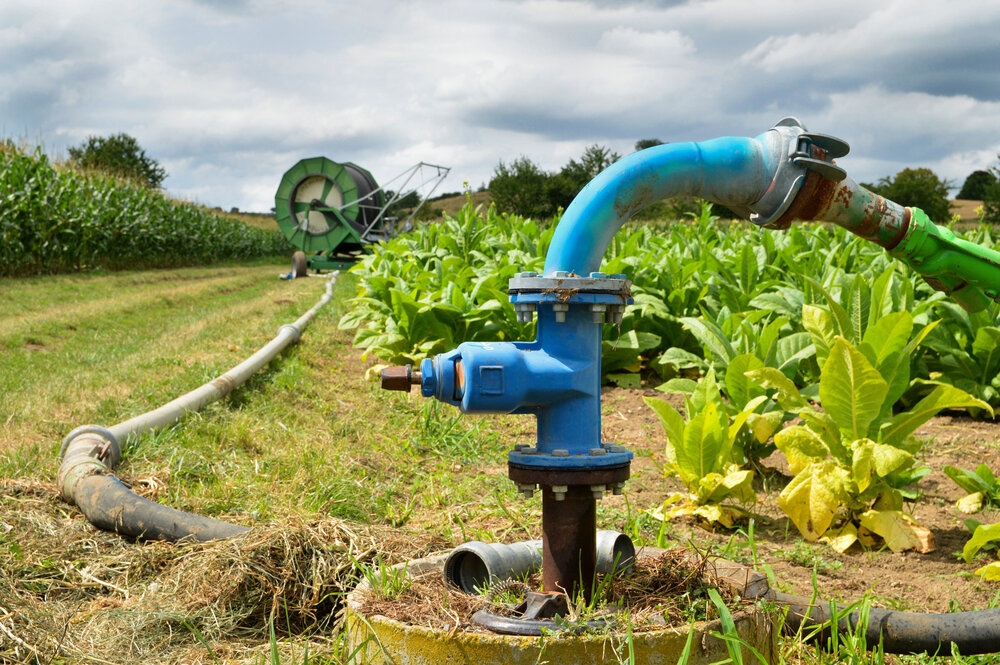
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for priming an irrigation pump
In the intricate landscape of global agriculture, one persistent challenge that many international B2B buyers face is effectively priming an irrigation pump. Whether you are operating in the arid climates of Africa or the humid regions of South America, understanding the nuances of pump priming is essential for ensuring optimal water flow and irrigation efficiency. This comprehensive guide delves into various types of irrigation pumps, their specific applications, and the critical processes involved in priming them, providing you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions.
We explore the essential criteria for vetting suppliers, including reliability, product quality, and after-sales support. Additionally, we address cost considerations, helping you balance budget constraints with the need for high-performance equipment. By equipping you with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide empowers B2B buyers from diverse regions, including the Middle East and Europe, to streamline their procurement processes and enhance their operational efficiency. As irrigation systems become increasingly vital to sustaining agricultural productivity, understanding the intricacies of pump priming not only mitigates operational risks but also positions your business for success in a competitive market.
Understanding priming an irrigation pump Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Priming Pumps | Built-in suction check valve; can remove air automatically. | Agriculture, horticulture, industrial | Pros: Easier operation, less manual intervention. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Centrifugal Pumps | Requires external priming; uses a foot valve to maintain prime. | Irrigation, water supply systems | Pros: Efficient for high flow rates. Cons: Needs regular maintenance to prevent air leaks. |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Positive displacement; can handle viscous liquids. | Fertilizer application, chemical transfer | Pros: Versatile, can handle different fluids. Cons: Limited flow rates compared to centrifugal. |
| Eductor Primers | Utilizes a vacuum to assist in priming; often requires additional components. | Large agricultural operations | Pros: Effective for larger systems, can prime quickly. Cons: Complexity in setup and maintenance. |
| Electric Vacuum Pumps | Creates a vacuum to remove air; can be used in remote locations. | Irrigation, aquaculture | Pros: Low energy consumption, effective in various conditions. Cons: Dependency on electricity can be a drawback. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Self-Priming Pumps?
Self-priming pumps are designed with an integrated suction check valve, allowing them to automatically remove air from the system. This feature significantly reduces the manual effort required to prime the pump, making it ideal for agricultural and horticultural applications where efficiency is paramount. Buyers should consider the higher initial investment against the long-term operational savings and reduced labor costs.
How Do Centrifugal Pumps Function in Priming?
Centrifugal pumps rely on an external priming method, often utilizing a foot valve to maintain the prime. They are widely used in irrigation and water supply systems due to their ability to handle large volumes of water efficiently. However, they require regular maintenance to prevent air leaks, which can disrupt operations. B2B buyers should weigh the efficiency benefits against the maintenance requirements when selecting this type.
