Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pumping water from a lake for irrigation
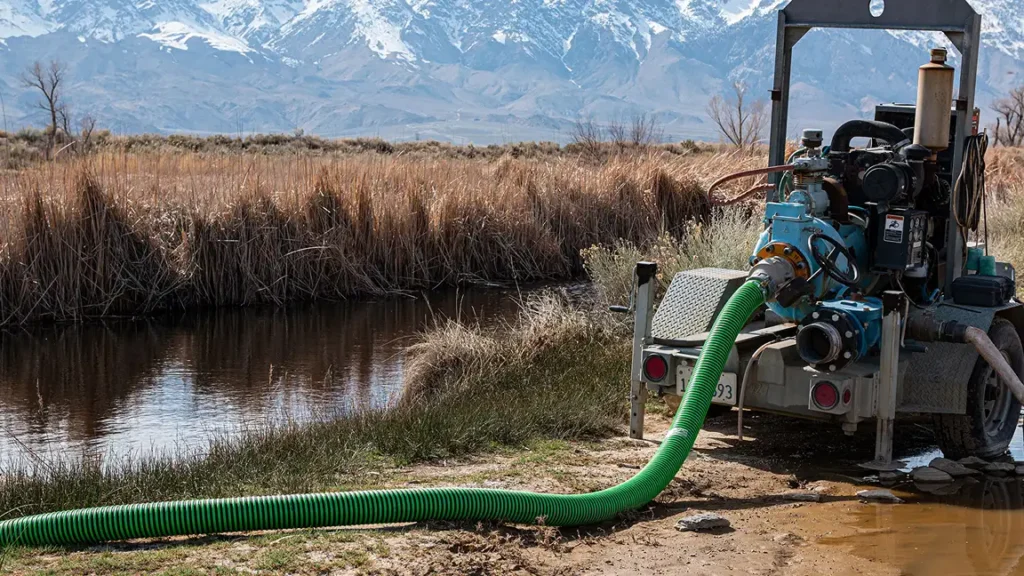
Pumping water from a lake for irrigation presents a unique opportunity for businesses aiming to enhance their agricultural productivity while reducing costs. However, navigating the complexities of sourcing the right pumping systems can be daunting. With varying regulations, water quality considerations, and equipment options, international B2B buyers must approach this process with a strategic mindset. This comprehensive guide serves as your roadmap, detailing the types of lake irrigation systems available, their applications across different agricultural settings, and crucial factors for supplier vetting.
We delve into the myriad benefits of utilizing lake water, including significant cost savings compared to traditional water sources and the environmental advantages of sustainable practices. By understanding the nuances of pricing, installation requirements, and maintenance, you’ll be equipped to make informed purchasing decisions tailored to your specific needs.
This guide is particularly geared toward B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Brazil. By leveraging actionable insights and expert recommendations, you can confidently navigate the global market for lake irrigation solutions, ensuring your agricultural practices are both efficient and environmentally responsible. Empower your business with the knowledge needed to harness natural resources effectively and sustainably.
Understanding pumping water from a lake for irrigation Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pumps | High flow rates, self-priming, suitable for large volumes | Agricultural irrigation, golf courses, sports facilities | Pros: Efficient for large areas; Cons: May require frequent maintenance. |
| Submersible Pumps | Operate underwater, compact design, energy-efficient | Residential landscaping, small farms | Pros: Space-saving; Cons: Limited to shallow depths. |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Handle viscous fluids, adjustable flow rates | Fertilizer applications, chemical irrigation | Pros: Versatile for various liquids; Cons: Slower flow rates. |
| Solar-powered Pumps | Renewable energy source, low operational costs | Remote irrigation systems, eco-friendly projects | Pros: Sustainable; Cons: Dependent on sunlight availability. |
| Booster Pumps | Increase pressure in existing systems, compact size | Urban irrigation systems, pressure-sensitive applications | Pros: Enhances existing systems; Cons: Can be costly to install. |
What Are Centrifugal Pumps and Their Applications?
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in large-scale irrigation systems due to their ability to move large volumes of water efficiently. They are particularly suited for agricultural applications, golf courses, and sports facilities where extensive areas need to be irrigated. When considering a centrifugal pump, buyers should evaluate the flow rate requirements and the potential need for regular maintenance, as these pumps can require more upkeep compared to other types.
How Do Submersible Pumps Function in Irrigation?
Submersible pumps are designed to operate underwater, making them ideal for smaller applications such as residential landscaping and small farms. Their compact design allows for installation in tight spaces, while their energy efficiency can lead to cost savings. Buyers should consider the depth of the water source and the specific irrigation needs, as submersible pumps are generally limited to shallower depths.
What Benefits Do Diaphragm Pumps Offer?
Diaphragm pumps are known for their ability to handle viscous fluids and provide adjustable flow rates, making them suitable for applications like fertilizer distribution and chemical irrigation. Their versatility allows for efficient irrigation in various agricultural settings. However, buyers should be aware that diaphragm pumps typically have slower flow rates compared to centrifugal options, which may impact their suitability for larger areas.
