Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for irrigation pump from river
As international B2B buyers increasingly seek sustainable and cost-effective solutions for agricultural irrigation, the challenge of sourcing reliable irrigation pumps from rivers becomes paramount. These pumps not only facilitate access to abundant water resources but also enhance productivity by utilizing natural sources. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of irrigation pumps suited for river use, exploring their applications, benefits, and technical specifications.
In addition to providing insights into different pumping systems, this guide covers essential aspects such as supplier vetting, pricing structures, and regulatory considerations across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By addressing these critical factors, we empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and local water laws.
Understanding the nuances of each pump type, from submersible to centrifugal, and their respective advantages for specific agricultural practices will enhance your procurement strategy. Whether your focus is on maximizing yield or ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, this guide equips you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the global market for irrigation pumps from rivers. Join us in exploring how to effectively leverage these vital resources for sustainable agricultural practices.
Understanding irrigation pump from river Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Submersible Pump | Operates underwater, ideal for deep water sources | Agricultural irrigation, landscaping | Pros: Efficient in deep water; low maintenance. Cons: Installation can be complex. |
| Centrifugal Pump | Uses rotational energy to move water; versatile | Large-scale irrigation, municipal systems | Pros: High flow rates; adaptable for various applications. Cons: Requires a constant power source. |
| Hydraulic Ram Pump | Utilizes water’s kinetic energy; no external power needed | Remote areas, eco-friendly projects | Pros: Low operational costs; sustainable. Cons: Limited to specific flow conditions. |
| Diaphragm Pump | Positive displacement pump; handles viscous fluids well | Chemical irrigation, wastewater treatment | Pros: Handles solids; precise flow control. Cons: Higher initial costs; maintenance-intensive. |
| Solar-Powered Pump | Operates on solar energy; eco-friendly | Sustainable agriculture, remote applications | Pros: Reduces electricity costs; low environmental impact. Cons: Dependent on sunlight; potential for higher upfront costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Submersible Pumps for River Irrigation?
Submersible pumps are designed to operate underwater, making them ideal for deep water sources like rivers or lakes. They are typically constructed from corrosion-resistant materials and are capable of handling significant water volumes. B2B buyers should consider the pump’s horsepower and flow rate to ensure it meets the irrigation needs. Their efficiency and low maintenance requirements make them popular in agricultural and landscaping applications, although installation can be complex and may require professional assistance.
How Do Centrifugal Pumps Function in Irrigation Systems?
Centrifugal pumps utilize rotational energy to move water, making them versatile for various applications, including large-scale irrigation and municipal water systems. They are known for their high flow rates and ability to adapt to different irrigation setups. B2B buyers should evaluate factors such as power source availability and pump size based on their operational requirements. While they offer high efficiency, they do require a constant power supply, which can be a consideration in areas with unstable electricity.
What Makes Hydraulic Ram Pumps Suitable for Remote Areas?
Hydraulic ram pumps are unique in that they utilize the kinetic energy of flowing water to lift a portion of that water to a higher elevation without the need for external power. This makes them especially suitable for remote areas and eco-friendly projects. B2B buyers should assess the flow conditions of the river to determine the feasibility of this pump type. While they have low operational costs, their effectiveness is limited to specific flow conditions, which can restrict their use in some scenarios.
Why Choose Diaphragm Pumps for Chemical Irrigation?
Diaphragm pumps are positive displacement pumps that excel at handling viscous fluids and slurries, making them ideal for chemical irrigation and wastewater treatment applications. They provide precise flow control and can handle solids without clogging. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and maintenance requirements when evaluating diaphragm pumps, as they can be higher compared to other types. Their robustness and reliability make them a strong choice for specialized irrigation needs.
What Are the Benefits of Solar-Powered Pumps in Sustainable Agriculture?
Solar-powered pumps harness solar energy to operate, providing a sustainable solution for irrigation in remote or off-grid locations. They significantly reduce electricity costs and have a minimal environmental impact. B2B buyers should consider the solar panel capacity and pump specifications to ensure they meet their irrigation demands. While they offer long-term savings and environmental benefits, potential buyers should be aware of their dependence on sunlight and the possibility of higher upfront costs for installation and equipment.
Key Industrial Applications of irrigation pump from river
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Irrigation Pump from River | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Irrigation for Crop Production | Enhances crop yield and reduces dependency on rainfall | Pump size, flow rate, filtration system, and durability |
| Landscaping and Parks | Watering Green Spaces and Gardens | Improves aesthetics and health of plants | Energy efficiency, ease of installation, and maintenance |
| Aquaculture | Water Supply for Fish Farms | Ensures optimal aquatic conditions for fish growth | Water quality control, pump capacity, and environmental regulations |
| Construction | Dust Control and Soil Compaction | Reduces dust and improves worksite safety | Portability, pump power, and adaptability to site conditions |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Cooling Systems for Equipment | Enhances operational efficiency and equipment lifespan | Reliability, pump materials, and compatibility with existing systems |
How is ‘Irrigation Pump from River’ Used in Agriculture and What Problems Does it Solve?
