Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for master valve irrigation diagram
Navigating the intricate landscape of the global market for master valve irrigation systems presents a unique set of challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those seeking to optimize irrigation efficiency in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Nigeria. The master valve irrigation diagram serves as a pivotal component in understanding how these systems function, offering insights into the automation and management of water supply. As irrigation needs evolve, the demand for reliable, cost-effective solutions becomes paramount, making it essential for buyers to grasp the various types, applications, and specifications of master valves.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of master valve irrigation diagrams, exploring the different types of valves available, their applications in various irrigation systems, and the critical factors for supplier vetting. It will also address cost considerations and maintenance requirements, empowering international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. By equipping buyers with actionable insights and expert knowledge, this guide aims to enhance operational efficiency and sustainability in agricultural and landscaping projects, ultimately driving profitability and resource conservation. Engage with this resource to elevate your understanding and navigate the complexities of sourcing effective master valve solutions tailored to your specific regional needs.
Understanding master valve irrigation diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Solenoid Master Valve | Operated by an electric controller, usually closed when not in use | Agriculture, landscaping, commercial irrigation | Pros: Efficient control, minimizes water loss. Cons: Requires electrical setup, potential for solenoid failure. |
| Manual Master Valve | Operated manually, often used in smaller systems | Small farms, residential gardens | Pros: Simple operation, lower initial cost. Cons: Labor-intensive, less efficient in large systems. |
| Flow-Sensing Master Valve | Integrates flow sensors to detect leaks | Large commercial landscapes, sports fields | Pros: Automated leak detection, reduces water waste. Cons: Higher upfront cost, complex installation. |
| Anti-Siphon Master Valve | Prevents backflow, typically installed above ground | Residential irrigation, small farms | Pros: Enhances safety, prevents contamination. Cons: Limited pressure handling, can be expensive. |
| Contamination-Proof Master Valve | Designed to filter out debris, protecting downstream components | Municipal systems, industrial applications | Pros: Reduces maintenance, prolongs system life. Cons: Higher cost, requires regular filter checks. |
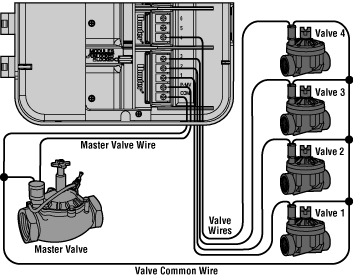
What are the characteristics of Electric Solenoid Master Valves?
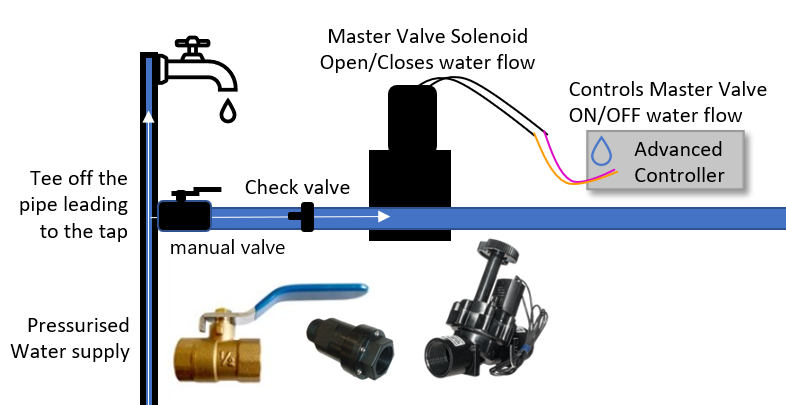
Electric solenoid master valves are commonly utilized in modern irrigation systems due to their automated operation. They are typically installed at the main water supply point and are controlled by an irrigation controller. This type of valve opens and closes based on the signals received from the controller, allowing for efficient water management. B2B buyers should consider the compatibility of these valves with their existing systems, as well as the electrical requirements for installation and maintenance.
How do Manual Master Valves differ in application?
Manual master valves are straightforward and cost-effective options for smaller irrigation systems. They require manual operation to open or close, making them ideal for small farms or residential gardens where automation is less critical. While they are less efficient for large-scale applications, their simplicity and lower initial cost make them appealing for B2B buyers focused on budget constraints. However, buyers should be aware of the labor costs associated with manual operation.
What advantages do Flow-Sensing Master Valves offer for large applications?
Flow-sensing master valves are designed for larger commercial landscapes and sports fields, integrating flow sensors to monitor water usage. This technology allows for the automatic detection of leaks, significantly reducing water waste and potential damage. B2B buyers in sectors where water conservation is critical will find this type of valve advantageous, although the higher upfront cost and complexity of installation may require careful budgeting and planning.
Why are Anti-Siphon Master Valves important for safety?