What Are the Advantages of Solar-Powered Pumps?
Solar-powered pumps utilize renewable energy, making them an excellent choice for remote irrigation systems and eco-friendly projects. They offer low operational costs and reduce dependence on conventional energy sources. However, potential buyers need to consider the availability of sunlight in their location, as this can affect the pump’s performance and reliability.
How Do Booster Pumps Enhance Irrigation Systems?
Booster pumps are designed to increase pressure in existing irrigation systems, making them ideal for urban applications where pressure sensitivity is crucial. Their compact size allows for easy integration into current systems. While booster pumps can enhance efficiency, buyers should be prepared for potentially higher installation costs and the need for proper sizing to avoid overloading existing systems.
Key Industrial Applications of pumping water from a lake for irrigation
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pumping water from a lake for irrigation | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Irrigation for crop production | Reduces dependency on municipal water sources, lowering costs and enhancing crop yield. | Assess local water regulations and pump capacity requirements. |
| Landscaping and Golf Courses | Irrigation for greens and landscaping projects | Ensures optimal growth conditions for plants and turf, enhancing aesthetic appeal and property value. | Evaluate pump efficiency, filtration systems, and maintenance support. |
| Commercial Horticulture | Supplying water for nurseries and greenhouses | Provides a sustainable water source, improving plant health and reducing operational costs. | Consider water quality, pump automation, and compatibility with existing systems. |
| Sports Facilities | Irrigation for athletic fields and parks | Maintains field quality and usability, supporting event schedules and reducing downtime. | Focus on pump durability, ease of installation, and water distribution options. |
| Aquaculture | Water management for fish farms and aquatic plants | Enhances growth rates and health of aquatic life, ensuring sustainable production. | Investigate water sourcing laws, pump performance metrics, and filtration needs. |
How is Pumping Water from a Lake Used in Agriculture for Irrigation?
Pumping water from lakes for agricultural irrigation offers farmers a reliable and cost-effective solution to water scarcity. By utilizing natural water sources, farmers can reduce their reliance on expensive municipal water supplies, significantly lowering operational costs. Additionally, lake water often contains nutrients beneficial for crops, enhancing overall yield. Buyers in this sector must consider local water regulations, the capacity of pumps to meet irrigation needs, and the sustainability of their water source to ensure compliance and efficiency.
What Role Does Pumping Water Play in Landscaping and Golf Courses?
In the landscaping and golf course industry, pumping water from lakes is crucial for maintaining lush greenery and healthy turf. This method ensures a consistent and adequate water supply, which is essential for aesthetic appeal and property value. Implementing an efficient irrigation system can also minimize water waste, aligning with sustainable practices. Buyers should prioritize pump efficiency, filtration systems to prevent clogging, and reliable maintenance support to sustain long-term operations.
How is Pumping Water Beneficial for Commercial Horticulture?
For commercial horticulture, utilizing lake water for irrigation supports nurseries and greenhouses by providing a sustainable water source. This practice not only enhances plant health and growth but also reduces operational costs linked to water procurement. Buyers must evaluate the water quality to ensure it meets the specific needs of various plant species, as well as consider automation features for ease of use and efficiency in water distribution.
Why is Pumping Water Essential for Sports Facilities?
Sports facilities rely on effective irrigation systems to maintain the quality of athletic fields and parks. Pumping water from lakes allows for consistent moisture levels, ensuring that fields remain playable and aesthetically pleasing for events. This reduces downtime and enhances user satisfaction. Key considerations for buyers in this sector include the durability of the pumping equipment, ease of installation, and the capability to manage large water volumes efficiently.
How Does Pumping Water Support Aquaculture?
In aquaculture, the management of water quality is vital for the health of fish and aquatic plants. Pumping water from lakes provides a controlled environment that can be adjusted for optimal growth conditions. This approach not only supports sustainable production but also enhances growth rates and overall health of aquatic life. Buyers should investigate local water sourcing laws, performance metrics of pumping systems, and necessary filtration requirements to ensure compliance and operational success.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pumping water from a lake for irrigation’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Legal Regulations for Water Use in Irrigation
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion regarding the legal implications of pumping water from lakes for irrigation. In many regions, water rights and regulations can vary significantly, leading to uncertainty about what is permissible. This situation can create anxiety for businesses that rely on consistent and legally compliant water access, especially in countries where water scarcity is a pressing issue. Buyers may worry about the potential for fines, legal action, or interruptions to their irrigation operations if they inadvertently breach water use laws.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these legal complexities, B2B buyers should begin by conducting thorough research on local water rights and regulations. This includes consulting with local environmental protection agencies or water management districts to clarify what is permissible in their specific region. It’s advisable to seek legal counsel specializing in environmental law to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations. Additionally, buyers should consider obtaining the necessary permits before initiating any pumping activities. Establishing a partnership with a reliable local irrigation consultant can also provide valuable insights into navigating these regulations and ensuring that the irrigation system is designed with compliance in mind.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Consistent Water Quality for Irrigation
The Problem: Another critical pain point for buyers is the variability in water quality when pumping from a lake. Lakes can have fluctuating nutrient levels, sediment, and biological contaminants that may harm crops or disrupt irrigation systems. Poor water quality not only risks the health of plants but can also lead to costly damage to irrigation equipment, which translates to increased operational costs and lost productivity.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should implement a comprehensive water quality assessment strategy before establishing their irrigation system. This includes regular testing for parameters such as pH, turbidity, and nutrient levels. Investing in high-quality filtration systems can mitigate risks associated with sediment and contaminants, ensuring that only clean water is used for irrigation. Buyers can also consider integrating water treatment options, such as UV purification or chemical treatments, to enhance water quality. Collaborating with agronomists or irrigation specialists can provide tailored solutions that align with the specific crop needs and local conditions, ensuring that water quality supports optimal growth.