In the agricultural sector, irrigation pumps sourced from rivers are critical for ensuring reliable water supply for crop production, especially in regions prone to drought. These pumps facilitate the efficient transfer of water from surface sources to fields, significantly enhancing crop yields and reducing reliance on unpredictable rainfall. Buyers in this sector must consider the pump’s flow rate, size, and the filtration systems required to maintain water quality, particularly in areas where sedimentation is a concern.
What Role Does ‘Irrigation Pump from River’ Play in Landscaping and Parks?
For landscaping and park maintenance, irrigation pumps from rivers are utilized to maintain lush green spaces and gardens. These systems provide a sustainable and cost-effective water source that supports plant health and aesthetics. Businesses must assess the energy efficiency of the pumps, ease of installation, and ongoing maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance, particularly in urban areas where water conservation is becoming increasingly important.
How Does ‘Irrigation Pump from River’ Benefit Aquaculture Operations?
In aquaculture, irrigation pumps are essential for providing a consistent water supply to fish farms, which is crucial for maintaining the right aquatic environment. These pumps help regulate water quality and temperature, promoting healthy fish growth and productivity. Buyers need to focus on the pump’s capacity, filtration capabilities, and compliance with environmental regulations to ensure sustainable operations in this sector.
In What Ways Do ‘Irrigation Pump from River’ Systems Support Construction Activities?
During construction projects, irrigation pumps from rivers can be employed for dust control and soil compaction. By supplying water to control dust, these pumps enhance safety and visibility on job sites while also aiding in the compaction process for stable foundations. Key considerations for sourcing include the portability of the pumps, their power output, and their adaptability to varying site conditions, ensuring they can meet the demands of different construction environments.
How is ‘Irrigation Pump from River’ Used in Industrial Manufacturing Cooling Systems?
In industrial manufacturing, irrigation pumps sourced from rivers are often integrated into cooling systems for machinery and equipment. By providing a constant supply of water, these pumps help maintain optimal operating temperatures, thereby enhancing efficiency and extending equipment lifespan. Buyers should prioritize reliability and the materials used in pump construction to withstand industrial environments, as well as compatibility with existing systems to minimize operational disruptions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘irrigation pump from river’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Legal Compliance for Water Rights
The Problem:
B2B buyers often encounter significant hurdles when it comes to understanding the legal aspects of pumping water from rivers. Water rights can vary widely by region, especially in places like Africa and South America, where regulations may be complex and local authorities enforce them stringently. For instance, a buyer may invest in an irrigation pump and related infrastructure only to discover that their intended use of river water violates local laws, leading to potential fines or legal actions. This uncertainty can result in wasted resources and halted operations.
The Solution:
To navigate the legal landscape effectively, it is crucial for buyers to conduct thorough research on local water rights and regulations before purchasing an irrigation pump. This involves consulting with local governmental agencies responsible for water management, such as environmental protection departments or water resources authorities. Establishing relationships with these entities can provide clarity on the legal framework governing surface water usage. Additionally, consider seeking legal counsel or hiring a consultant who specializes in water rights to ensure compliance. Buyers should also explore obtaining necessary permits in advance to mitigate risks and create a solid foundation for their irrigation project.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Reliable Water Quality for Agricultural Use
The Problem:
Another common pain point is the challenge of maintaining water quality when using river water for irrigation. Many B2B buyers may underestimate the impact of biological contaminants such as bacteria and sediments present in surface water. For instance, irrigation from contaminated sources can lead to crop damage and health risks, affecting both yield and marketability. This is particularly concerning in regions where food safety is under strict scrutiny.
The Solution:
To address water quality issues, it is essential for buyers to invest in robust filtration and purification systems as part of their irrigation setup. A combination of sediment filters, UV purifiers, and reverse osmosis systems can significantly reduce contaminants, ensuring that the water used for irrigation is safe and suitable for crops. Additionally, regular water quality testing should be implemented to monitor for harmful pathogens and sediment levels. Partnering with suppliers who can provide high-quality filtration solutions and ongoing support can further enhance the efficacy of the irrigation system while safeguarding agricultural outputs.
