the necessity of pressure regulation to prevent system damage and ensure efficient water delivery.
Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of more sophisticated PRVs that are not only reliable but also capable of handling varying pressures and flow rates. The integration of smart technology in recent years has further revolutionized the sector, allowing for automated adjustments and real-time monitoring of irrigation systems. This historical progression reflects the growing understanding of the critical role that effective water management plays in sustainable agriculture and the need for continuous innovation in the irrigation pressure reducing valve market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of irrigation pressure reducing valve
How do I solve high water pressure issues in my irrigation system?
To address high water pressure in your irrigation system, installing a pressure reducing valve is essential. This valve will lower the incoming pressure to a safe level suitable for your irrigation components, preventing damage to emitters and tubing. Ensure that the chosen valve is compatible with your system’s specifications, including the desired pressure range (typically between 10 to 30 PSI for drip systems). Regularly check and maintain the valve to ensure optimal performance and longevity.What is the best pressure reducing valve for drip irrigation systems?
The ideal pressure reducing valve for drip irrigation systems should maintain a consistent pressure between 10 to 30 PSI, depending on the specific requirements of your emitters. Look for valves designed for low-flow applications, as they are specifically engineered to function efficiently within drip systems. Additionally, consider factors such as flow rate compatibility, durability against corrosion, and ease of installation. Consulting with suppliers for recommendations based on your unique system design can also be beneficial.What are the key factors to consider when sourcing pressure reducing valves internationally?
When sourcing pressure reducing valves internationally, consider factors such as supplier reliability, product quality, and compliance with local regulations. Evaluate the supplier’s certifications and experience in the industry, especially if they have experience with agricultural or irrigation products. Additionally, assess the shipping options, lead times, and potential customs duties. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers can clarify any uncertainties regarding product specifications and logistics.What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect for pressure reducing valves?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for pressure reducing valves can vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units to several hundred, depending on the manufacturer’s production capabilities and inventory. It is advisable to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are testing a new product line. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for smaller orders, particularly for first-time buyers or trial orders.How do I ensure the quality of pressure reducing valves from international suppliers?
To ensure the quality of pressure reducing valves from international suppliers, request product samples for testing prior to placing larger orders. Verify that the products meet international quality standards, such as ISO or other relevant certifications. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance processes and any warranties they offer. Establishing a clear communication channel with the supplier can also facilitate addressing any quality concerns promptly.What payment terms are typical when sourcing pressure reducing valves internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of pressure reducing valves typically include options like advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, often ranging from 30% to 50% of the total order value. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk tolerance. Understanding the payment process and currency exchange implications can also help avoid potential financial issues.What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing pressure reducing valves?
When importing pressure reducing valves, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Choose between air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on your urgency and budget. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, to facilitate a smooth customs clearance process. Working with a freight forwarder can also help streamline logistics management.Can I customize pressure reducing valves for my specific irrigation needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for pressure reducing valves to meet specific irrigation requirements. Customization can include alterations in pressure settings, flow rates, or materials used in construction. When discussing your needs with suppliers, provide detailed specifications to ensure the product aligns with your system. Keep in mind that custom orders may have longer lead times and potentially higher costs, so plan accordingly.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Irrigation Pressure Reducing Valve Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. DripWorks – Pressure Regulators
Domain: dripworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Drip Irrigation Pressure Regulators reduce incoming water pressure to a set pressure usable by a drip system. They are essential when the incoming pressure is too high for emitters or fittings. The flow rate of the regulator should match the system, and pressure regulation takes effect only after the minimum specified flow passes through. Available options include low-flow, medium-flow, and high-f…
2. Rainbird – Drip Irrigation Essentials
Domain: store.rainbird.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Filters, Valves & Pressure Regulators for Drip Irrigation Systems. Key products include: 1/2 in Barbed On/Off Valve ($3.99), 1/4 inch Barbed Shut-Off Valve (Pack of 2) ($2.99), 3/4IN FHT 25PSI REGULATOR ($7.99), LCRBY100D – 1 in. Large Capacity Disc Filter ($36.98), LCRBY150D – 1 1/2 in. Large Capacity Disc Filter ($83.34), LFV075 – 3/4 in. Low Flow Drip Irrigation Valve ($32.74), PRB100 – 1 in. P…
3. Irrigation King – BALDR 1-1/2 Pressure Reducing Valve
Domain: irrigationking.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Pressure Reducing & Sustaining Valves for Irrigation. Ideal for high-flow drip and low-pressure sprinkler systems. Operate manually or with a controller and timer for automatic zone control. Built for tough agricultural and commercial environments. Products include:
– BALDR 1-1/2″ Pressure Reducing Valve with 24V AC Solenoid – NPT, was $342.78, Special Price $197.00
– BALDR 2″ Pressure Reducing …
4. Senninger – Pressure Regulators
Domain: senninger.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Senninger® black and white pressure regulators are known for their accuracy, durability, and efficiency in irrigation systems. Key models include: Mini Pressure Regulator (Flows: 0.5 to 3.5 gpm, Pressures: 15 to 40 psi), PRLG (Flows: 0.5 to 7.0 gpm, Pressures: 10 to 40 psi), PRL (Flows: 0.5 to 8.0 gpm, Pressures: 6 to 40 psi), PSR™2 (Flows: 0.5 to 15 gpm, Pressures: 6 to 50 psi), Filter Regulator …
5. Rain Bird – Pressure Regulators
Domain: sprinklersupplystore.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Rain Bird Pressure Regulators include various models such as PRS-Dial, PRS-050-30, XACZ-075-PRF, XCZ-100-PRB-COM, and XACZ-100-PRF. Key specifications are:
– PRS-Dial: Regulates outlet pressure up to 100 PSI, adjustable between 15 to 100 PSI.
– PRS-050-30: Inlet pressure of 15 to 70 psi, flow rate of 0.50 to 4.00 GPM, providing 30 psi pressure regulation.
– XACZ-075-PRF: 3/4″ Low Flow Anti-Siph…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for irrigation pressure reducing valve
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of irrigation pressure reducing valves is pivotal for optimizing agricultural efficiency and sustainability, particularly in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the critical role these valves play in regulating water pressure, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance the performance of drip irrigation systems. The selection of the right pressure regulator, tailored to specific flow rates and system requirements, not only minimizes the risk of damage from excessive pressure but also improves water conservation efforts.
Moreover, establishing strong partnerships with reliable suppliers can ensure access to high-quality products and ongoing support. As global demand for efficient irrigation solutions continues to grow, embracing innovative technologies and sustainable practices will be essential for agricultural success.
International buyers are encouraged to proactively engage with manufacturers and distributors, leveraging their expertise to navigate the complexities of irrigation systems. Together, we can pave the way for a more sustainable agricultural future, ensuring that every drop of water is utilized effectively.