Scenario 3: Managing Pump Efficiency and Energy Costs
The Problem: Energy consumption is a significant concern for businesses using pumps to extract water from lakes for irrigation. Many buyers struggle with the high costs associated with running pumps, particularly in regions where electricity prices are steep. Inefficient pumping systems can lead to excessive energy use, resulting in inflated operational costs that can severely impact the bottom line.
The Solution: To enhance pump efficiency and reduce energy costs, buyers should invest in energy-efficient pumping systems that are appropriately sized for their irrigation needs. Selecting pumps with variable frequency drives (VFDs) allows for adjustments in pump speed based on real-time demand, optimizing energy use. Regular maintenance of pumps and associated equipment is crucial to ensure they operate at peak efficiency; this includes checking for blockages, wear, and ensuring proper alignment. Additionally, buyers should consider the possibility of integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar power, to further reduce reliance on grid electricity. Engaging with experienced irrigation system designers can also help buyers create a more efficient system that minimizes energy consumption while maximizing water output.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pumping water from a lake for irrigation
What Are the Key Materials for Pumping Water from a Lake for Irrigation?
When selecting materials for pumping water from a lake for irrigation, it is crucial to consider properties such as durability, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with various media. Below, we analyze four common materials used in this application, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Thermoplastic Materials
Key Properties: Thermoplastics, such as PVC and polypropylene, exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and can handle temperatures up to 60°C (140°F). They are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, making them suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: Thermoplastics are relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, allowing for lower production costs. However, they may not withstand high-pressure applications as effectively as metals, limiting their use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: These materials are compatible with freshwater, making them ideal for lake irrigation systems. However, they may degrade over time when exposed to UV light unless treated.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM for the United States or DIN for Europe. In regions like Africa and South America, local regulations may also dictate the use of specific materials.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers superior strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-pressure applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and is often used in pump casings and fittings.
Pros & Cons: While stainless steel is highly durable and long-lasting, it comes at a higher cost compared to thermoplastics. The manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment and skilled labor.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including freshwater and some chemicals, making it versatile for different irrigation needs. Its durability ensures a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
International Considerations: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards such as JIS in Japan or ASTM in the U.S. Additionally, stainless steel grades should be selected based on local environmental conditions, particularly in coastal areas where saltwater exposure is a concern.
3. Cast Iron
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its exceptional strength and durability, withstanding high pressures and temperatures. It is often used in pump housings and impellers.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of cast iron is its ability to handle heavy-duty applications, making it suitable for large-scale irrigation systems. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly coated, and its weight can complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is suitable for freshwater applications but may require additional coatings or treatments to prevent rust and corrosion. This can increase maintenance requirements over time.
International Considerations: Buyers should consider local regulations regarding the use of cast iron, particularly in regions with high humidity or saline environments. Compliance with standards like ASTM or DIN is essential for ensuring product quality.
4. Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics (FRP)
Key Properties: FRP combines the lightweight nature of plastics with the strength of fiberglass, offering excellent corrosion resistance and the ability to handle a wide range of temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons: FRP is highly durable and resistant to chemical degradation, making it suitable for various irrigation applications. However, it can be more expensive than traditional plastics and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: FRP is particularly effective in environments where chemical exposure is a concern, making it ideal for agricultural applications that may involve fertilizers or other chemicals.
International Considerations: Compliance with international standards is crucial for FRP products, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations. Buyers should also consider local manufacturing capabilities, as FRP may not be as widely produced in some areas.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for Pumping Water from a Lake for Irrigation | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic Materials | Lightweight pumps and fittings for freshwater irrigation | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited pressure resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure pump casings and fittings | Superior strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty pump housings for large-scale irrigation systems | Exceptional durability and strength | Prone to corrosion without proper treatment | Medium |
| Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastics | Chemical-resistant applications in agriculture | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and specialized manufacturing needed | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers considering pumping water from lakes for irrigation, helping to ensure that the right materials are chosen for specific applications and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pumping water from a lake for irrigation
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Irrigation Pump Systems?