Scenario 3: Selecting the Right Pump for Variable River Conditions
The Problem:
B2B buyers frequently face the dilemma of selecting the appropriate irrigation pump that can adapt to the variable flow conditions of a river. Rivers can experience fluctuations in water levels due to seasonal changes, weather events, or upstream usage, which can render some pumps ineffective. Selecting an inappropriate pump could lead to inadequate water supply for irrigation, resulting in crop stress or failure.
The Solution:
To ensure the right pump selection, buyers should conduct a comprehensive assessment of the river’s flow characteristics, including seasonal variations and average flow rates. This information is crucial for sizing the pump accurately. It is advisable to consult with irrigation experts or pump manufacturers who can recommend pumps specifically designed for variable flow conditions, such as submersible or centrifugal pumps. Additionally, implementing a variable speed drive can optimize pump performance, allowing it to adjust its output based on real-time water availability. Incorporating a collection tank can also help buffer against fluctuations, ensuring a consistent water supply for irrigation needs. By making informed choices based on river conditions, buyers can achieve more reliable irrigation outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for irrigation pump from river
What Are the Key Materials Used in Irrigation Pumps from Rivers?
When selecting materials for irrigation pumps designed to draw water from rivers, several factors must be considered, including performance properties, cost, and regional compliance standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the construction of these pumps.
How Does Cast Iron Perform in Irrigation Pumps?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent strength and durability, with a temperature rating of up to 300°F and good pressure resistance. It has a moderate corrosion resistance, often enhanced with coatings.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of cast iron is its robustness, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it is relatively heavy, which can complicate installation and transportation. Additionally, while cast iron is cost-effective, it may require more maintenance due to corrosion over time, especially in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Cast iron pumps are well-suited for pumping water with moderate levels of debris and sediment, making them ideal for river applications. However, they may not be the best choice for areas with highly corrosive water conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for material specifications. Cast iron may be favored for its availability and lower cost, but buyers should consider the implications of maintenance in their specific climate.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Irrigation Pumps?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 800°F. It also offers high tensile strength, making it suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and low maintenance requirements, even in corrosive environments. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which may be a barrier for budget-conscious buyers. Manufacturing stainless steel components can also be more complex, leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel pumps are ideal for applications where water quality is critical, such as drinking water or irrigation in sensitive crops. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe often prefer stainless steel due to its compliance with health and safety standards. It is essential to verify that the stainless steel used meets relevant certifications, such as JIS or EN standards.
How Does Polypropylene Compare in Terms of Cost and Performance?
Key Properties: Polypropylene is a lightweight thermoplastic that offers good chemical resistance and can handle temperatures up to 200°F. It is not as strong as metals but provides adequate performance for many irrigation applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of polypropylene is its low cost and ease of installation, making it attractive for budget-sensitive projects. However, its lower strength and temperature limits may restrict its use in high-demand situations.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene pumps are suitable for low-pressure applications and can be used in environments with less abrasive materials. They are often used for irrigation in areas with less demanding conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Vietnam and Nigeria should assess the availability of polypropylene components and ensure they meet local quality standards. Its affordability makes it a popular choice for smaller farms or less intensive agricultural operations.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Irrigation Pump Design?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating of up to 400°F. It is also strong, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which simplifies installation and reduces transportation costs. However, it is generally more expensive than cast iron and can be prone to scratching and denting, which may affect its longevity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum pumps are effective in applications where weight is a concern, such as portable irrigation systems. They are also suitable for freshwater applications but may not perform as well in highly abrasive or saline environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet specific standards for durability and corrosion resistance, especially in coastal or humid regions. Its higher cost may be a consideration for budget-limited projects.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Irrigation Pumps
| Material | Typical Use Case for irrigation pump from river | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty river pumping | High durability | Prone to corrosion, heavy | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Drinking water and sensitive crop irrigation | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Polypropylene | Low-pressure irrigation in less demanding areas | Low cost, easy installation | Lower strength, temperature limits | Low |
| Aluminum | Portable irrigation systems | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | More expensive, prone to damage | Medium |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for irrigation pumps from rivers, ensuring that they can make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for irrigation pump from river
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing an Irrigation Pump from a River?
The manufacturing process for irrigation pumps designed to extract water from rivers involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is essential to ensuring that the final product meets the demands of the agricultural and industrial sectors, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, typically involving corrosion-resistant metals and durable plastics. Common materials include stainless steel for the pump casing, thermoplastic for impellers, and reinforced PVC for suction hoses. These materials are sourced based on their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to water, mud, and varying temperatures. Suppliers often conduct a thorough evaluation of material properties to ensure they meet industry standards.