What Makes Diaphragm Pumps Suitable for Specific Applications?
Diaphragm pumps operate on a positive displacement principle, making them suitable for transferring viscous liquids and chemicals. Their versatility allows them to be used in fertilizer applications and chemical transfers, where precise handling is crucial. However, their flow rates are generally lower compared to centrifugal pumps, so buyers should consider application requirements when making a purchase decision.
Why Consider Eductor Primers for Large Operations?
Eductor primers utilize a vacuum mechanism to assist in priming and are particularly beneficial for large agricultural operations. They can prime quickly and effectively, making them ideal for systems that require rapid water delivery. However, their complexity in setup and maintenance might pose challenges for some buyers. Understanding the operational environment is critical when considering this option.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Electric Vacuum Pumps?
Electric vacuum pumps create a vacuum to remove air, making them effective in various irrigation and aquaculture settings. Their low energy consumption is an attractive feature, especially in remote locations where power availability may vary. However, reliance on electricity can be a disadvantage in areas with inconsistent power supply. B2B buyers should assess the reliability of their power sources when considering this pump type.
Key Industrial Applications of priming an irrigation pump
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Priming an Irrigation Pump | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Crop Irrigation Systems | Ensures efficient water delivery for crop health | Quality of pumps, compatibility with existing systems |
| Horticulture | Greenhouse Watering Systems | Maintains optimal moisture levels for plant growth | Durability under varying climates, ease of maintenance |
| Landscaping | Turf and Lawn Irrigation | Promotes healthy lawns and landscapes | Energy efficiency, cost of operation, and reliability |
| Aquaculture | Fish Farm Water Management | Supports optimal aquatic environments | Water quality control, pump capacity, and filtration needs |
| Municipal Water Supply | Community Irrigation Projects | Enhances water distribution for public spaces | Compliance with local regulations, durability, and service support |
How is Priming an Irrigation Pump Used in Agriculture?
In agriculture, priming an irrigation pump is essential for ensuring that water is effectively delivered to crops. This process helps eliminate air from the pump system, allowing for consistent water flow. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, understanding the local water availability and pump specifications is crucial. Reliable pumps can significantly enhance crop yields, making it vital to source durable and efficient models that can withstand local conditions.
What Role Does Priming Play in Horticulture?
In horticulture, priming irrigation pumps is critical for greenhouse operations where consistent moisture levels are necessary for plant health. The ability to maintain precise water delivery prevents over- or under-watering, which can be detrimental to sensitive plants. Buyers should consider pumps that are easy to prime and maintain, especially in areas with fluctuating temperatures and humidity levels. Sourcing pumps that are compatible with automated systems can further streamline operations.
Why is Priming Important for Landscaping Applications?
For landscaping businesses, priming irrigation pumps ensures that water is evenly distributed across lawns and gardens, promoting lush growth. A well-primed pump minimizes downtime, allowing for timely maintenance of landscapes. Buyers must focus on energy-efficient pumps that can handle varying pressure requirements. Additionally, sourcing pumps that are robust enough to endure outdoor conditions will reduce long-term replacement costs.
How Does Priming Benefit Aquaculture Operations?
In aquaculture, priming irrigation pumps is vital for maintaining water quality in fish farms. Properly primed pumps facilitate effective water circulation, which is essential for oxygenation and temperature regulation. International buyers in this sector should prioritize pumps that can handle specific aquatic environments and provide filtration solutions. Ensuring that pumps meet local environmental regulations will also be a key consideration for sourcing.
What is the Importance of Priming in Municipal Water Supply Systems?
For municipal water supply systems, priming irrigation pumps is crucial for community irrigation projects. Properly primed pumps enhance water distribution efficiency, ensuring that public spaces receive adequate irrigation. Buyers must consider compliance with local regulations regarding pump specifications and performance standards. Additionally, sourcing reliable pumps that offer long-term service support can significantly benefit municipal projects, reducing maintenance and operational costs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘priming an irrigation pump’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Maintaining a Consistent Prime in Remote Areas
The Problem: For B2B buyers operating irrigation systems in remote locations, the challenge of maintaining a consistent prime in irrigation pumps can be significant. Many operations face logistical issues, such as lack of immediate access to repair services or replacement parts. This can lead to prolonged downtime during crucial growing seasons, causing stress and financial loss. For instance, if a pump loses prime due to air leaks or a faulty foot valve, it can be difficult to quickly troubleshoot and resolve the issue without on-site assistance.
