Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for irrigation system master valve
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing an effective irrigation system master valve can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These critical components serve as the backbone of efficient irrigation systems, controlling the flow of pressurized water and preventing costly leaks that can lead to environmental waste and property damage. As stakeholders in agriculture and landscaping strive for sustainable practices, understanding the nuances of master valves—including their types, applications, and essential features—becomes paramount.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of master valves, from normally open to normally closed configurations, and their respective benefits in diverse applications. Additionally, we will explore vital aspects of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and integration with advanced technologies like flow sensors. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and a clear understanding of the market landscape, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices. Whether you are based in Nigeria, Brazil, or elsewhere, navigating the intricacies of master valves will help optimize your irrigation systems, drive sustainability, and enhance operational efficiency.
Understanding irrigation system master valve Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normally Open Master Valve (NOMV) | Stays open by default, allowing continuous water flow until closed by a signal. | Residential and commercial irrigation systems needing constant access to water. | Pros: Easy access to water; suitable for mixed-use. Cons: Vulnerable to leaks; lacks protection against power outages. |
| Normally Closed Master Valve (NCMV) | Closes by default, only opening when a signal is received from the controller. | Commercial irrigation systems where water management is critical. | Pros: Prevents water waste; protects against leaks during off-hours. Cons: May require more complex installation and calibration. |
| Slow-Opening Master Valve | Gradual opening and closing to minimize water surges. | Large agricultural systems or high-value landscapes. | Pros: Reduces risk of water hammer; protects infrastructure. Cons: Slower response time may delay water delivery. |
| Pressure Regulating Master Valve | Integrates pressure regulation to maintain consistent flow. | Systems in areas with fluctuating water supply pressures. | Pros: Enhances system efficiency; protects against pressure-related damage. Cons: Higher upfront cost; may require specialized maintenance. |
| Flow-Sensing Master Valve | Equipped with flow sensors to detect and respond to anomalies. | Advanced irrigation systems needing real-time monitoring. | Pros: Immediate leak detection; automates system response. Cons: Complexity in installation; requires compatible controller. |
What Are the Characteristics of Normally Open Master Valves (NOMV)?
Normally Open Master Valves (NOMV) are designed to remain open until a signal from the irrigation controller commands them to close. This design allows for continuous access to pressurized water, making it suitable for residential and commercial applications where users may need immediate water access for various tasks. However, buyers should consider the potential for leaks and the lack of protective features during power outages, which can lead to water waste and damage.
How Do Normally Closed Master Valves (NCMV) Operate?
Normally Closed Master Valves (NCMV) are closed by default and only open when activated by the irrigation controller. This feature is particularly advantageous for commercial applications, where it can prevent leaks and water waste during non-irrigation periods. Buyers should evaluate the installation complexity and ensure proper calibration for optimal performance, as these valves require precise integration with the overall irrigation system.
Why Choose Slow-Opening Master Valves?
Slow-Opening Master Valves are specifically engineered to open and close gradually, which helps mitigate water surges that can damage irrigation infrastructure. These valves are ideal for large agricultural systems or high-value landscapes where maintaining system integrity is critical. Buyers should weigh the benefits of surge protection against the potential delay in water delivery, which may affect irrigation schedules.
What Benefits Do Pressure Regulating Master Valves Offer?
Pressure Regulating Master Valves incorporate pressure regulation mechanisms to maintain consistent flow rates, especially in regions with variable water supply pressures. These valves enhance system efficiency and protect irrigation components from pressure-related damage. While they come with a higher initial investment, buyers should consider the long-term savings from reduced damage and increased operational efficiency.
How Do Flow-Sensing Master Valves Enhance Irrigation Systems?
Flow-Sensing Master Valves are equipped with sensors that monitor flow rates and detect anomalies such as leaks or blockages in real time. This technology is particularly beneficial for advanced irrigation systems that require immediate responsiveness to changes in flow. Buyers must ensure compatibility with their existing controllers and be prepared for the complexities associated with installation and maintenance, as these systems can be more sophisticated than standard valves.