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage involves shaping them into the required components. Techniques such as casting, machining, and injection molding are commonly employed. For example, pump casings may be cast from metal to create a robust and leak-proof structure, while impellers are typically molded from high-strength plastic to enhance efficiency and reduce weight. These methods not only ensure precise dimensions but also contribute to the overall performance and longevity of the pump.
Assembly Process
The assembly phase brings together all the individual components, which may include the motor, impeller, casing, and various fittings. This stage often requires skilled labor to ensure that each part is correctly fitted and aligned. Automated assembly lines are increasingly common, particularly for larger manufacturers, as they enhance consistency and speed. During this phase, critical components such as seals and gaskets are installed to prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance.
Finishing Touches
The final stage involves finishing processes such as painting, coating, and testing. Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and enhance the durability of the pump. Quality assurance tests are conducted to ensure that pumps meet performance specifications, including flow rate and pressure output. This stage is crucial for ensuring the product’s readiness for the market and its ability to withstand the conditions it will face in the field.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in Manufacturing Irrigation Pumps?
Quality control (QC) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for irrigation pumps. It ensures that the products not only meet industry standards but also satisfy customer expectations. International standards such as ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications like CE and API play a significant role in establishing these QC measures.
Understanding International Standards
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers aiming for ISO certification must demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. CE marking indicates that a product meets European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, while API standards are critical for pumps used in petroleum and natural gas applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective QC processes include several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing cycle:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components as they arrive at the facility. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards prevents defects later in the process.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, IPQC checks are implemented to monitor operations and detect any deviations from established quality standards. This step often includes real-time inspections and measurements.
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, FQC tests the finished pumps for performance and safety. These tests may include pressure tests, flow rate measurements, and operational checks to ensure compliance with specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent QC standards to mitigate risks associated with product performance and compliance.
Conducting Audits and Inspections
One effective way to verify a supplier’s QC processes is through on-site audits. These audits allow buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, review QC documentation, and evaluate the implementation of quality standards in real time. Additionally, buyers may engage third-party inspection agencies to conduct independent evaluations of the supplier’s QC practices.
Reviewing Quality Reports
Suppliers should provide comprehensive quality reports that detail their QC processes, test results, and compliance with relevant standards. Buyers should request these documents as part of the supplier selection process. Analyzing these reports can offer insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and their ability to meet international standards.
Understanding Certification Nuances
It’s essential for buyers to understand the nuances of certifications, as they can vary significantly between countries and industries. For example, while a CE mark may be sufficient for the European market, additional certifications may be required for specific applications or regions. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers possess the necessary certifications for the target market to avoid potential compliance issues.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance testing for irrigation pumps involves various methods to ensure the product’s reliability and performance. Common testing methods include:
Hydraulic Testing: This test evaluates the pump’s ability to perform under pressure. It simulates operational conditions to ensure that the pump can handle the required flow rates without leaks or failures.
Performance Testing: This method assesses the pump’s efficiency, including its flow rate and head pressure capabilities. Performance tests are typically conducted in controlled environments to ensure accurate measurements.
Durability Testing: To evaluate the longevity of the pump, manufacturers may conduct accelerated aging tests, exposing the pump to extreme conditions to simulate years of use in a shorter timeframe.
Safety and Compliance Testing: Ensuring compliance with safety standards is critical, particularly for pumps used in applications involving drinking water or agricultural irrigation. Tests may include assessing materials for harmful substances and ensuring that the design prevents hazards.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for irrigation pumps from rivers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. This knowledge not only enhances procurement strategies but also ensures that the products meet the rigorous demands of their intended applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘irrigation pump from river’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in identifying and procuring irrigation pumps suitable for extracting water from rivers. By following this step-by-step checklist, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions that meet their irrigation needs while complying with local regulations and standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by determining the specific requirements for your irrigation pump. This includes understanding the flow rate, head height, and the type of pump (e.g., submersible or surface) that best suits your water source. Knowing these specifications will help narrow down your options and ensure that the pump can effectively meet your irrigation demands.
- Flow Rate: Assess the amount of water needed for your irrigation system. Calculate the gallons per minute (GPM) required based on the size of the area to be irrigated.
- Head Height: Measure the vertical distance from the river to the highest point of your irrigation system to ensure the pump can deliver water effectively.
Step 2: Research Local Regulations and Water Rights
Understanding the legal framework surrounding water extraction is critical. Different regions have varying laws regarding water rights, and failing to comply can result in fines or legal issues.
- Check with Local Authorities: Contact state or local water resource departments to gather information about regulations that govern the pumping of surface water.
- Understand Water Rights: Familiarize yourself with concepts like Riparian Rights and Prior Appropriation that may apply in your area to avoid potential legal complications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it is essential to conduct thorough due diligence. This step ensures you partner with reputable manufacturers who can provide reliable products.