The Solution: To mitigate this problem, B2B buyers should invest in high-quality, self-priming pumps specifically designed for remote operations. These pumps typically feature built-in mechanisms to prevent air from entering the system, which helps maintain a consistent prime. Buyers should also consider implementing a preventive maintenance program that includes regular inspections of the pump and associated piping. Additionally, sourcing reliable suppliers who offer on-site training for local technicians can empower teams to troubleshoot and perform basic repairs, thereby reducing downtime. Investing in remote monitoring technology can also alert operators to potential issues before they escalate, ensuring a proactive approach to pump management.
Scenario 2: Issues with Pumping Water from Variable Sources
The Problem: Many agricultural businesses source water from different locations, such as wells, rivers, or reservoirs, which can vary significantly in quality and pressure. When attempting to prime an irrigation pump from these variable sources, users often encounter challenges like inconsistent water flow, sediment clogging, or the presence of debris. Such variability can result in frequent pump priming failures, leading to inefficiencies and increased operational costs.
The Solution: To address these challenges, buyers should implement a robust filtration system before the water reaches the pump. Using a combination of sediment filters and strainers can significantly reduce debris and sediment, ensuring a cleaner and more consistent water supply. Furthermore, selecting pumps that are specifically engineered to handle variable pressure and flow conditions can make a substantial difference. Educating the team on the importance of pre-filtering water and regularly maintaining the filtration system will enhance pump performance and longevity. In addition, consider investing in adjustable pumps that can adapt to varying pressure conditions, which may reduce the frequency of priming issues.
Scenario 3: Complications Due to Seasonal Changes
The Problem: In regions with distinct seasonal changes, such as Africa or South America, B2B buyers often face difficulties when reactivating irrigation pumps after prolonged periods of inactivity, such as during winter or dry seasons. Pumps that sit idle can lose prime due to evaporation or temperature fluctuations, leading to increased labor costs and operational delays when it’s time to prime them again. The risk of damage to the pump components from freezing or other seasonal factors further complicates the situation.
The Solution: To effectively prepare for seasonal changes, businesses should establish a seasonal maintenance routine that includes thorough inspections and appropriate winterization techniques. This could involve draining the pump and piping to prevent freeze damage, as well as using antifreeze solutions where applicable. Buyers should also consider investing in pump models designed for easy winterization and reactivation, which can simplify the priming process. Additionally, training staff on best practices for seasonal maintenance can ensure that pumps are correctly primed and ready for operation as soon as the growing season begins. By planning ahead and implementing these strategies, businesses can minimize disruptions and maintain efficient irrigation operations year-round.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for priming an irrigation pump
What Are the Key Materials for Priming an Irrigation Pump?
When selecting materials for priming an irrigation pump, it’s essential to consider various factors such as durability, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the priming process, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties: PVC is known for its excellent chemical resistance, lightweight nature, and ability to withstand moderate pressures (up to 150 PSI). It is also resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various water types.
Pros & Cons: The durability of PVC is a significant advantage; it does not rust or corrode easily. However, it can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light, which may lead to cracking. Additionally, while PVC is relatively inexpensive, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: PVC is compatible with most water media, including saline and acidic waters. However, it is essential to avoid using PVC in high-temperature applications, as this can lead to deformation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM D1785 or DIN 8061. In regions like Africa and South America, where UV exposure is high, selecting UV-stabilized PVC can enhance longevity.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers high tensile strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and can handle high temperatures and pressures (up to 300 PSI). Its durability makes it a preferred choice for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to corrosion, even in harsh environments. However, it is more expensive than other materials and can be prone to pitting in certain corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including potable water, making it suitable for various irrigation applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 or JIS G3459 is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe may prefer stainless steel due to its durability and aesthetic appeal, while also considering the higher initial investment.
3. Rubber
Key Properties: Rubber is flexible, has good elasticity, and can withstand moderate pressures (up to 50 PSI). It is also resistant to abrasion and impacts, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility of rubber allows for easy installation and adaptability in various configurations. However, it can degrade over time due to UV exposure and chemical interactions, leading to a shorter lifespan compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Rubber is suitable for sealing and flexible connections in the pump system. It is essential to choose rubber compounds that are compatible with the specific media being pumped.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for rubber materials that meet local standards, such as ASTM D2000 or ISO 1629. In regions with extreme temperatures, selecting rubber with enhanced thermal stability is advisable.
4. Polypropylene
Key Properties: Polypropylene is lightweight, has good chemical resistance, and can handle temperatures up to 200°F. It is also resistant to fatigue and has a low moisture absorption rate.
Pros & Cons: The cost-effectiveness and lightweight nature of polypropylene make it an attractive option. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to metals and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is compatible with a variety of liquids, including acids and bases, making it versatile for irrigation systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D4101 is essential. Buyers in Africa and South America may find polypropylene to be a cost-effective solution, but should also consider its limitations in high-pressure scenarios.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for priming an irrigation pump | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Priming lines and connections | Excellent chemical resistance | Brittle under UV exposure | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure applications | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and potential pitting | High |
| Rubber | Seals and flexible connections | Flexibility and easy installation | Degrades with UV exposure | Med |
| Polypropylene | Lightweight connections and fittings | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower tensile strength | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their irrigation pump priming processes. By carefully considering the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance performance and longevity in diverse environmental conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for priming an irrigation pump
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Priming an Irrigation Pump?