Anti-siphon master valves are crucial for preventing backflow contamination in irrigation systems. Typically installed above ground, they are often used in residential settings and small farms to ensure safe water usage. While they provide significant safety benefits, such as protecting potable water supplies, B2B buyers should consider their limitations in terms of pressure handling and potential costs associated with installation and maintenance.
How do Contamination-Proof Master Valves enhance system longevity?
Contamination-proof master valves feature built-in filtration systems that protect against debris and contaminants, making them ideal for municipal systems and industrial applications. This design reduces the frequency of maintenance and extends the lifespan of the irrigation system. For B2B buyers, the investment in these valves can lead to long-term savings through reduced downtime and maintenance costs, although the initial purchase price is generally higher. Regular checks on the filtration system are also necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Key Industrial Applications of master valve irrigation diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of master valve irrigation diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Efficient irrigation management for large-scale farms | Reduces water waste and enhances crop yield | Compatibility with existing systems and local water quality |
| Landscaping and Turf Care | Automated irrigation systems for commercial landscapes | Ensures uniform water distribution, promoting healthy growth | Durability and resistance to environmental factors |
| Municipal Water Management | Water conservation in public parks and gardens | Minimizes water loss and operational costs | Compliance with local regulations and standards |
| Greenhouse Operations | Precise control of irrigation systems in controlled environments | Optimizes resource use and improves plant health | Customization for specific crop needs |
| Sports Facilities | Automated irrigation for athletic fields and stadiums | Maintains optimal playing conditions and aesthetics | System scalability and ease of maintenance |
How Is the ‘Master Valve Irrigation Diagram’ Used in Agriculture?
In the agriculture sector, the master valve irrigation diagram facilitates the efficient management of irrigation systems on large-scale farms. By acting as a fail-safe mechanism, the master valve minimizes water waste, especially during off-peak hours when the system is not in operation. This is crucial for regions in Africa and South America, where water scarcity is a significant issue. Buyers in these areas should consider compatibility with existing irrigation systems and local water quality to ensure optimal performance.
What Role Does the Master Valve Play in Landscaping and Turf Care?
In landscaping and turf care, the master valve irrigation diagram is essential for automated irrigation systems that service commercial landscapes. It ensures uniform water distribution across various zones, promoting healthy plant growth and reducing the risk of overwatering. This is particularly valuable in the Middle East, where drought conditions necessitate efficient water use. Buyers should prioritize durability and resistance to environmental factors when sourcing master valves for landscaping applications.
How Can Municipal Water Management Benefit from Master Valves?
Municipal water management sectors leverage the master valve irrigation diagram for water conservation in public parks and gardens. The master valve helps minimize water loss by shutting off the supply when irrigation zones are not in use, leading to significant operational cost savings. For municipal buyers, compliance with local regulations and standards is crucial, as it ensures that the irrigation systems are both effective and environmentally responsible.
Why Is the Master Valve Important in Greenhouse Operations?
In greenhouse operations, the master valve irrigation diagram allows for precise control over irrigation systems, ensuring that crops receive the exact amount of water needed. This optimization is essential for improving plant health and maximizing resource use, especially in Europe, where high-value crops are grown. Buyers should look for customization options tailored to specific crop needs to enhance system efficiency.
What Advantages Does the Master Valve Offer Sports Facilities?
Sports facilities utilize the master valve irrigation diagram for automated irrigation of athletic fields and stadiums. This system maintains optimal playing conditions and enhances the aesthetic appeal of the grounds. Scalability and ease of maintenance are key considerations for buyers in this sector, as they often require systems that can adapt to varying field sizes and usage demands.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘master valve irrigation diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Installation Complexity of Master Valves
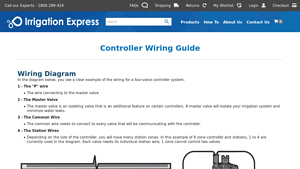
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges during the installation of master valves due to the intricate wiring and connectivity requirements. The need for a proper understanding of how to connect the master valve to the irrigation controller can lead to confusion, resulting in installation errors that may compromise system functionality. This is particularly prevalent in regions where technical expertise is limited, causing delays in project timelines and increasing costs.
The Solution: To mitigate installation issues, buyers should invest time in thorough training or consult detailed installation guides specific to their irrigation system. It is critical to follow wiring diagrams accurately, ensuring that the common wire and control wires are connected correctly to the master valve. Additionally, leveraging resources such as online tutorials or engaging with experienced contractors can provide practical insights. For those operating in areas with limited resources, partnering with local irrigation specialists can facilitate a smoother installation process, ensuring that the master valve functions as intended within the irrigation system.