Key Industrial Applications of irrigation system master valve
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Irrigation System Master Valve | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Large-scale crop irrigation systems | Enhances water efficiency and reduces waste, protecting crops from drought conditions. | Material durability, size compatibility, and flow capacity. |
| Landscaping & Turf Management | Sports fields and public parks irrigation | Minimizes water loss and ensures consistent watering schedules, improving turf health. | Pressure regulation features and compatibility with flow sensors. |
| Horticulture | Greenhouses and nurseries | Controls water supply effectively, preventing overwatering and ensuring optimal plant growth. | Resistance to chemicals and environmental factors. |
| Municipal Water Management | Urban irrigation systems | Reduces water leakage and waste, supporting sustainable urban development initiatives. | Compliance with local regulations and ease of integration with existing systems. |
| Industrial Facilities | Cooling systems in manufacturing plants | Prevents water wastage and system damage, ensuring operational efficiency. | Compatibility with high-pressure systems and robust construction. |
How is the Irrigation System Master Valve Used in Agriculture?
In agriculture, irrigation system master valves are crucial for large-scale crop irrigation systems. They control the flow of water, allowing for efficient distribution across vast fields. By minimizing leaks and ensuring that water is only supplied when needed, these valves help protect crops from drought and reduce water wastage. Buyers in this sector should consider the durability of materials, the valve’s size compatibility with existing systems, and its flow capacity to meet diverse irrigation needs.
What Role Does the Master Valve Play in Landscaping and Turf Management?
In landscaping and turf management, particularly for sports fields and public parks, master valves are essential for maintaining healthy turf. They prevent unnecessary water loss by ensuring that water only flows when irrigation zones are active. This capability supports consistent watering schedules, enhancing turf quality and longevity. Buyers should prioritize valves with pressure regulation features and those compatible with flow sensors to optimize performance and resource management.
How is the Master Valve Beneficial for Horticulture?
In horticulture, particularly within greenhouses and nurseries, irrigation system master valves are integral to managing water supply. They allow for precise control over irrigation, preventing overwatering, which can lead to root rot and other plant health issues. The valves must be resistant to various chemicals and environmental factors, ensuring long-term reliability. Buyers should focus on sourcing valves that can withstand the specific conditions of their horticultural applications.
Why is the Master Valve Important for Municipal Water Management?
Municipal water management systems utilize irrigation system master valves to optimize urban irrigation efforts. These valves help reduce water leakage and waste, aligning with sustainability goals in urban development. By ensuring that water is only supplied when necessary, municipalities can significantly lower operational costs and enhance resource conservation. Buyers must ensure compliance with local regulations and consider ease of integration with existing irrigation infrastructure.
How Can Industrial Facilities Benefit from Master Valves?
In industrial facilities, particularly those with cooling systems, irrigation system master valves play a vital role in preventing water wastage and protecting equipment from damage. These valves ensure that water is supplied efficiently, maintaining operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector should look for valves that are compatible with high-pressure systems and constructed robustly to endure the demanding industrial environment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘irrigation system master valve’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing Water Waste Efficiently
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those managing large agricultural or commercial properties, face the challenge of water waste due to unnoticed leaks in irrigation systems. Without a master valve, the mainline remains pressurized at all times, which can lead to continuous water loss if a valve fails or a pipe cracks. This not only wastes a precious resource but can also escalate operational costs significantly, especially in regions where water is scarce and expensive.
The Solution: To combat this issue, buyers should prioritize the installation of a normally closed master valve (NCMV) in their irrigation systems. An NCMV shuts off the water supply when the system is not in use, drastically reducing the risk of leaks going unnoticed for extended periods. When sourcing the master valve, ensure it is compatible with the existing irrigation controller and consider models that integrate with flow sensors. These sensors can alert operators to discrepancies in flow rates, enabling quick responses to potential leaks. Regular maintenance checks should also be scheduled to ensure that the valve and associated components are functioning properly, thus preventing water waste and reducing overall costs.
Scenario 2: Protecting Property from Water Damage
The Problem: In regions with heavy clay soils or where infrastructure is sensitive to water exposure, unnoticed irrigation leaks can lead to severe property damage, including soil erosion and foundation issues. B2B buyers are often concerned about the potential for extensive repair costs and operational disruptions that can arise from such damage, particularly if the irrigation system is running during off-hours when leaks may go undetected.
The Solution: Implementing a master valve with an integrated flow sensor can be a game-changer for property protection. This setup allows for real-time monitoring of water flow, automatically shutting off the system if a leak is detected. When selecting a master valve, buyers should look for features that enhance durability and resistance to debris, especially in environments prone to clogging. Additionally, regular training for operational staff on how to respond to alerts from the flow sensor can further mitigate risks, ensuring that any leaks are promptly addressed before they can cause significant damage.