Manufacturing an irrigation pump that is efficient and reliable involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure that the final product meets the high standards expected by international B2B buyers.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality materials, such as stainless steel or reinforced plastics, are typically selected for their durability and resistance to corrosion. The selection process may involve sourcing materials from certified suppliers who adhere to international standards. Material testing for tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and environmental compatibility is also conducted to ensure that only the best materials are used.
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, the next phase is forming. This may involve processes like casting, forging, or machining. For instance, the pump casing might be cast in a mold, while components like impellers could be machined to precise specifications. Advanced techniques such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining ensure high accuracy and repeatability, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the pump’s performance.
Assembly Process
During the assembly phase, various components—such as the motor, impeller, and seals—are brought together. Automated assembly lines are often employed to enhance efficiency, but skilled technicians also play a vital role in quality checks. This stage includes ensuring that all seals are correctly installed to prevent air leaks, which can hinder the pump’s ability to prime effectively.
Finishing Operations
Finally, finishing operations such as painting, coating, or polishing are applied to enhance durability and aesthetics. Protective coatings are particularly important to prevent corrosion, especially in environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals. This stage may also involve a final inspection to ensure that the pump meets all design specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Irrigation Pumps?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for irrigation pumps, which must perform reliably under varying conditions. QA processes are designed to adhere to international standards, such as ISO 9001, as well as industry-specific certifications like CE and API.
International Standards and Certifications
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized quality management standard that helps organizations ensure that they meet customer and regulatory requirements. Manufacturers of irrigation pumps often pursue ISO certification to demonstrate their commitment to quality. Similarly, CE marking indicates that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements, while API standards are crucial for pumps used in oil and gas applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. Any subpar materials are rejected to prevent defects later in the manufacturing process.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor production processes. This includes measuring tolerances, checking component fit, and testing assembly integrity.
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs after assembly and finishing. This may involve testing the pump for operational efficiency, checking for leaks, and ensuring compliance with all relevant standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Irrigation Pumps?
Testing methods are crucial to ensuring the reliability and performance of irrigation pumps. Various tests may be conducted, depending on the intended use and regional regulations.
Hydraulic Testing
Hydraulic tests are performed to verify the pump’s performance under actual working conditions. This involves checking flow rates, pressure levels, and the pump’s ability to maintain prime. Such tests are essential for identifying potential issues before the pump is deployed in the field.
Leak Testing
Leak testing is another critical assessment, ensuring that all seals and joints are secure. Common methods include pressure decay tests, where the pump is pressurized and monitored for any drop in pressure that indicates a leak.
Performance Testing
Performance tests evaluate the pump’s efficiency, including its power consumption and output against design specifications. These tests are essential for B2B buyers who seek energy-efficient solutions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Control of Their Suppliers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is paramount to ensuring product reliability.
Supplier Audits
Conducting audits of potential suppliers is an effective way to assess their quality control practices. This involves a thorough review of their manufacturing processes, quality assurance protocols, and adherence to relevant standards.
Quality Reports and Certifications
Buyers should request quality reports and certifications from suppliers. These documents provide insights into the supplier’s compliance with international standards and their commitment to quality.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can be conducted at various stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet specified requirements before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers face unique challenges regarding quality control, particularly when dealing with suppliers from diverse regions. Buyers must be aware of regional regulations, cultural differences in manufacturing practices, and varying standards of quality assurance.
Regulatory Compliance
Understanding the regulatory environment in the supplier’s country is essential. For instance, compliance with local environmental regulations may vary significantly between regions, impacting the manufacturing process and the final product.
Cultural Factors
Cultural differences can influence manufacturing practices. For example, communication styles and work ethics vary, affecting how quality control measures are implemented. Establishing clear expectations and open lines of communication can mitigate these challenges.
Long-Term Partnerships
Building long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can enhance quality assurance efforts. Such partnerships allow for continuous improvement and adaptation to changing market conditions, ensuring that both parties remain aligned on quality objectives.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source high-quality irrigation pumps tailored to their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘priming an irrigation pump’
To assist B2B buyers in efficiently sourcing equipment for priming irrigation pumps, this checklist outlines key steps to ensure a successful procurement process. The following steps will guide you through evaluating suppliers, determining necessary equipment, and ensuring compliance with local standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements of your irrigation system is crucial. Identify the type of pump you are using (e.g., centrifugal, self-priming), the flow rate needed, and the maximum lift height. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that the equipment you procure is suitable for your needs.