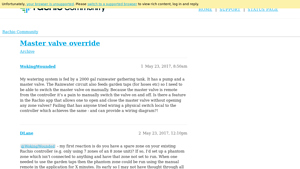
Scenario 2: Maintenance and Leak Detection Challenges
The Problem: Once installed, master valves can create complications in ongoing maintenance, especially in detecting leaks. Because the master valve can obscure issues when zone valves are operational, buyers often find themselves unaware of leaks until significant damage occurs, leading to costly repairs and water waste. This is particularly problematic in environments where water conservation is crucial, such as arid regions in Africa or South America.
The Solution: To enhance leak detection, buyers should implement regular maintenance schedules that include visual inspections of the entire irrigation system, even during off-hours when systems are typically running. Utilizing flow sensors in conjunction with master valves can significantly improve leak detection capabilities. These sensors monitor water flow and can alert operators to irregularities, enabling prompt action. Furthermore, investing in smart irrigation controllers that integrate with flow sensors can automate the process, ensuring that any potential leaks are identified and managed efficiently, ultimately saving costs and minimizing water loss.
Scenario 3: Selecting the Right Master Valve for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with choosing the appropriate type of master valve that suits their specific irrigation needs. The variety of valve types, such as brass or plastic, and the considerations regarding pressure ratings can be overwhelming. This decision is crucial, as selecting the wrong valve can lead to premature failures, costly repairs, and even system inefficiencies, particularly in high-pressure environments typical in Europe and the Middle East.
The Solution: To select the right master valve, buyers should conduct a comprehensive assessment of their irrigation system’s requirements, including expected water pressure and environmental conditions. It is advisable to consult with manufacturers or experienced irrigation professionals who can provide insights on suitable valve types based on material durability and pressure ratings. Buyers should prioritize valves that meet or exceed the pressure demands of their systems to ensure longevity. Additionally, considering features like self-cleaning mechanisms or built-in filters can enhance performance and reduce maintenance needs. By making informed decisions upfront, buyers can avoid costly mistakes and ensure optimal operation of their irrigation systems.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for master valve irrigation diagram
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Master Valves in Irrigation Systems?
When selecting materials for master valves in irrigation systems, especially in diverse international markets, it is essential to consider various factors such as performance properties, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used for master valves: brass, PVC, stainless steel, and polyethylene (PE).
How Does Brass Perform as a Material for Master Valves?
Brass is a popular choice for master valves due to its excellent pressure rating, typically ranging from 150 PSI to 300 PSI. It offers good corrosion resistance, especially in environments with varying water quality. The durability of brass valves is notable, as they can withstand high temperatures and pressures without significant wear.
Pros: Brass valves are robust and have a long lifespan, making them suitable for high-pressure applications. They are also less prone to leaks compared to plastic options.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to other materials. Brass can also be susceptible to dezincification in aggressive water conditions, which can compromise its integrity over time.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with a wide range of media, including potable water, making it a versatile choice for various irrigation needs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Germany and Nigeria should ensure compliance with local standards such as DIN or ASTM. The preference for brass may be influenced by its reputation for reliability in high-pressure systems.
What Are the Benefits of PVC for Master Valves?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is another widely used material for master valves, especially in lower-pressure applications. PVC valves typically have a pressure rating of up to 150 PSI. They are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and easy to install, making them a cost-effective option.
Pros: The affordability and ease of installation make PVC a favored choice for many irrigation systems. It is also resistant to many chemicals found in water sources.
Cons: PVC is less durable than brass and can become brittle over time, especially when exposed to UV light or extreme temperatures. It is also not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: PVC is compatible with a variety of media, but its limitations in high-pressure scenarios can lead to failures in demanding environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like South America, where PVC is commonly used, buyers should ensure that their products meet local standards for pressure and chemical resistance.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare for Master Valves?
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for harsh environments. It typically has a pressure rating that can exceed 300 PSI, which is advantageous for high-pressure irrigation systems.
Pros: Stainless steel valves are highly durable and can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. Their corrosion resistance makes them ideal for use in areas with aggressive water conditions.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is the cost, as stainless steel is more expensive than both brass and PVC. Additionally, they can be heavier, which may complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media and is particularly suitable for agricultural applications where water quality can vary significantly.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should check for compliance with relevant standards, as stainless steel valves can be subject to specific regulations regarding material quality and safety.
What Role Does Polyethylene (PE) Play in Master Valves?
Polyethylene (PE) is often used in irrigation systems due to its flexibility and resistance to corrosion. PE valves are typically rated for lower pressures, around 100 PSI, making them suitable for specific applications.
Pros: PE is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and flexible, which can simplify installation in complex layouts.
Cons: Its lower pressure rating limits its use in high-pressure systems, and it can be less durable than metals over time.