The manufacturing of irrigation pump systems designed for extracting water from lakes involves several critical stages, each aimed at ensuring efficiency, durability, and reliability. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages involved:
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality materials are essential for the longevity and performance of irrigation pumps. Common materials include:
- Thermoplastics: Utilized for their corrosion resistance, lightweight properties, and ease of molding.
- Aluminum: Often used for pump frames and bases due to its strength and lightweight characteristics.
- Stainless Steel: Selected for components exposed to water to prevent rust and degradation over time.
- Rubber and PVC: Employed in hoses and seals for their flexibility and sealing capabilities.
The selection of materials is influenced by the specific requirements of the irrigation systems, such as flow rate, pressure, and environmental conditions.
How Are Pump Components Formed?
Once materials are prepared, they undergo various forming techniques to create the individual components of the pump system. Techniques include:
- Injection Molding: Commonly used for producing thermoplastic parts, allowing for intricate designs and high-volume production.
- CNC Machining: Employed for precision components, such as pump impellers and housings, ensuring exact tolerances.
- Metal Fabrication: Involves cutting, bending, and assembling metal parts for structural components, ensuring robustness.
These techniques are crucial in achieving the desired specifications and ensuring that each part fits seamlessly into the overall system.
What Is the Assembly Process for Irrigation Pumps?
The assembly stage is where all manufactured components come together to form the final product. This typically includes:
- Sub-Assembly of Components: Individual parts, such as motors, impellers, and housings, are first assembled into sub-units.
- Main Assembly Line: Sub-units are then combined on the assembly line, with careful attention to alignment and connections.
- Integration of Electrical Components: For electric pumps, motors are integrated with electrical systems, including wiring and control panels.
Quality control is critical during this stage to ensure that the assembly process adheres to design specifications.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used?
The finishing stage involves applying protective coatings and treatments to enhance durability and aesthetics. Common finishing techniques include:
- Powder Coating: Applied to metal components to provide a protective layer against corrosion and wear.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques like anodizing or galvanizing are used to improve resistance to environmental factors.
- Quality Inspection: Final inspection for any defects or inconsistencies before the product is packaged and shipped.
These finishing touches not only improve the product’s lifespan but also its visual appeal for potential buyers.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Pumping Systems?
Quality assurance is a fundamental aspect of manufacturing irrigation pumps to ensure that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Here’s how quality assurance is typically implemented:
What International Standards Are Relevant for Pump Manufacturing?
International quality standards such as ISO 9001 are crucial for maintaining consistent quality in manufacturing processes. Compliance with these standards ensures that:
- Quality Management Systems (QMS): Organizations have an effective system in place for managing quality.
- Continuous Improvement: Companies are committed to ongoing improvements based on customer feedback and performance metrics.
In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are also essential, especially for pumps intended for different markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to monitor quality at various stages. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process to catch any defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the completed product to ensure it meets all specifications and performance criteria.
These checkpoints help in identifying issues early, reducing waste, and ensuring a high-quality end product.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the performance and safety of irrigation pumps, including:
- Hydrostatic Testing: Ensures the pump can withstand high pressures without leaking.
- Flow Rate Testing: Measures the efficiency and capacity of the pump under various conditions.
- Electrical Safety Testing: Confirms that all electrical components meet safety regulations.
These tests provide assurance that the pumps will operate reliably under actual field conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control processes. Here are some effective ways to verify supplier quality:
What Audits and Reports Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should conduct thorough audits of potential suppliers, looking for:
- ISO Certification Documentation: Ensures compliance with international quality standards.
- Internal Quality Audit Reports: These documents provide insights into the supplier’s quality management processes and any corrective actions taken.
- Supplier Performance Metrics: Historical data on defect rates and customer satisfaction can help gauge reliability.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer additional assurance regarding a supplier’s quality control practices. These services can provide:
- Unbiased Assessments: Independent evaluations of manufacturing processes and product quality.
- Verification of Compliance: Confirmation that products meet specified standards and regulations.
Third-party inspections are particularly valuable for international buyers who may face challenges in assessing suppliers from different regions.
What QC Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of certain nuances in quality control:
- Local Regulations: Understanding local regulations regarding water usage and pump specifications can impact compliance.
- Cultural Differences in Manufacturing: Variations in manufacturing practices and quality expectations can affect product delivery and performance.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Challenges: Buyers should consider potential delays in shipping and customs clearance, which can impact the availability of replacement parts and service.
By comprehensively understanding these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting irrigation pump suppliers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pumping water from a lake for irrigation’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring effective systems for pumping water from lakes for irrigation purposes. By following this step-by-step checklist, buyers can ensure they select the right equipment and suppliers, leading to successful irrigation solutions that meet their specific needs.