- Consider local conditions: Factor in the environmental conditions where the pump will operate, such as altitude and temperature variations, which can affect performance.
Step 2: Assess Supplier Experience and Reputation
Choose suppliers with a proven track record in the irrigation sector. Look for companies that specialize in pumps and have experience in your region, as they will better understand local challenges and regulations.
- Request references: Ask for testimonials or case studies from other businesses that have utilized their products, particularly in similar geographical or operational contexts.
Step 3: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the pumps and related equipment comply with local safety and environmental regulations. This is especially important in regions like Africa and South America, where standards can vary significantly.
- Check certifications: Look for internationally recognized certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) that indicate adherence to quality and safety standards.
Step 4: Evaluate the Availability of Spare Parts and Support
A reliable supply of spare parts and technical support is essential for the long-term operation of your irrigation system. Assess whether the supplier offers readily available parts and responsive customer service.
- Inquire about warranties: Understand the warranty terms and conditions, which can be an indicator of the supplier’s confidence in their products.
Step 5: Review Delivery and Logistics Capabilities
Consider the supplier’s ability to deliver products in a timely manner, especially if you operate in remote areas. Delays can significantly impact agricultural operations, so it’s vital to understand their logistics processes.
- Ask about shipping options: Inquire about their shipping methods and any partnerships with local distributors that can facilitate quicker delivery.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Collect quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Look beyond the initial cost; consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance and operational efficiency.
- Understand payment options: Clarify payment terms, including deposits, credit options, and any discounts for bulk purchases, to manage your cash flow effectively.
Step 7: Conduct a Trial or Demonstration
If possible, arrange for a trial run or demonstration of the pump before making a purchase. This will allow you to assess its performance and compatibility with your existing systems.
- Evaluate user-friendliness: Pay attention to the ease of operation and maintenance, as these factors will influence your team’s ability to effectively manage the equipment.
By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions when sourcing equipment for priming irrigation pumps, ensuring that your investment supports your operational goals while adhering to local standards and conditions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for priming an irrigation pump Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Priming an Irrigation Pump?
When considering the cost structure for priming an irrigation pump, several components come into play. Materials constitute a significant part of the expense, including water, hoses, fittings, and potentially a foot valve. The choice of materials can vary widely; for instance, using high-quality hoses and fittings may raise initial costs but can enhance durability and reduce maintenance expenses in the long run.
Labor costs also factor into the equation, particularly if the priming process requires skilled technicians. The complexity of the irrigation system and the local labor rates will influence this component. Additionally, manufacturing overhead must be accounted for, especially for suppliers who produce pumps and related equipment. This includes utilities, rent, and other operational costs.
Tooling and Quality Control (QC) processes are crucial in ensuring the reliability of the pumps. Investing in robust tooling can lead to more efficient production and fewer defects, thus minimizing long-term costs associated with repairs or replacements. Lastly, logistics costs, encompassing transportation and warehousing, can vary based on geographical location and the proximity of suppliers to the end users.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Priming an Irrigation Pump?
Several factors influence the pricing of priming an irrigation pump. Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) are essential; larger orders typically reduce the per-unit cost, making it more economical for businesses operating at scale. Additionally, specifications and customization can impact pricing significantly. A customized pump may involve higher initial costs due to specialized materials and engineering but could offer better efficiency or longevity.
The quality of materials and certifications also plays a crucial role in pricing. Pumps that meet international standards or certifications may incur higher costs due to rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. Furthermore, supplier factors such as reputation, reliability, and service offerings can influence pricing dynamics. The terms of delivery, or Incoterms, also affect costs; for example, FOB (Free On Board) pricing might be more favorable for buyers who wish to manage shipping logistics.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs for Priming an Irrigation Pump?
International B2B buyers should consider several strategies to negotiate better pricing for priming an irrigation pump. Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is crucial; this includes not just the initial purchase price but also maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs. A cheaper pump might lead to higher long-term costs if it requires frequent repairs or replacements.
Buyers should also be prepared to negotiate terms with suppliers. Building a relationship based on trust and transparency can yield better pricing and service agreements. Additionally, consider exploring bulk purchasing agreements or long-term contracts, which can lead to discounts and more favorable payment terms.