- Request Documentation: Ask for company profiles, product certifications, and case studies that demonstrate their experience in providing irrigation solutions.
- Seek References: Reach out to other businesses or organizations that have utilized the supplier’s products, particularly in your region, to gauge performance and service quality.
Step 4: Assess Product Quality and Features
Investigate the quality of the pumps being offered by potential suppliers. Not all pumps are created equal, and understanding the features can help you choose a reliable and efficient model.
- Material and Design: Look for pumps made from durable materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Features like corrosion resistance and self-priming capabilities are advantageous.
- Warranty and Support: Ensure that the supplier provides a solid warranty and customer support options to address any issues that may arise post-purchase.
Step 5: Consider Additional Components
Irrigation systems often require more than just a pump. Evaluate the necessity for additional components that may enhance the effectiveness of your system.
- Filtration Systems: Since water from rivers can contain contaminants, consider pumps that come with built-in filtration options to ensure water quality.
- Storage Solutions: Assess if a collection tank is needed to store water, which can improve the efficiency and longevity of the pump by reducing the workload.
Step 6: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have narrowed down your options, request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers. Comparing pricing is essential to ensure you receive a competitive offer.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ensure that the quotes include all costs associated with the pump, including shipping, installation, and any necessary accessories.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term operational costs, such as maintenance and energy consumption.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase
After thorough evaluation and comparison, choose the supplier that best meets your needs and finalize your purchase. Ensure all terms are clear, including delivery timelines and after-sales support.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently source an irrigation pump from a river that aligns with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for irrigation pump from river Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Irrigation Pumps Sourced from Rivers?
When evaluating the cost structure for irrigation pumps sourced from rivers, several key components come into play. The primary cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. High-quality, corrosion-resistant materials such as fiberglass-reinforced thermoplastics increase durability but also raise the initial expense. Typical materials might also include stainless steel for pump components and heavy-duty PVC for hoses and filters.
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Labor costs vary by region, with countries in Africa and South America often having lower wage rates compared to Europe. However, manufacturing overhead, which includes utilities, factory rent, and administrative expenses, can be substantial. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these costs.
Tooling and Quality Control: The tooling costs associated with creating molds and fixtures for pump production can be high, especially for customized solutions. Additionally, robust quality control measures are essential to ensure reliability and compliance with local and international standards, adding to the overall expense.
Logistics: Transportation costs must also be factored in. Shipping pumps internationally can be costly, particularly for bulky or heavy items. Incoterms will dictate who bears these costs, influencing the final pricing structure.
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin to cover their expenses and risks, which can vary based on market competition and demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Irrigation Pumps?
Several factors influence the pricing of irrigation pumps for international buyers.
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to achieve cost efficiency.
Specifications and Customization: Custom pumps designed for specific applications or unique requirements can significantly increase costs. Clear communication of needs can help suppliers provide accurate quotes and avoid unexpected expenses.
Quality and Certifications: Pumps that meet international quality standards (ISO, CE, etc.) may come at a premium but offer better reliability and warranty options, reducing long-term costs associated with maintenance and replacement.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and customer service, but they often provide better value in terms of product quality and after-sales support.
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms is crucial, as they determine who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transport. This can significantly affect the total landed cost of the product.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Navigating Costs?
Navigating the cost landscape for irrigation pumps requires strategic planning and negotiation skills.
Negotiation Strategies: Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing. Be prepared to discuss volume discounts, payment terms, and potential for long-term partnerships, which can yield favorable pricing.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider not only the upfront costs but also the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and operational efficiency over the pump’s lifespan. This holistic view can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should be aware of potential hidden costs such as tariffs, import duties, and local taxes. Conducting thorough market research and engaging local experts can help mitigate these risks.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis aims to provide a comprehensive overview of cost structures and pricing influences, actual prices may vary based on specific supplier negotiations, regional market conditions, and individual buyer requirements. It is advisable to request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing irrigation pump from river With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Irrigation Pumps from Rivers
When considering irrigation solutions, businesses often seek the most efficient and cost-effective methods tailored to their specific needs. While irrigation pumps from rivers offer significant advantages, such as access to abundant water resources, it’s essential to evaluate alternative solutions that may better suit particular circumstances. Below, we compare irrigation pumps from rivers with other viable options, including groundwater pumps and rainwater harvesting systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Irrigation Pump From River | Groundwater Pump | Rainwater Harvesting System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High flow rate; suitable for large areas | Reliable, consistent supply; can be tailored to demand | Variable; depends on rainfall; may require backup |
| Cost | Moderate initial setup; ongoing maintenance costs | Higher installation costs; long-term operational efficiency | Lower setup cost; potential savings on water bills |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires legal checks and setup time | More straightforward if well is already present | Requires installation of collection system; relatively simple |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and potential legal compliance | Low maintenance if properly installed; occasional checks needed | Minimal maintenance; regular cleaning of filters required |
| Best Use Case | Large agricultural operations; areas with abundant river access | Areas with limited surface water; consistent irrigation needs | Urban areas with seasonal rainfall; sustainable practices |
Groundwater Pumps: A Reliable Alternative
Groundwater pumps provide a dependable source of water for irrigation, particularly in regions where surface water is scarce. These pumps tap into underground aquifers, offering a consistent supply that can be tailored to the specific water needs of the crops. While the initial installation costs can be higher, groundwater systems often require less maintenance once operational. However, over-extraction can lead to depletion of aquifers, making sustainable management essential.