Impact on Application: PE is suitable for non-potable water applications and is often used in agricultural irrigation systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Africa, where irrigation systems may face varied environmental conditions, buyers should ensure that PE products meet local standards for durability and pressure ratings.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Master Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for master valve irrigation diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | High-pressure irrigation systems | Excellent durability and pressure rating | Higher cost and potential dezincification | High |
| PVC | Low to medium-pressure irrigation systems | Cost-effective and easy to install | Less durable and UV sensitive | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environments and high-pressure systems | Exceptional corrosion resistance | High cost and heavier weight | High |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Agricultural irrigation systems | Lightweight and flexible | Lower pressure rating and durability | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in master valves for irrigation systems, offering actionable insights for B2B buyers across various international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for master valve irrigation diagram
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Master Valve?
The manufacturing process for a master valve irrigation diagram consists of several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets rigorous quality standards and operational specifications.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used for Master Valves?
The first step involves selecting appropriate materials, typically high-grade plastics or brass, which are known for their durability and resistance to corrosion. Depending on the application, manufacturers might also consider materials that can withstand specific environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures or exposure to various chemicals. Quality control begins at this stage with the inspection of raw materials to confirm they meet defined specifications, including pressure ratings and compatibility with irrigation systems.
Forming: How Are Master Valves Shaped and Assembled?
The forming stage involves several techniques, such as injection molding for plastic components or machining for brass parts. This stage requires precision to ensure that the valve components fit together seamlessly. Manufacturers often employ CNC machines for metal parts to achieve high accuracy and consistency. During this phase, quality checkpoints are established to monitor tolerances and dimensions, ensuring each part conforms to the design specifications.
Assembly: What Techniques Are Used to Assemble Master Valves?
Once the individual components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This process may involve manual assembly or automated systems, depending on the production scale. Key techniques include welding, sealing, and the installation of electrical components, such as solenoids. Each assembly step is accompanied by quality checks, such as torque tests to ensure that connections are secure and leak-free.
Finishing: What Finishing Processes Enhance Durability?
The finishing stage includes surface treatments such as coating, painting, or polishing to enhance the valve’s resistance to wear and environmental factors. This stage often incorporates additional quality control measures, including visual inspections and functional testing. A well-finished product not only looks appealing but also performs reliably over its operational lifespan.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Standard in Master Valve Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of master valves to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. Adherence to these standards ensures consistent product quality and encourages continuous improvement in manufacturing processes. Additionally, certifications such as CE marking indicate compliance with European safety and environmental standards, while API certifications are crucial for ensuring the quality of valves used in oil and gas applications.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented?
Quality control in the manufacturing process typically involves several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step verifies that raw materials meet specified standards before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing help identify defects early in the process, reducing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product undergoes rigorous testing, including pressure tests and functional tests, to confirm performance before shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Master Valves?
Testing methods for master valves include hydrostatic testing to assess pressure resistance, leakage testing to ensure seals are intact, and electrical testing for solenoid functionality. These tests are critical in confirming that the valves can operate effectively under real-world conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to high-quality standards:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the operational processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control measures, including testing results and certifications.
- Third-party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to assess product quality before shipment can help mitigate risks associated with purchasing.
What Are the Nuances of QC and Certification for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification. For example, certain regions may have unique regulatory requirements that affect product certifications. Buyers should also consider the logistical aspects of shipping and compliance with local laws, which may differ from those in the supplier’s country.
Conclusion: Why Is Quality Assurance Critical for Master Valves in Irrigation Systems?
In conclusion, the manufacturing and quality assurance processes for master valves are complex and critical to the performance of irrigation systems. By understanding these processes, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality products that meet their operational needs. Adhering to international standards, implementing rigorous quality controls, and verifying supplier practices are essential strategies for mitigating risk and ensuring reliability in irrigation solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘master valve irrigation diagram’
The following practical sourcing guide offers a structured approach for B2B buyers seeking to procure a master valve irrigation diagram. This checklist ensures that you cover all critical aspects during the procurement process, facilitating informed decision-making.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the technical requirements of your irrigation system. Understanding the specifications of the master valve, including its type (electric solenoid, for example) and pressure ratings, is crucial for compatibility with your existing setup.
- Considerations: Identify the pressure range and flow rate your system operates under, as these factors determine the appropriate master valve specifications.
Step 2: Research Reputable Suppliers
Identify potential suppliers who specialize in irrigation components. Research their market reputation, product offerings, and customer feedback to ensure reliability.
- Action Items: Use platforms like industry trade shows, online directories, and professional networks to find qualified suppliers. Prioritize those with proven expertise in master valve irrigation systems.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify the certifications and quality standards of your shortlisted suppliers. Compliance with international standards (like ISO) ensures that the products meet safety and performance criteria.
- Importance: Certifications can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability, which is critical for minimizing risks in irrigation projects.
Step 4: Request Detailed Product Information
Ask suppliers for detailed specifications, including diagrams, installation guides, and maintenance requirements for the master valves. This information is essential for assessing the product’s suitability for your needs.