Finally, awareness of pricing nuances specific to regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe is essential. Factors like local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and import duties can significantly impact costs. Buyers in these markets should conduct thorough research and engage with local experts to navigate these complexities effectively.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for priming an irrigation pump can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct comprehensive market research and seek multiple quotes to establish a competitive pricing structure that aligns with their specific needs and budget.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing priming an irrigation pump With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Priming an Irrigation Pump
In the agricultural and landscaping sectors, ensuring that irrigation systems operate efficiently is vital for productivity and resource management. While priming an irrigation pump is a common practice to maintain water flow, several alternative solutions can achieve similar results. Understanding these options helps B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Priming An Irrigation Pump | Self-Priming Pumps | Eductor or Vacuum Priming Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for restoring flow; requires manual intervention | Automatically maintains prime; reliable for consistent performance | High efficiency in removing air; suitable for large systems |
| Cost | Low initial cost; ongoing labor costs | Higher upfront cost; lower maintenance expenses | Moderate to high initial investment; potential savings in labor |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires manual setup; can be time-consuming | Simple installation; minimal ongoing effort | Complex setup; requires specialized equipment |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed to ensure functionality | Low maintenance; self-sustaining | Moderate maintenance; requires monitoring of vacuum systems |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for smaller systems or seasonal use | Best for continuous operation where consistency is key | Suitable for larger operations or when air removal is critical |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Self-Priming Pumps?
Self-priming pumps are designed with integrated mechanisms that allow them to maintain prime without manual intervention. This technology is particularly beneficial for operations requiring continuous irrigation, as it reduces downtime significantly. The main advantage is the labor-saving aspect, as operators do not need to manually prime the system frequently. However, the initial investment is higher compared to traditional pumps, which may deter budget-conscious buyers.
How Do Eductor or Vacuum Priming Systems Work, and What Are Their Benefits?
Eductor or vacuum priming systems utilize a vacuum mechanism to eliminate air from the suction line and pump. This method is highly efficient, particularly in large-scale irrigation setups where air entrapment can hinder performance. The primary benefit is the ability to quickly restore flow without the need for manual priming, making it ideal for extensive agricultural operations. However, these systems can require a more complex setup and higher maintenance to ensure that vacuum levels are consistently monitored.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Choosing the right solution for irrigation pump priming depends on several factors, including the scale of operations, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. For smaller, seasonal operations, traditional priming may suffice, while larger operations with continuous irrigation needs may benefit from the efficiency of self-priming pumps or vacuum systems. B2B buyers should evaluate their specific requirements, considering both upfront and long-term costs, to select the most appropriate solution that aligns with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for priming an irrigation pump
What Are the Key Technical Properties to Consider When Priming an Irrigation Pump?
When it comes to priming an irrigation pump, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of the pump, such as stainless steel or cast iron, significantly affects its durability and resistance to corrosion. Stainless steel is often preferred for its longevity in harsh environments, making it suitable for agricultural applications. Selecting the right material is essential for minimizing maintenance costs and ensuring the pump can handle varying water qualities.Pump Capacity (Flow Rate)
Measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s), the flow rate indicates how much water the pump can move. This specification is vital for determining whether the pump can meet irrigation demands, especially during peak usage times. Buyers should assess their irrigation needs to select a pump with an appropriate flow rate to optimize water delivery and minimize energy consumption.Suction Lift
This refers to the maximum height from which the pump can draw water. It is a critical parameter that affects the pump’s efficiency, especially in regions with varied topography. Understanding suction lift is essential for ensuring that the pump can effectively source water from its designated location, preventing issues like cavitation that can lead to system failure.Operating Pressure
Measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bars, the operating pressure indicates the force with which the pump can deliver water. This is particularly important in pressurized irrigation systems, where adequate pressure is required to distribute water evenly across the field. Buyers should select pumps that can sustain the necessary pressure for their specific irrigation setup.Efficiency Rating
The efficiency rating, often expressed as a percentage, reflects how effectively the pump converts electrical energy into hydraulic energy. High-efficiency pumps reduce energy costs and enhance overall system performance, making them a worthwhile investment for B2B buyers. Look for pumps with efficiency ratings above the industry standard to maximize return on investment.
Which Trade Terminology Is Important for Priming an Irrigation Pump?
Familiarity with industry-specific terms can streamline the procurement process for irrigation pumps. Here are some key terms that buyers should know:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When sourcing pumps, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure compatibility and quality, particularly when dealing with replacement parts or upgrades.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Larger orders may lead to cost savings, but buyers must balance this with their actual needs to avoid excess stock.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing information for a specific product or service. This process is essential for B2B buyers looking to compare prices and negotiate terms with multiple suppliers. An effective RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms for irrigation pump purchases.Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, as they clarify who bears the costs and risks associated with transportation, insurance, and customs clearance.Backflow Preventer
A device designed to prevent the reverse flow of water, ensuring that irrigation systems do not contaminate the water supply. Knowledge of backflow preventers is crucial for buyers to comply with local regulations and maintain water quality, especially in agricultural applications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring irrigation pumps, ensuring that they select the right equipment for their specific agricultural needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the priming an irrigation pump Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends for Priming an Irrigation Pump?