Rainwater Harvesting Systems: A Sustainable Solution
Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for irrigation and other uses. This method is particularly beneficial in regions with seasonal rainfall patterns, allowing businesses to utilize a natural resource without relying on external water supplies. The initial setup costs are generally lower than those of groundwater systems, and the ongoing operational costs can lead to significant savings on water bills. However, the effectiveness of this solution is highly dependent on local rainfall patterns, and additional infrastructure may be required to ensure a consistent supply.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Irrigation Solution
When evaluating irrigation options, B2B buyers must consider their specific needs, including water availability, cost constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Irrigation pumps from rivers can be highly effective in regions with ample water flow but may involve complex legal and maintenance considerations. Groundwater pumps offer reliability but come with higher initial costs, while rainwater harvesting systems present a sustainable alternative that can save costs but may not provide a consistent supply. By carefully assessing these factors, businesses can select the most suitable irrigation solution for their agricultural or landscaping needs, ensuring efficient water management and sustainability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for irrigation pump from river
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Irrigation Pumps from Rivers?
When considering irrigation pumps sourced from rivers, several technical properties are critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some essential specifications to keep in mind:
Pump Capacity (Flow Rate)
The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s), indicates how much water the pump can move. For agricultural applications, a higher flow rate is crucial, as it determines the volume of water available for irrigation. B2B buyers must assess their irrigation needs to select pumps that can deliver adequate water supply to their fields.Power Rating (Horsepower)
The power rating, typically denoted in horsepower (HP), indicates the pump’s capability to lift water from the source. Higher horsepower pumps are essential for deeper water sources or longer discharge distances. Selecting the appropriate power rating ensures efficient operation and can prevent unnecessary wear on the pump.Material Grade
The material grade of the pump housing and components affects durability and corrosion resistance. Common materials include stainless steel, cast iron, and thermoplastics. B2B buyers should prioritize pumps made from corrosion-resistant materials to ensure longevity, especially in environments with high sediment or chemical content in the water.Suction Lift Capability
This specification refers to the maximum vertical distance the pump can lift water from the source. It is crucial for determining whether a pump can draw water from a river or lake effectively. Pumps with higher suction lift capabilities are more versatile and can be used in various water source scenarios.Efficiency Rating
The efficiency rating of a pump indicates how effectively it converts input power into hydraulic energy. A higher efficiency rating results in lower energy costs and reduced environmental impact. B2B buyers should consider efficiency ratings when evaluating long-term operational costs.Filtration System Compatibility
Many irrigation pumps require compatible filtration systems to prevent debris from damaging the pump. Pumps may come with built-in filters, or buyers may need to purchase them separately. Ensuring compatibility with effective filtration systems can enhance pump performance and reduce maintenance frequency.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Irrigation Pumps?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms that buyers should be familiar with:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When sourcing irrigation pumps, knowing the OEM can help buyers assess quality and compatibility with existing systems.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is vital for buyers to avoid excess inventory and manage cash flow effectively, particularly when dealing with international suppliers.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific goods or services. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate and competitive pricing for irrigation pumps tailored to their needs.Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation, ensuring smoother transactions.Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Knowing the lead time is critical for planning irrigation schedules and ensuring that equipment is available when needed.Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the performance of the pump. Understanding warranty conditions can help buyers assess the risk associated with their investment and ensure they have recourse in case of defects.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing irrigation pumps from rivers, ultimately leading to better operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the irrigation pump from river Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Irrigation Pump from River Sector?
The irrigation pump market, particularly for those utilizing river water, is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. As agricultural practices increasingly seek sustainable and efficient water management solutions, the demand for irrigation pumps from rivers is surging. Key drivers include the rising need for food security, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where agricultural productivity is critical for economic stability. Moreover, the integration of smart technology into irrigation systems—such as IoT devices and automated controls—facilitates real-time monitoring and management, optimizing water usage and enhancing crop yields.