1. Identify Your Water Requirements
Understanding the volume and flow rate of water needed for irrigation is essential. Assess the area to be irrigated, the type of crops or plants, and the irrigation method you plan to use. This information will help you determine the necessary pump capacity and specifications.
2. Define Your Technical Specifications
Once you know your water requirements, define the technical specifications for the pump system. Consider factors such as horsepower, maximum suction lift, and pressure ratings. Ensure the specifications align with the irrigation demands of your operation to prevent system inefficiencies.
3. Research Local Regulations and Permits
Before proceeding, verify local regulations regarding water extraction from lakes. Different regions may have specific legal requirements or permits needed for such activities. Engaging with local water management authorities can help you navigate these regulations and avoid potential legal issues.
4. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they have a solid track record. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and references from other businesses in similar sectors. Check for certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards, which can indicate reliability and quality.
5. Assess Product Quality and Features
Investigate the quality of the pumping systems offered by suppliers. Look for features that enhance performance, such as corrosion-resistant materials, energy efficiency, and ease of maintenance. Products that include advanced filtration systems can help ensure clean water and prolong the life of the pump.
6. Consider Installation and Support Services
Evaluate whether the supplier provides installation and ongoing support services. A supplier that offers comprehensive installation assistance can save time and ensure the system is set up correctly. Additionally, inquire about warranty options and after-sales support to address any future issues that may arise.
7. Compare Pricing and Value
Finally, obtain quotes from multiple suppliers and compare not just the prices but also the value offered. Consider the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and energy consumption. Choosing a supplier that provides a balance of quality and cost-effectiveness can lead to long-term savings and operational efficiency.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing pumping systems for lake irrigation, ensuring they choose solutions that meet their needs and contribute to successful agricultural outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pumping water from a lake for irrigation Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Pumping Water from a Lake for Irrigation?
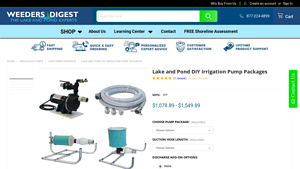
When assessing the financial outlay for pumping water from a lake for irrigation, several cost components come into play. Materials include the pump systems, filters, hoses, and any additional components necessary for installation and operation. Depending on the specifications, prices for pump packages can range from approximately $1,078.89 to $1,549.89, with factors such as pump horsepower and filtration capacity influencing these costs.
Labor costs will vary based on the complexity of the installation. For example, simpler systems may require less specialized labor, while larger, more sophisticated setups—such as those serving commercial or large agricultural needs—will necessitate skilled technicians for installation and maintenance.
Manufacturing overhead encompasses the indirect costs associated with producing the irrigation systems, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Tooling costs might be incurred if custom components are needed, especially for larger-scale or specialized projects.
Quality control (QC) measures are essential in ensuring that the irrigation systems meet industry standards and regulations. This can involve testing materials and finished products, which adds to the overall cost. Logistics costs also play a role, as shipping and handling from suppliers to the installation site can differ significantly based on distance and transportation methods.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Irrigation Pump Systems?
Several factors can influence pricing, particularly for international buyers. Volume or Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing; larger orders often lead to discounts. Additionally, specifications and customization—like pump size or filtration capacity—can lead to variations in price.
The choice of materials also impacts costs. For instance, pumps made from higher-quality, corrosion-resistant materials may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to lower maintenance expenses over time. Supplier factors such as reputation, reliability, and after-sales support can also affect pricing; established suppliers may command higher prices due to their proven track record.
Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international B2B buyers. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions and can have implications for costs related to shipping, insurance, and customs duties.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Prices on Irrigation Systems?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings. Start by conducting thorough market research to understand standard pricing for the necessary equipment and services. Use this information as leverage during negotiations.
Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. This holistic view can justify a higher initial investment if it leads to lower long-term expenses.
Pricing nuances can also arise from local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and economic factors in the buyer’s region. Buyers should be prepared to discuss these aspects openly with suppliers to reach mutually beneficial agreements.
Finally, always request a detailed quote that breaks down all costs, ensuring transparency. This can help in identifying any hidden fees and allows for more effective negotiation.