The global irrigation pump sector is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing agricultural productivity demands and the need for efficient water management practices. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the focus on enhancing food security is pushing farmers and agricultural businesses to invest in advanced irrigation systems. Notably, the adoption of smart irrigation technologies, including automated priming systems and IoT-enabled pumps, is gaining traction. These innovations not only optimize water usage but also reduce labor costs, making them attractive options for international B2B buyers.
Emerging sourcing trends highlight a shift towards local suppliers and manufacturers, which can offer quicker lead times and better support services. This trend is particularly pronounced in Africa and South America, where businesses seek to establish reliable partnerships that align with regional agricultural practices. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is transforming the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare products, read reviews, and engage with multiple suppliers from various geographies seamlessly. As the market becomes more competitive, understanding local regulations and ensuring compliance with international standards will be crucial for B2B buyers looking to source irrigation pumps effectively.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Priming of Irrigation Pumps?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the irrigation pump sector. The environmental impact of irrigation practices, particularly in water-scarce regions, necessitates a shift towards more sustainable technologies. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to eco-friendly practices, such as using recycled materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Additionally, certifications such as ISO 14001 or Green Seal can provide assurance of a supplier’s dedication to minimizing environmental harm.
Ethical sourcing also plays a vital role in shaping buyer decisions. As consumers and businesses become more environmentally conscious, B2B buyers are expected to support suppliers that uphold ethical labor practices and transparent supply chains. This focus on ethical sourcing not only enhances brand reputation but also fosters customer loyalty. Suppliers who prioritize sustainability and ethical standards are better positioned to meet the evolving expectations of their clients in the irrigation sector, particularly in markets where consumers are increasingly demanding responsible sourcing.
What Is the Historical Context of Priming Irrigation Pumps and Its Relevance Today?
The practice of priming irrigation pumps has evolved significantly since the early days of agriculture. Initially, manual methods dominated the landscape, often requiring significant labor and time. As agricultural practices advanced, so did the technology behind irrigation pumps. The introduction of self-priming pumps revolutionized the industry by eliminating the need for manual priming, thus enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
In recent years, the integration of technology, such as smart sensors and automated systems, has further transformed pump priming. These advancements not only improve operational efficiency but also allow for real-time monitoring and data collection, which is critical for optimizing irrigation practices. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is essential, as it informs purchasing decisions and highlights the importance of investing in modern, efficient systems that cater to the growing demands of the agricultural sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of priming an irrigation pump
How do I solve issues with my irrigation pump losing prime?
To address a pump losing prime, first, ensure the foot valve is functioning properly, as a faulty valve can lead to air ingress. Check for any leaks in the suction line or pump casing, as even small leaks can disrupt prime. If your pump has a bleed valve, open it to release trapped air. Additionally, ensure that the pump is properly filled with water; you may need to manually add water through the priming port. Regular maintenance checks can help prevent these issues from recurring.What is the best type of irrigation pump for agricultural use?
The best type of irrigation pump depends on your specific needs, such as the water source, flow rate, and lift requirements. Centrifugal pumps are commonly used for surface water irrigation due to their efficiency in moving large volumes of water. Submersible pumps are ideal for deep well applications, while self-priming pumps offer versatility for varying conditions. It’s essential to assess the total dynamic head (TDH) required for your application to select the most suitable pump for your operations.What factors should I consider when sourcing irrigation pumps internationally?
When sourcing irrigation pumps internationally, consider the supplier’s reputation, production capacity, and experience in the agricultural sector. Verify certifications and compliance with international quality standards. Assess the logistical aspects, including shipping times, customs duties, and delivery terms. Understanding local market demands and regional regulations can also help ensure a smooth procurement process. Engaging with local representatives can provide valuable insights into supplier reliability and product suitability.How can I verify the quality of irrigation pumps before purchasing?
To verify the quality of irrigation pumps, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. Conduct factory audits or third-party inspections to assess manufacturing practices and quality control processes. If possible, seek samples or conduct performance tests to evaluate pump efficiency and durability. Customer testimonials and case studies can also provide insights into long-term performance and reliability. Establishing a clear communication channel with the supplier can facilitate transparency throughout the purchasing process.What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for irrigation pumps?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for irrigation pumps can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs based on production costs and inventory management practices, ranging from a few units to several dozen. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify the MOQ upfront and explore the possibility of smaller trial orders, especially if you are entering a new market. This approach allows you to evaluate product quality and market response before committing to larger purchases.What payment terms are commonly offered by international suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among international suppliers. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, and net payment options (e.g., net 30, net 60 days). Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow and operational needs. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can also lead to more flexible payment arrangements over time.How do I ensure timely delivery of irrigation pumps from international suppliers?