Scenario 3: Enhancing System Control and Automation
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the complexity of managing large irrigation systems, especially when attempting to implement automated controls that can adapt to varying environmental conditions. Without a master valve, maintaining optimal irrigation levels can be inefficient and labor-intensive, leading to over- or under-watering and negatively impacting crop yield or landscape health.
The Solution: To optimize control and automation, buyers should consider integrating a master valve with advanced irrigation controllers capable of real-time data analysis. When sourcing a master valve, it is essential to ensure compatibility with smart irrigation technology, such as weather sensors and soil moisture detectors. This integration allows the master valve to respond dynamically, opening or closing based on immediate water needs rather than relying solely on preset schedules. Additionally, regular updates and software training for the team can enhance the effectiveness of this system, ensuring that they can adapt quickly to changing conditions and maintain efficient water use across the entire property.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for irrigation system master valve
What Are the Common Materials Used for Irrigation System Master Valves?
When selecting materials for irrigation system master valves, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material affects performance, durability, and overall system efficiency. Below, we analyze four common materials used in master valves: brass, plastic (PVC), glass-filled nylon, and stainless steel.
How Does Brass Perform as a Material for Master Valves?
Brass is a popular choice for irrigation system master valves due to its excellent mechanical properties. It has a high temperature and pressure rating, making it suitable for various applications. Brass is also highly resistant to corrosion, especially in environments with fluctuating pH levels.
Pros: Brass valves are durable and can withstand high pressures, making them ideal for large-scale irrigation systems. They also have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance.
Cons: The primary drawback of brass is its higher cost compared to plastic alternatives. Additionally, brass valves can be heavier, which may complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with both potable and non-potable water, making it versatile for different irrigation needs. However, brass may not be suitable for systems using reclaimed water due to potential leaching.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or JIS, particularly concerning drinking water safety.
What Are the Advantages of Plastic (PVC) in Master Valve Applications?
Plastic, particularly PVC, is another common material for irrigation master valves. PVC is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and has a good pressure rating, although it is lower than brass.
Pros: The main advantages of PVC include its low cost and ease of installation. PVC valves are also resistant to many chemicals, making them suitable for various irrigation applications.
Cons: PVC has a lower temperature tolerance and can become brittle over time, especially when exposed to UV light. This can lead to failures in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: PVC valves are generally suitable for non-potable water systems but may not be the best choice for applications involving hot water or high-pressure scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the PVC used meets local standards. In regions like the Middle East, where UV exposure is high, selecting UV-resistant PVC is critical.
How Does Glass-Filled Nylon Compare for Master Valves?
Glass-filled nylon is a composite material known for its strength and durability. It offers a good balance of mechanical properties and is resistant to corrosion and chemicals.
Pros: Glass-filled nylon is lightweight and has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it easy to handle and install. It also performs well under varying temperatures and pressures.
Cons: While it is durable, glass-filled nylon can be more expensive than standard plastic options. Its performance can also be affected by extreme temperatures, leading to potential brittleness.
Impact on Application: This material is suitable for both potable and non-potable water systems, making it versatile. However, it may not be the best choice for applications with high thermal loads.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers in Europe, compliance with standards such as EN or ISO is essential, particularly for potable water applications.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Master Valves?
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, making it an ideal choice for harsh environments. It has a high pressure and temperature rating, suitable for demanding irrigation systems.
Pros: Stainless steel valves are incredibly robust and have a long lifespan, making them a worthwhile investment for large-scale systems. They also offer excellent compatibility with various media.
Cons: The main drawback is the high cost of stainless steel compared to other materials. Additionally, its weight can pose challenges during installation.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is highly versatile and can be used in both potable and non-potable systems. It is particularly beneficial in regions with aggressive water chemistry.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel used complies with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, particularly for food-grade applications.
Summary Table of Material Properties for Irrigation System Master Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for irrigation system master valve | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | High-pressure irrigation systems | Excellent durability and pressure rating | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Plastic (PVC) | Non-potable irrigation systems | Low cost and easy installation | Lower temperature tolerance | Low |
| Glass-Filled Nylon | Versatile irrigation applications | Lightweight with good strength | More expensive than standard plastic | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environmental conditions | Exceptional corrosion resistance | High cost and weight | High |
This material selection guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions when sourcing irrigation system master valves, ensuring compatibility with local standards and specific application requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for irrigation system master valve
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Irrigation System Master Valves?