Conclusion: Understanding Costs and Pricing in Lake Irrigation
While the costs associated with pumping water from a lake for irrigation can vary widely based on several factors, understanding the detailed breakdown of these costs will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By considering key cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, buyers can enhance their purchasing power and optimize their investments in irrigation systems.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier terms, and specific project requirements. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pumping water from a lake for irrigation With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Water Irrigation Solutions
In the quest for effective irrigation solutions, particularly in regions with water scarcity or fluctuating supply, businesses must evaluate various methods to meet their agricultural needs. Pumping water from a lake for irrigation is a popular choice, but it’s essential to explore other viable alternatives. This analysis provides a comparative overview of different irrigation methods, focusing on their performance, costs, implementation ease, maintenance requirements, and ideal use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Pumping Water From A Lake For Irrigation | Rainwater Harvesting | Drip Irrigation Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable, continuous supply; nutrient-rich water | Dependent on rainfall; can be inconsistent | High efficiency; precise water delivery |
| Cost | Moderate initial setup; low ongoing costs | Low to moderate setup costs; variable maintenance | Higher initial investment; lower operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires installation of pumps and filtration systems | Simple collection systems; minimal technology | Requires professional installation; ongoing adjustments needed |
| Maintenance | Moderate; periodic filter cleaning and pump checks | Low; occasional tank cleaning | Moderate; regular checks on emitters and pressure |
| Best Use Case | Suitable for large-scale agriculture or landscaping | Urban settings with limited space; supplemental irrigation | Ideal for water-sensitive crops and arid regions |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting involves capturing and storing rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces for irrigation purposes. This method is particularly beneficial in urban environments where space is limited, and it can provide a sustainable water source. Its main advantages include low initial setup costs and low maintenance requirements. However, its effectiveness is heavily reliant on local rainfall patterns, which can lead to inconsistencies in water supply. Businesses in regions with erratic precipitation may find this method insufficient for their irrigation needs.
Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient method that delivers water directly to the plant roots through a network of tubing and emitters. This technology minimizes water wastage and optimizes nutrient delivery, making it ideal for crops that require precise watering. While the initial investment in a drip irrigation system can be higher than other methods, the long-term operational costs are typically lower due to reduced water usage. The complexity of installation and the need for regular maintenance to ensure emitter functionality can be drawbacks for some users.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Irrigation Solution
When selecting an irrigation solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific agricultural needs, local environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Pumping water from a lake offers a reliable and nutrient-rich water source, making it suitable for extensive agricultural operations. In contrast, rainwater harvesting is best for urban settings with limited space, while drip irrigation is ideal for water-sensitive crops in arid regions. By assessing these factors, businesses can make informed decisions to implement the most effective irrigation strategy for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pumping water from a lake for irrigation
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Pumping Water from a Lake for Irrigation?
When selecting pumping systems for lake irrigation, understanding the technical specifications is crucial for ensuring efficiency and sustainability. Here are some essential properties to consider:
Horsepower (HP)
Horsepower is a measure of the pump’s power output. Common options range from 1 HP to 2 HP for residential applications. Higher horsepower ratings can manage larger volumes of water and are suitable for extensive irrigation setups. B2B buyers must assess the horsepower needed based on the size of the area to be irrigated and the elevation of the water source.Flow Rate (GPM)
The flow rate, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM), indicates how much water the pump can deliver in a specific timeframe. For example, a pump with a flow rate of 55 GPM is ideal for larger landscapes, while lower rates may suffice for smaller gardens. Understanding flow rate is vital for meeting irrigation demands without overloading the system.Maximum Suction Lift
This specification indicates the maximum vertical distance the pump can draw water from the lake to the irrigation system. A typical maximum suction lift can be around 25 feet. Knowing this parameter helps buyers determine if the pump can effectively draw water from deeper bodies of water, avoiding costly installation issues.Material Composition
Pumps are often constructed from thermoplastic or fiberglass-reinforced materials, which offer varying levels of corrosion resistance and durability. High-quality materials extend the lifespan of the pump and reduce maintenance costs, making this an essential consideration for buyers in diverse environments.Voltage and Electrical Specifications
Pumps may operate on different voltage systems (e.g., 110v or 220v). Buyers should ensure compatibility with local electrical standards and consider the associated power draw (amperage) to avoid electrical failures. Understanding these specifications can also influence installation costs and requirements.Filter Capacity
The filter system’s capacity (e.g., 40 or 80 gallons) is crucial for maintaining water quality. A well-designed filtration system prevents debris from clogging the irrigation system, ensuring efficient operation. B2B buyers should prioritize pumps with robust filtration capabilities, especially in environments with high sediment levels.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Lake Irrigation Pumping?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are some key terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of irrigation pumps, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure they are receiving quality components.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is crucial for B2B buyers to understand, as it can impact inventory management and cash flow, particularly for smaller operations that may not require large quantities.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers use to solicit price quotes from suppliers. Including detailed specifications in the RFQ ensures that suppliers provide accurate pricing, enabling better decision-making based on cost and performance.Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of predefined commercial terms used in international trade that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, reducing the risk of misunderstandings.Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is received. Understanding lead times is vital for project planning and ensuring timely irrigation system installations, especially in agricultural cycles that depend on precise timing.Service Level Agreement (SLA)
An SLA is a contract that outlines the expected service levels between a supplier and a buyer. In the context of irrigation pumps, an SLA can detail maintenance, response times for repairs, and warranty conditions, providing buyers with peace of mind regarding their investment.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting irrigation pumping systems from lakes, ensuring operational efficiency and compliance with local regulations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pumping water from a lake for irrigation Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Pumping Water from a Lake for Irrigation?