Emerging trends in sourcing indicate a shift towards localized supply chains, which can reduce lead times and transportation costs. B2B buyers are also prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate agility in adapting to changing market conditions, such as fluctuations in water availability or regulatory changes. In Europe and the Middle East, stricter environmental regulations are pushing buyers to seek more efficient, eco-friendly pumping solutions. Additionally, the rise of online marketplaces and digital platforms for sourcing equipment is transforming traditional procurement methods, allowing for greater transparency and competitive pricing.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Irrigation Pump from River Market?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern business practices, and the irrigation pump sector is no exception. The environmental impact of sourcing practices is under increased scrutiny, with buyers looking for suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly materials and processes. Pumps designed for river use must not only be energy-efficient but also constructed from sustainable materials that minimize ecological footprints.
Ethical sourcing is critical as well, particularly in regions where water rights and environmental sustainability are contentious issues. B2B buyers are encouraged to partner with manufacturers who possess ‘green’ certifications, ensuring that their products adhere to environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Energy Star can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By investing in ethically sourced and sustainable irrigation pumps, businesses can improve their brand reputation while also contributing positively to local ecosystems and communities.
What Is the Evolution of the Irrigation Pump from River Sector?
The history of irrigation pumps from rivers dates back centuries, with early systems relying on manual labor and simple mechanisms like buckets and troughs. With the advent of the Industrial Revolution, mechanical pumps began to emerge, significantly enhancing efficiency in water extraction and distribution. The introduction of electric pumps in the 20th century revolutionized agricultural practices, allowing for the large-scale irrigation of crops and facilitating the growth of modern agriculture.
In recent decades, technological advancements have further transformed the sector, leading to the development of submersible and centrifugal pumps that are tailored for river applications. The focus has shifted towards not just efficiency, but also sustainability and smart technology integration, reflecting the growing awareness of environmental concerns and the need for responsible water management. Today, the irrigation pump market continues to evolve, driven by innovation and the pressing demands of global food security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of irrigation pump from river
How do I determine the right size of an irrigation pump for my needs?
To size an irrigation pump correctly, you need to assess your water needs, including flow rate and pressure requirements. Consider the type of crops you’re irrigating, the distance from the water source, and the elevation change. A flow rate of 10 gallons per minute (GPM) is typical for small to medium agricultural operations. Consult with pump manufacturers or local agricultural extension services to evaluate your specific requirements and ensure the pump can deliver adequate pressure and flow for your irrigation system.What is the best type of irrigation pump for drawing water from a river?
The best type of irrigation pump for drawing water from a river typically depends on the river’s depth and flow conditions. Submersible pumps are ideal for deeper bodies of water, as they can be submerged and provide higher efficiency. For shallow rivers, surface pumps or hydraulic ram pumps may be more suitable. Evaluate the specific characteristics of your water source and consult with suppliers to identify the most efficient pump type for your irrigation needs.What are the legal requirements for pumping water from a river in my country?
Legal requirements for pumping water from a river vary by country and sometimes even by region. Generally, you must obtain permits or licenses from local water management authorities. It’s crucial to research riparian rights or prior appropriation laws applicable in your area. Consult with local environmental protection agencies or legal advisors to ensure compliance and avoid potential fines or legal issues associated with unauthorized water extraction.How can I vet suppliers when sourcing irrigation pumps internationally?
When sourcing irrigation pumps internationally, vet suppliers by checking their certifications, customer reviews, and industry reputation. Request product samples and detailed specifications to assess quality. Additionally, inquire about their experience in your specific market and their ability to meet local regulatory standards. Utilizing platforms like Alibaba or TradeKey can provide insights into supplier reliability, and consider visiting the supplier’s manufacturing facility if feasible for a comprehensive assessment.What customization options are available for irrigation pumps?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for irrigation pumps, including size, material, and power specifications. You can request specific features such as enhanced filtration systems, variable speed controls, or different voltage options. Be clear about your operational needs and discuss potential modifications with suppliers to ensure the pump meets your irrigation requirements. Custom solutions can enhance efficiency and performance in specific agricultural applications.What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for irrigation pumps?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for irrigation pumps vary by supplier and product type. Typically, MOQs can range from a single unit for high-end pumps to several hundred units for bulk orders. Discuss your needs with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your budget and operational capacity. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses, so it’s worth exploring these options.What payment terms are commonly offered for international purchases of irrigation pumps?