To ensure timely delivery, establish clear timelines and milestones with your supplier at the outset of the order process. Confirm shipping methods and logistics partners to be used, and consider using Incoterms (like FOB, CIF) to clarify responsibilities. Regular communication during the production phase can help address any potential delays early. Additionally, factor in customs clearance times and local regulations, especially if you are importing to regions with strict import controls.What should I know about warranty and support for irrigation pumps?
When purchasing irrigation pumps, inquire about warranty terms, including duration and coverage specifics. A standard warranty typically ranges from one to three years, depending on the manufacturer. Understand the process for claiming warranty service, including any documentation required. Additionally, assess the availability of technical support and spare parts, as ongoing support is crucial for maintaining pump efficiency. Establishing a relationship with the supplier for future service needs can help ensure long-term operational success.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Priming An Irrigation Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Water Pump Setup Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Water Pump Setup Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. TWL Irrigation – Centrifugal and Displacement Pumps
Domain: twl-irrigation.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: TWL Irrigation offers various irrigation products including centrifugal and displacement pumps. Centrifugal pumps are the most commonly used for irrigation, utilizing centrifugal force to move water. They can be self-priming or non-self-priming, with self-priming models designed to start without priming. Key features include wet inlets that require water in the intake pipe and casing for operation…
3. Berkeley – 4X3 Centrifugal Pump
Domain: talk.newagtalk.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: – Foot valve: Essential for priming the pump by pouring water in; needs to be leak-proof.
– Pump type: Berkeley 4X3 centrifugal pumps with 10 horsepower motors.
– Priming method: Requires bleeding air from the top of the pump casing; water can be poured in from various points.
– Waterline connection: Installed through an approved backflow preventer to maintain priming.
– Static head: Pump operates…
4. Do It Yourself – Lawn Irrigation Pump
Domain: doityourself.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Lawn irrigation pump, water source from pond, requires priming, process involves unscrewing top part of pump, filling with clean water, ensuring output valve is open, and plugging in the unit. Rainbird controller located in basement.
5. AN PUMP – Centrifugal Irrigation Pumps
Domain: angroupcn.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: AN PUMP supplies a variety of centrifugal irrigation pumps, including: end suction pump, split case pump, multistage pump, mixed flow pump, and self-priming pump. These pumps can be equipped with either diesel engines or electric motors and can be directly connected with couplings or pulleys. There are many options to choose from.
6. ABI Irrigation – Electric Primer Pump
Domain: abi-irrigation.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Irrigation Pump Primer – Electric Primer Pump | ABI Irrigation
Key Features:
– Available in DC, AC, and Hand Pump Priming units.
– Ideal for irrigation and slurry pumps, pivots, and other applications.
– ABI Perfect Primers designed for fast, reliable priming in installations with high suction lifts or long suction lines.
– Suitable for propane, natural gas, PTO, and diesel-powered irrigation pum…
7. The Farming Forum – Electric Pump Solutions
Domain: thefarmingforum.co.uk
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Electric pump for priming main pump, exhaust powered primer (approx. £2500), hand suction pump, foot valve, Caprari pump.
8. JustAnswer – Lawn Sprinkler Pump Priming Guide
Domain: justanswer.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: How to Prime a Lawn Sprinkler Pump: Step-by-Step Guide. Lawn sprinkler pumps often face airlocks and failure to build proper suction. To prime a lawn sprinkler pump, first ensure the pump housing is filled with water. Open the priming port or cap and pour water in until full. Close the port securely to prevent air entry. Check all suction hoses for leaks or cracks that can introduce air. Turn on t…
9. DIY – Essential Plumbing Components
Domain: diy.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: PVC faucet, water pump, intake stop valve, check valve, back flow prevention valve, lake screen, filter.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for priming an irrigation pump
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Irrigation Pump Priming?
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of priming an irrigation pump is essential for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Key takeaways for international B2B buyers include the importance of selecting high-quality components, such as reliable foot valves and self-priming pumps, which can significantly reduce maintenance challenges and downtime. Additionally, investing in training and support for operational staff can enhance the effectiveness of irrigation systems, particularly in regions with varying climatic conditions.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Pump Priming Process?
Strategic sourcing is invaluable in streamlining procurement processes, enabling buyers to secure the best materials and technologies at competitive prices. By fostering relationships with trusted suppliers, companies can ensure timely access to essential components, thereby enhancing operational resilience.
What’s Next for International Buyers in the Irrigation Sector?
As you navigate the complexities of irrigation pump management, consider leveraging local insights and innovations tailored to your specific market. Embrace opportunities for collaboration and investment in sustainable technologies that cater to the unique challenges faced in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing strategic sourcing and continuous improvement, your organization can lead the way in efficient irrigation practices. Engage with suppliers today to explore solutions that will drive your irrigation success tomorrow.