The market for pumping water from lakes for irrigation is witnessing significant growth, driven by an increasing global demand for sustainable agricultural practices and efficient water management. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where water scarcity is a pressing issue, leveraging natural water bodies for irrigation has emerged as a viable solution. Technological advancements in pump design and automation are streamlining operations, reducing costs, and enhancing efficiency. For instance, sophisticated irrigation systems can now be monitored and controlled remotely, allowing for precise water management that optimizes usage and minimizes waste.
Emerging trends include the adoption of solar-powered pumps, which reduce reliance on traditional energy sources and lower operational costs. Additionally, the integration of IoT technologies in irrigation systems enables real-time data collection on water levels, pump performance, and environmental conditions, leading to informed decision-making. As countries prioritize food security and sustainable farming practices, international B2B buyers are increasingly sourcing advanced pumping solutions that offer both reliability and efficiency.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Pumping Water from a Lake for Irrigation Sector?
Sustainability is a critical consideration in the pumping water from lakes for irrigation. Utilizing lake water not only conserves groundwater resources but also provides an eco-friendly alternative to traditional irrigation methods. The environmental impact of sourcing water from natural bodies must be managed carefully to avoid over-extraction, which can lead to ecological imbalances. Consequently, ethical sourcing practices are essential. This includes ensuring that water extraction complies with local regulations and environmental guidelines to protect aquatic ecosystems.
Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications and eco-friendly materials. Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, signal a supplier’s dedication to minimizing their ecological footprint. Furthermore, using materials that are recyclable or sustainably sourced in the manufacturing of irrigation equipment can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious buyers. As the market evolves, those who prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing will likely gain a competitive edge.
How Has the Pumping Water from a Lake for Irrigation Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the pumping water from lakes for irrigation can be traced back to traditional farming practices that relied heavily on manual labor and rudimentary tools. Over the decades, technological advancements have transformed this sector significantly. The introduction of mechanized pumps in the early 20th century marked a pivotal shift, allowing farmers to efficiently extract water from lakes and distribute it across larger areas.
As environmental awareness grew in the late 20th century, sustainable practices began to shape the industry. Modern systems now incorporate advanced technologies such as variable frequency drives and automation, which not only improve efficiency but also support responsible water management. Today, the focus is on integrating smart technology with sustainable practices, ensuring that irrigation systems are not only effective but also environmentally sound. This ongoing evolution presents B2B buyers with a wide array of choices, enabling them to select solutions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pumping water from a lake for irrigation
How do I determine the legal requirements for pumping water from a lake for irrigation?
Understanding the legal framework surrounding water usage is crucial for B2B buyers. Start by consulting local environmental protection agencies or water resource departments in your region. Regulations can vary significantly between countries and even within regions of the same country. Make sure to check if you need permits, and ensure your intended use complies with local riparian rights and sustainable practices to avoid legal conflicts.What is the best type of pump for lake irrigation systems?
The ideal pump for lake irrigation depends on your specific requirements, including the size of your irrigation area and the volume of water needed. Centrifugal pumps are commonly used due to their efficiency in transferring large volumes of water. For smaller applications, submersible pumps can be effective. It’s advisable to consult with suppliers to identify pumps that match your performance needs, taking into account factors such as horsepower, flow rate, and energy source.How do I vet suppliers for lake irrigation systems?
When sourcing suppliers, consider their experience and reputation in the market. Request references from previous clients and check online reviews. Ensure the supplier adheres to international quality standards and certifications. Conduct site visits if possible, and evaluate their product range for customization options. A reliable supplier should also provide comprehensive after-sales support and warranty options to guarantee the longevity of your irrigation system.What customization options are available for lake irrigation systems?
Many suppliers offer customizable solutions to meet specific irrigation needs. You can tailor pump sizes, filtration systems, and hose lengths based on your landscape and water source characteristics. Some companies may provide add-on components, such as timers, controllers, and multi-port adapters, allowing you to enhance system functionality. Be sure to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options.What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for irrigation pumps?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers. Some may offer flexible MOQs for smaller projects, while others may require bulk orders for discounts. It’s essential to communicate your project scale and budget with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Consider the logistics of shipping and storage, especially if you are importing products across international borders.What payment terms should I expect when purchasing irrigation systems?
Payment terms can differ widely based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of your order. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial deposits, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection, such as letters of credit or escrow services. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts to avoid misunderstandings.How can I ensure quality assurance for my irrigation system?
Quality assurance starts with choosing a reputable supplier who adheres to international standards. Request documentation regarding quality control processes, testing procedures, and certifications for the pumps and components. Consider conducting your own inspections upon delivery and ask for warranties that cover defects and performance issues. Regular maintenance checks will also help ensure the longevity and reliability of your irrigation system.What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing irrigation equipment?