Payment terms for international purchases of irrigation pumps often include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. Common practices involve a deposit (usually 30-50%) with the balance due before shipping. Ensure you clarify payment terms upfront and consider using secure payment methods like PayPal or escrow services to protect your investment. Discussing these terms early can help avoid misunderstandings later in the transaction process.How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for irrigation pumps before shipment?
To ensure quality assurance (QA) for irrigation pumps before shipment, request detailed product specifications and certifications from the supplier. Conduct factory inspections or third-party quality checks to verify that the pumps meet industry standards and your specific requirements. Establish clear acceptance criteria and testing protocols for pump performance, durability, and safety. Maintaining open communication with the supplier throughout the manufacturing process can also help address any concerns before shipment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Irrigation Pump From River Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. World Water Reserve – Ultimate Guide to Water Pumping
Domain: worldwaterreserve.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Ultimate Guide to Pumping Water from a River, Lake, or Creek; includes information on water rights, usage of surface water, how to pump water, and how to size a water pump; emphasizes the importance of checking local laws and regulations; discusses Riparian Rights and Prior Appropriation doctrines; outlines domestic uses of surface water for gardening, irrigation, drinking, cooking, and bathing; r…
2. Goulds – Submersible Pump 25GS20
Domain: lawnsite.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Irrigation system fed from a river; Access and rights to use less than 100 GPM from a river, planning to use about 30 GPM; VU-Flow 30 or 60 mesh filter; Hunter I-20 or Rainbird 5000 heads considered; Goulds submersible pump (25GS20) with a 2 hp motor; Pump installed in PVC well screen on cinderblocks; Concerns about using Maxi-paw heads due to negative feedback; Need for pressure relief valve; Dis…
3. JustAnswer – Surface Centrifugal Pump Solutions
Domain: justanswer.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: For pumping water 150–200 feet from a river with a gentle slope, consider a surface centrifugal pump with adequate horsepower to overcome distance and elevation. Use a suction line with a strainer to prevent debris intake from the rocky riverbed. A pressure or storage tank sized based on daily water needs helps maintain steady flow and reduces pump cycling. Ensure electrical wiring is safely insta…
4. RPS – Pro Irrigation Surface Pumps
Domain: rpssolarpumps.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: High Volume Irrigation from a Creek using RPS Pro Irrigation Surface Pumps. The pump provides high flow rates and can reach up to 45 PSI, suitable for various irrigation methods (sprinklers, drip, soaker hoses). Maximum suction lift is 25 feet, with a recommendation to place the pump within 20 linear feet of the water source. The pump is wired to the RPS Pro Controller for maximum efficiency and v…
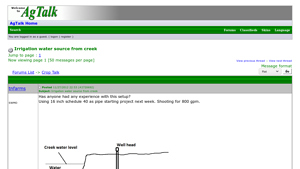
5. NewAgTalk – Electric Turbine Pump System
Domain: talk.newagtalk.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: – Pipe: 16 inch schedule 40 pipe
– Target Flow Rate: 800 gpm
– Pump Type: Electric turbine pump
– Elevation Difference: 8 feet from creek water level to pump site
– Intake Pipe: 20 feet long with hundreds of slices
– Horizontal Pipe Depth: 6 feet below water level, water level approximately 9-10 feet depending on creek level
– Concerns: Silt accumulation, need for cleaning, potential for trash and…
6. Jet – 1 1/2 HP Jet Pump
Domain: finehomebuilding.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: 1 1/2 HP Jet Pump, lifts water up to 90 feet, 3/4″ garden hose for intake, 1/2″ garden hose for branch sprinkler/soaker lines, 10/2 wire for electrical connection, 240 V power supply, 300′ wire length, draws about 4 amps, 1″ PVC intake line, 1/2 HP Myers jet pump, 1/4″ PVC line, 8 gallons per minute flow rate, total installation cost approximately $1,400.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for irrigation pump from river
In the evolving landscape of irrigation solutions, strategic sourcing of river-based irrigation pumps offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers. By understanding local water rights, selecting the right pump type based on specific needs, and considering the environmental impact, businesses can optimize their water management strategies. Leveraging surface water not only reduces costs compared to conventional sources but also enhances the sustainability of agricultural practices across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
For buyers, investing in high-quality, tailored pump packages that suit their unique requirements ensures efficient water delivery and maximizes crop yield. The integration of filtration systems and pressure tanks further guarantees safe and effective water use for both irrigation and domestic purposes.
Looking ahead, the demand for reliable irrigation solutions will only grow as climate challenges intensify. Now is the time for businesses to engage with suppliers who can provide innovative, compliant, and efficient pump systems. As you consider your sourcing strategies, prioritize partnerships that align with your goals for sustainability and operational excellence—this is key to thriving in the competitive agricultural landscape.