- What to Look For: Ensure that the product data includes pressure ratings, material specifications (plastic vs. brass), and any unique features, such as self-cleaning mechanisms.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and analyze their pricing structures, including shipping and warranty terms. Comparing costs alongside product features helps in making an economical yet informed choice.
- Budget Consideration: Look beyond the initial purchase price; consider the total cost of ownership, including installation and maintenance.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Investigate the level of after-sales support offered by the supplier, including availability of technical assistance and warranty policies. A strong support system can significantly ease the installation and maintenance process.
- Key Questions: Inquire about the warranty duration and coverage, as well as the supplier’s responsiveness to post-purchase queries or issues.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Establish Communication
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize your order and establish clear lines of communication. Ensure that both parties agree on delivery timelines and any additional requirements.
- Action Steps: Confirm all details in writing, including specifications, pricing, and delivery schedules, to avoid misunderstandings later on.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for master valve irrigation diagrams, ensuring that they choose products that enhance the efficiency and reliability of their irrigation systems.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for master valve irrigation diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Master Valve Irrigation Diagrams?
When sourcing master valve irrigation diagrams, it is crucial to understand the multifaceted cost structure involved. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-quality solenoid valves, typically made from brass or durable plastic, are essential for longevity and efficiency. Additional components, such as wiring and connectors, also contribute to the overall material costs. Selecting reliable suppliers can help mitigate costs while ensuring quality.
Labor: Labor costs encompass both the assembly of the irrigation systems and installation. Skilled technicians are often required for installation, particularly in complex systems, which can elevate labor costs. It’s advisable to assess local labor rates when considering total expenses.
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: Overhead costs include expenses related to factory operations, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Tooling costs, necessary for precision manufacturing, can vary based on the complexity of the irrigation diagrams. These factors should be accounted for in the pricing strategy.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of master valves and irrigation systems is critical. QC processes, including testing for leaks and operational efficiency, add to costs but are essential for minimizing future repair expenses and potential system failures.
Logistics: Transportation and storage costs are crucial, especially for international buyers. The choice of shipping method (air, sea, or land) will affect the logistics budget, as will the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer’s location.
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their risks and ensure profitability. Understanding the industry standards for margins can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Master Valve Irrigation Diagram Sourcing?
Several price influencers can impact the overall cost of sourcing master valve irrigation diagrams.
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) with suppliers can yield significant savings, making it worthwhile to evaluate your project requirements closely.
Specifications and Customization: Customization options, such as specific valve types or unique wiring configurations, can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these custom features are necessary for their irrigation systems or if standard products will suffice.
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality and certification of materials can affect both price and performance. Opting for certified products may involve higher initial costs but can reduce long-term maintenance expenses.
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and service levels of suppliers can influence pricing. Engaging with suppliers who have a proven track record in your region can lead to better terms and support.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. These terms define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total cost of ownership.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Master Valve Irrigation Diagrams?
To navigate the complex landscape of pricing for master valve irrigation diagrams, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
Negotiate Terms: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms with suppliers. Discussing volume discounts and payment terms can lead to favorable pricing arrangements.
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the TCO rather than just the upfront costs. Consider factors like installation, maintenance, and operational efficiency when assessing the value of the irrigation system.
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional pricing fluctuations due to economic conditions, tariffs, and logistics complexities. Conducting market research can provide insights into competitive pricing.
Conduct Regular Supplier Assessments: Regularly evaluating supplier performance and product quality can help identify cost-saving opportunities and enhance system reliability.
Disclaimer Regarding Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for master valve irrigation diagrams can vary significantly based on factors such as supplier location, market conditions, and specific project requirements. Therefore, it is advisable for buyers to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing master valve irrigation diagram With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Master Valve Irrigation Systems
When considering irrigation systems, the master valve irrigation diagram represents a widely used method for managing water flow. However, it’s essential to evaluate alternative solutions that may better suit specific agricultural or landscaping needs. This section will compare the master valve irrigation system with two viable alternatives: Flow Sensor Technology and Pressure Regulating Valves. Each option has unique features that can influence performance, cost, and ease of implementation.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Master Valve Irrigation Diagram | Flow Sensor Technology | Pressure Regulating Valves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for leak management; ensures water is shut off when zones are inactive. | Detects leaks and irregularities in water flow, allowing for real-time adjustments. | Maintains consistent water pressure, optimizing irrigation efficiency. |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; ongoing maintenance required. | Higher upfront cost; savings from reduced water usage can offset expenses over time. | Lower initial cost; minimal maintenance required. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation and wiring. | Complex installation; may require integration with existing systems. | Simple installation; can often be installed by end-users. |
| Maintenance | Regular checks necessary to ensure functionality; potential for failure. | Low maintenance; requires periodic calibration. | Minimal maintenance; generally reliable over time. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large-scale agricultural operations needing control over multiple zones. | Suitable for systems where water conservation is critical, especially in drought-prone areas. | Best for residential or small-scale operations where consistent pressure is needed. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Flow Sensor Technology
Flow sensors are advanced devices that monitor water flow within an irrigation system. They detect irregularities such as leaks by measuring flow rates and can send alerts to the controller for immediate action. The primary advantage of flow sensors is their ability to provide real-time data, allowing for proactive management of the irrigation system. However, they come with a higher initial investment and may require professional installation, which can deter some buyers. Over time, the potential savings from reduced water usage can outweigh the initial costs, making them an attractive option for water-conscious operations.