When importing irrigation systems, factor in shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Work with suppliers experienced in international shipping to ensure compliance with import regulations in your country. Consider the mode of transport—air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger orders. Additionally, plan for local logistics upon arrival, including storage and installation of the equipment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Pumping Water From A Lake For Irrigation Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Weeders Digest – Lake Irrigation Pump Packages
Domain: weedersdigest.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Lake Irrigation Pump Packages include options for 1 HP (115V and 220V), 1.5 HP (115V and 220V), and 2 HP (220V) pumps. The 2 HP package features a standard cage and does not include a plug. Suction hose lengths available are 10 ft and 33 ft. The packages come with various components: 1 or 1.5 HP packages include a pump mounting base with stakes, a 40-gallon Big Foot filter with filter matting, a f…
2. Pump Solutions – Elevation & Pressure Requirements
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Water Source: Lake; Pump Location: 10 feet from water’s edge, 5 feet above waterline; Sprinkler Zone Length: 168′ to 283′; Elevation Gain: 26 feet from pump to highest point; Pump Requirements: Size and type needed for elevation gain and distance, adequate pressure/gpm; Pipe Size: Diameter needed for proper flow and pressure; Sprinkler Heads: Type suitable for length and pressure; Zone Configurati…
3. PlumbingForums – Submersible Pump for Lake Irrigation
Domain: plumbingforums.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 1. Pump Type: Submersible pump recommended for lake water irrigation.
2. Power: Suggested range is 3/4 HP to 1.5 HP.
3. Pressure: Minimum of 40 psi recommended for effective sprinkler operation.
4. Flow Rate: 40 GPM at 40 psi mentioned; 10-12 sprinklers can be run simultaneously.
5. Installation: Should be placed below the low waterline or far enough out to ensure water availability.
6. Distance: …
4. Lawnsite – Goulds J10S Jet Pump
Domain: lawnsite.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1. Pump Type: Shallow-well jet pump or submersible pump. 2. Recommended Horsepower: 3/4 HP to 1 HP. 3. Flow Rate: 12 GPM desired, with standard setups flowing 20-25 GPM at 50 PSI. 4. Example Model: Goulds J10S shallow-well jet pump (1 HP). 5. Considerations: Filter water on both suction and outlet sides, use appropriate head for flexibility, and ensure proper installation for low maintenance. 6. A…
5. World Water Reserve – Ultimate Guide to Pumping Surface Water
Domain: worldwaterreserve.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Ultimate Guide to Pumping Water from a River, Lake, or Creek; includes information on water rights, domestic uses of surface water, how to pump water, and how to size a water pump. Discusses legal considerations for pumping water, types of water rights (Riparian Rights and Prior Appropriation), and the importance of checking local laws. Covers different types of pumps suitable for various water so…
6. Lawn Forum – Irrigation Solutions
Domain: thelawnforum.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 1. Irrigation System: 16 zone controller, pop-up sprinklers, pulsating sprinklers. 2. Water Source: 2-acre spring-fed pond. 3. Filtering: Need for a filtration system to prevent clogging of sprinkler heads, possibly a 2-stage filter (coarse and fine). 4. Pump Requirements: Need a pump with sufficient GPM, PSI, and lift to overcome a 45-foot elevation change. 5. Automation: Desire for a mostly auto…
7. Wayne Pumps – Lawn Irrigation Solutions
Domain: waynepumps.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Lawn pumps are used for irrigation by pumping water from lakes, ponds, or municipal sources. They can be portable or permanent-mount. Portable lawn sprinkler pumps can run up to 2 above-ground sprinklers with a total hose length of up to 100 feet. They require reinforced suction hoses or PVC pipes and standard garden hose size for discharge. Permanent installations are suited for underground sprin…
8. Terry Love – Shallow Well Pump Solutions
Domain: terrylove.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 1. 1hp Shallow Well Pump – Provided 75% of the required pressure for the sprinkler system. 2. 1 1/2 hp Wayne Sprinkler Pump – Currently not pushing water into the sprinkler system; designed for moving large volumes of water, not for pressure. 3. 1 1/4″ Continuous Tubing – 70 feet from the lake to the pump, with a check valve at the end to maintain prime. 4. Sprinkler System Requirements – Needs 10…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pumping water from a lake for irrigation
In summary, the strategic sourcing of lake water for irrigation presents a multifaceted opportunity for international buyers. By leveraging local water bodies, businesses can significantly reduce operational costs while enhancing the nutrient quality of irrigation water. This approach not only promotes environmental sustainability but also aligns with the increasing demand for efficient resource management in agriculture and landscaping across various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Investing in high-quality pumping systems and components is crucial to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of irrigation solutions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer customizable packages, expert support, and robust installation services. The legal considerations surrounding water rights must also be navigated carefully to maximize the benefits of using lake water for irrigation.
Looking ahead, the global push for sustainable agricultural practices will only intensify. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to take action by exploring innovative lake irrigation systems that meet their unique needs. By doing so, they can position themselves at the forefront of a growing market, ensuring both profitability and environmental stewardship. Engage with trusted suppliers today to harness the potential of lake water for a more sustainable future.