Pressure Regulating Valves
Pressure regulating valves (PRVs) are designed to maintain a consistent water pressure throughout the irrigation system. This technology prevents fluctuations that can lead to inefficient watering or damage to plants. PRVs are generally easier to install than master valves or flow sensors, making them suitable for residential or smaller-scale applications. The low maintenance requirements and cost-effectiveness are significant advantages. However, they do not provide the same level of leak detection and control as master valves, which can be a drawback for large agricultural operations.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Irrigation Solution
Selecting the appropriate irrigation system depends on various factors, including the scale of operation, budget constraints, and specific agricultural needs. For B2B buyers, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each solution is crucial. If leak detection and comprehensive control over multiple irrigation zones are priorities, the master valve irrigation diagram may be the best fit. Conversely, those focused on water conservation and real-time monitoring might find flow sensor technology more beneficial. Lastly, for smaller operations needing consistent pressure without extensive maintenance, pressure regulating valves could be the ideal choice. Evaluating these aspects will guide buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for master valve irrigation diagram
What Are the Critical Specifications for a Master Valve in an Irrigation Diagram?
When selecting a master valve for an irrigation system, several technical properties are crucial to ensure reliability, efficiency, and long-term performance. Here are some key specifications:
Material Grade
The material used for the master valve is pivotal for its durability and performance. Common materials include brass, PVC, and stainless steel. Brass is favored for its higher pressure rating and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for high-pressure systems. PVC is lighter and less expensive but may not withstand high pressures as effectively. Understanding the material grade helps B2B buyers assess the suitability of the valve for specific applications, especially in diverse climates and water conditions.Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the valve can handle without failing. A master valve should have a pressure rating at least double the expected operating pressure of the system. For example, if the operating pressure is 75 PSI, the valve should be rated for at least 150 PSI. This specification is essential for ensuring the valve’s longevity and preventing leaks or bursts, which can lead to costly repairs and water wastage.Flow Rate
The flow rate is a measure of how much water can pass through the valve in a given time, typically expressed in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM). Selecting a valve with an appropriate flow rate is critical for maintaining efficient irrigation coverage. An inadequate flow rate can lead to uneven watering, affecting crop yield and landscape health, particularly in agricultural settings or large commercial properties.Electrical Specifications
Since most master valves operate via an electric solenoid, understanding the electrical specifications, such as voltage and current rating, is vital. Typical specifications include 24V AC for residential systems. Ensuring compatibility with the existing irrigation controller prevents installation issues and operational failures, which can disrupt irrigation schedules.Seal Type
The type of seals used in the master valve affects its ability to prevent leaks. Common seal materials include rubber, silicone, and Teflon, each offering different levels of durability and resistance to environmental factors. Choosing the right seal type minimizes maintenance needs and extends the lifespan of the valve, which is particularly important for B2B buyers looking for long-term investments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Master Valve Irrigation Diagrams?
Understanding industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and decision-making in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms relevant to master valve irrigation systems:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the irrigation sector, working with OEMs can ensure high-quality components tailored for specific systems. B2B buyers often seek OEM products for reliability and compatibility with existing systems.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For irrigation components, understanding the MOQ can help buyers plan their purchases, especially when sourcing materials for large projects or installations. It also affects inventory management and cost efficiency.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document soliciting price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to compare prices, terms, and conditions from various suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping logistics, risk management, and cost allocation in cross-border transactions.Flow Sensor
A flow sensor is a device that measures the flow rate of water within an irrigation system. When integrated with a master valve, it can provide alerts for leaks or system inefficiencies, improving water management. Understanding the role of flow sensors can help buyers enhance the efficiency of their irrigation systems.Backflow Prevention
Backflow prevention refers to methods used to prevent contaminated water from flowing back into the clean water supply. This is crucial in irrigation systems to ensure water quality. B2B buyers must be aware of backflow prevention requirements to comply with local regulations and protect their investments.
By comprehending these essential specifications and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, leading to better irrigation system performance and sustainable water management practices.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the master valve irrigation diagram Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for Master Valve Irrigation Systems?
The global irrigation market is witnessing a significant transformation, driven by the increasing demand for efficient water management solutions. In regions like Africa and South America, where agriculture plays a crucial role in economic stability, the adoption of advanced irrigation technologies, including master valve systems, is on the rise. In Europe, particularly in countries like Germany, there is a strong push towards automation and smart irrigation systems, which utilize master valves to enhance efficiency and reduce water wastage.
Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled irrigation controllers are reshaping how master valves are integrated into irrigation systems. These innovations facilitate real-time monitoring and control, allowing for precise management of water resources. Furthermore, the trend towards sustainable agriculture is compelling businesses to seek out master valve solutions that not only optimize water usage but also integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources.
For international B2B buyers, understanding the local market dynamics is essential. Buyers in the Middle East may prioritize durable materials that withstand high-pressure environments, while those in Europe may seek solutions that comply with stringent environmental regulations. Additionally, the impact of climate change is prompting a shift towards more resilient irrigation systems, making it imperative for buyers to stay informed about the latest advancements in master valve technology.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence Your Master Valve Purchases?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the B2B procurement process, especially within the irrigation sector. The environmental impact of irrigation practices, particularly in water-scarce regions, has led to a heightened focus on sustainable sourcing. Buyers are now more inclined to seek master valve solutions that minimize water waste and reduce energy consumption.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to partner with manufacturers who prioritize eco-friendly materials and processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or the use of recyclable materials can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Investing in products that feature green certifications not only enhances a company’s reputation but also aligns with global sustainability goals. By choosing master valves that comply with these standards, B2B buyers can contribute to environmentally responsible practices, ensuring that their sourcing decisions reflect a commitment to sustainability.
How Has the Master Valve Irrigation Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of master valve technology is rooted in the increasing demand for efficient irrigation solutions. Initially, irrigation systems relied on manual controls, which were labor-intensive and prone to inefficiencies. The introduction of electric solenoid valves marked a significant advancement, allowing for automated control over water flow.
Over the years, as the importance of water conservation has become more pronounced, the design and functionality of master valves have improved. Modern systems now incorporate advanced features such as leak detection and flow monitoring, which enhance overall system reliability and performance.
The integration of smart technologies, such as IoT and data analytics, has further propelled the evolution of master valve systems. These innovations provide real-time insights, enabling farmers and irrigation managers to optimize water usage and enhance crop yields. As the sector continues to evolve, B2B buyers must stay abreast of these changes to ensure their procurement strategies align with the latest trends and technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of master valve irrigation diagram
How do I troubleshoot a malfunctioning master valve in my irrigation system?
To troubleshoot a malfunctioning master valve, first, check the power supply to the valve’s solenoid. Ensure that the wiring is correctly connected to the irrigation controller, especially the common and master valve terminals. If the valve remains closed when it should be open, inspect the solenoid for damage or debris. If necessary, replace the solenoid. Additionally, verify that the controller is functioning properly and that the programming is set correctly to initiate the watering cycle. Regular maintenance and checks can help prevent future issues.What is the best type of master valve for high-pressure irrigation systems?
For high-pressure irrigation systems, a brass master valve is often recommended due to its superior durability and pressure rating. Ensure the valve’s pressure rating is at least double the expected water pressure in your system. If using a plastic valve, select one with a high-pressure rating and consider options with built-in filtration to protect against dirt and debris. These features will enhance the longevity and reliability of the master valve, reducing maintenance costs over time.What should I consider when selecting a supplier for master valve irrigation diagrams?
When selecting a supplier, consider their experience in the irrigation industry and their reputation for quality. Look for suppliers who provide detailed technical support, including installation guides and troubleshooting resources. Verify their ability to offer customization options to meet your specific irrigation needs. Additionally, check for certifications or quality assurance processes that ensure compliance with international standards. Customer reviews and case studies can also provide insight into their reliability and service quality.What are the typical payment terms for international orders of master valves?
Payment terms for international orders typically vary by supplier but often include options like a letter of credit, advance payment, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms before placing an order. Some suppliers may require a deposit, while others might offer net payment terms based on agreed-upon timelines. Ensure that you understand any additional fees, such as currency conversion or transaction fees, that may apply to international transactions.What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for master valves, and can it be negotiated?
The MOQ for master valves can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from 10 to 100 units. However, many suppliers are open to negotiation, especially for first-time buyers or long-term partnerships. If you have specific needs or constraints, communicate these with your supplier. They may offer flexibility in pricing or quantity in exchange for a commitment to future orders, which can be beneficial for both parties.How can I ensure the quality of master valves from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, request product samples before placing large orders. Verify the supplier’s quality assurance processes, including certifications and adherence to international standards. Look for suppliers who conduct regular quality checks and provide detailed documentation on their manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider utilizing third-party inspection services to evaluate the quality of the products prior to shipment, ensuring they meet your specifications and standards.What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing master valves?
When importing master valves, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Evaluate whether to use air or sea freight based on urgency and cost. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, is prepared to avoid delays at customs. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs and duties that may apply to your order, and choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international shipping processes.Can master valves be customized to fit specific irrigation system requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for master valves to accommodate specific irrigation system requirements. Customizations may include adjustments in size, pressure ratings, and materials used. When discussing your needs with potential suppliers, provide detailed specifications and any unique features required for your project. This will help suppliers offer tailored solutions that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your irrigation system.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Master Valve Irrigation Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sprinkler Warehouse – Irrigation Master Valve
Domain: school.sprinklerwarehouse.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: An irrigation master valve is an electric valve installed at the supply point that controls water flow into the main piping system. When closed, it prevents water from being supplied to the irrigation system. It reduces water loss from leaky station valves and controls water loss in case of mainline damage, allowing repairs without shutting off the water supply. The master valve is typically the s…
2. Reddit – Master Valve 3300 Series
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Master valve (normally open superior 3300 series) in irrigation systems; purpose includes maintaining constant pressure, preventing leaks in the main line, and allowing flow to hose bibs while monitoring flow rates.
3. Hunter – X2 Master Valve
Domain: hunterirrigation.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: The X2 master valve is a normally closed valve installed at the supply point of the main line in an irrigation system. It opens only when the controller initiates a watering program, allowing water to flow when any of the irrigation zone valves are activated. The master valve shuts off water to the irrigation system when none of the zone valves are operating. Installation involves connecting a com…
4. Irrigation Express – Key Components
Domain: irrigationexpress.com.au
Introduction: 1. Master Valve: An isolating valve that minimizes water leaks in the irrigation system. 2. Common Wire: Connects to every valve communicating with the controller. 3. Station Wires: Individual wires for each valve; one zone cannot control two valves. 4. Con3way Gel Connectors: Connects all wires together, ideal for common wires. 5. Con2way Gel Connectors: Connects wires in opposite directions, sui…
5. Irrigation Tutorials – Master Valve
Domain: irrigationtutorials.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: A master valve is an automatic electric solenoid valve installed at the irrigation system’s connection to the water supply. It is wired to a master valve circuit on the irrigation controller, which turns the valve on and off. The master valve acts as a fail-safe, shutting off water when no zone valves are operating. Benefits include minimizing water loss from leaks and damage from mainline breaks,…
6. Rachio – Rainwater Irrigation System
Domain: community.rachio.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: This company, Rachio – Rainwater Irrigation System, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Hydrawise – HC Controller
Domain: support.hydrawise.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: The Hydrawise HC controller supports 6 to 54 zone valves, depending on the model. A master valve is an automatic valve installed at the irrigation system’s water supply connection, functioning as a backup or fail-safe valve. It shuts off water when no zone valves are operating. Any zone can be configured as a master valve through the Zones & Schedules page. Initially, no master valve is configured…
8. LandFX – Webinar with Dick Greenland
Domain: landfx.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {‘video_length’: ’31:51′, ‘presented_by’: ‘Dick Greenland’, ‘app_video_link’: ‘https://player.vimeo.com/external/229314029.m3u8?s=146fd03f1a036c059fed7ebfab21b4c03dcb8f38&oauth2_token_id=1264298558’, ‘webinar_vimeo_id’: ‘229314029’}
9. OpenSprinkler – OSPi
Domain: opensprinkler.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: OpenSprinkler Pi (OSPi) allows for the use of multiple master valves, enabling users to manage different water sources (e.g., city water and pump water) for irrigation systems. Users can configure master valves for specific zones and set them to operate automatically based on watering schedules. The firmware supports features like ‘parallel stations’ and the ability to program master valves to act…
10. The Lawn Forum – Master Valve & Flow Meter
Domain: thelawnforum.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Master Valve: An optional component in irrigation systems that can prevent massive water leaks by keeping the lines uncharged when not in use. It is suggested to install a master valve for better leak detection and pressure management. Flow Meter: Used in conjunction with a master valve for leak detection, alerts if water usage exceeds normal levels. Hunter HC 24 Controller: A specific irrigation …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for master valve irrigation diagram
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of master valve irrigation systems presents an invaluable opportunity for international B2B buyers to enhance operational efficiency and water management practices. By understanding the intricate roles of master valves—such as leak mitigation, system isolation, and overall irrigation control—businesses can make informed decisions that lead to significant cost savings and resource conservation.
The value of sourcing high-quality master valves cannot be overstated. Selecting the right components ensures durability and reliability, reducing the frequency of repairs and associated costs. Furthermore, as regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe face unique irrigation challenges, investing in advanced irrigation technology can drive sustainable agricultural practices and improve crop yields.
As you consider your procurement strategies, prioritize suppliers who offer robust, well-engineered solutions tailored to your specific regional needs. Take action today by engaging with manufacturers and distributors who understand your market dynamics. Together, we can cultivate a future of efficient water usage and sustainable growth in your irrigation projects.