The manufacturing of irrigation system master valves involves a series of well-defined stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets the necessary performance and reliability standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The selection of raw materials is crucial in the manufacturing process. Master valves are commonly made from materials such as glass-filled nylon, various plastics, or metals like brass or stainless steel. Depending on the intended application, manufacturers must choose materials that offer durability, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with reclaimed water systems.
Once selected, the materials undergo preparation, which may include cutting, machining, and treatment processes to ensure they are suitable for forming. For example, metal components may be coated to prevent rust, while plastic parts may be treated to enhance their UV resistance.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape the Components?
During the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into the various components of the master valve. This can involve several techniques, including injection molding for plastic parts and machining for metal components.
Injection molding is particularly effective for producing complex shapes with high precision and can accommodate features such as threads and grooves that are essential for valve assembly. For metal components, CNC machining is often employed to achieve exact tolerances, ensuring that parts fit together seamlessly.
Assembly: How Are the Components Put Together?
The assembly of master valves is a meticulous process that requires skilled labor and adherence to strict protocols. Components are brought together in a controlled environment, often using automated machinery for precision.
Key assembly tasks include fitting solenoids, seals, and other internal mechanisms. Proper alignment is crucial to prevent leaks and ensure the valve operates efficiently. Quality checks during assembly, such as visual inspections and functional tests, are vital to catch any potential defects before moving on to the finishing stage.
Finishing: What Processes Ensure the Valves Meet Quality Standards?
The finishing stage involves treating the assembled master valves to enhance their performance and durability. This may include surface treatments like powder coating or anodizing for metal parts, which improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Final inspections are conducted to ensure that each valve meets design specifications and quality standards. This stage is critical, as it directly impacts the longevity and reliability of the valves in the field.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Master Valve Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of irrigation system master valves. Implementing robust QA practices ensures that the final product not only meets international standards but also satisfies the specific needs of B2B buyers.
Which International Standards Are Relevant to Master Valve Manufacturing?
Manufacturers of irrigation system master valves must comply with various international standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. This certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply depending on the intended use of the valves. CE certification is particularly important for products sold in Europe, ensuring compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at critical stages of the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early. The three main QC checkpoints include:
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. Materials that do not pass IQC are rejected and returned to the supplier.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the quality of components as they are formed and assembled. This includes dimensional checks and functional tests to ensure components meet design specifications.
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the finished master valves. This may include pressure testing, leak testing, and functional performance assessments to verify that each valve operates as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensure reliability and performance. Here are several actionable steps buyers can take:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a proactive way to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers should request access to the supplier’s quality management system documentation, including their ISO certifications and internal QC procedures. On-site audits can further provide insights into the manufacturing environment and practices.
How Can Buyers Use Quality Reports and Certifications to Assess Suppliers?
Buyers should require suppliers to provide quality reports that detail the results of inspections and tests performed throughout the manufacturing process. These reports can include data on compliance with international standards and any third-party inspection results.
Certifications from recognized bodies can also serve as a reliable indicator of a supplier’s commitment to quality. Buyers should verify the validity of these certifications with the issuing organizations.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Ensuring Quality?
Third-party inspections can provide an unbiased assessment of a manufacturer’s quality control practices. Engaging a reputable third-party inspection service can help buyers identify potential issues before products are shipped. This can be particularly beneficial in international transactions, where buyers may not have the ability to conduct on-site inspections themselves.
How Do Quality Control Nuances Affect International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Different regions may have varying regulations and standards that affect the manufacturing and quality assurance of irrigation system master valves.
What Should Buyers Know About Regional Standards and Compliance?
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should familiarize themselves with local regulations that may impact their procurement process. For instance, some countries may require additional certifications for products that come into contact with water sources.
How Can Buyers Navigate Certification Differences Across Regions?
Navigating certification differences requires thorough research and potentially the assistance of local experts. Buyers should engage with suppliers who have a clear understanding of the certifications required in their specific market, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of regulatory issues.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for irrigation system master valves, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that contribute to the success and sustainability of their irrigation projects.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘irrigation system master valve’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure an irrigation system master valve. A master valve is a critical component that enhances water management efficiency and protects infrastructure, making its selection and installation vital for sustainable irrigation practices. This guide will help you navigate the procurement process with clear, actionable steps.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Consider factors such as the type of irrigation system, flow rates, and pressure requirements. Additionally, determine the valve size needed for your application, which can range from 1 to 8 inches (25 to 200 mm), ensuring compatibility with existing systems.
Step 2: Research Material Options
Choosing the right material for your master valve is essential for durability and performance. Common materials include glass-filled nylon, plastic, and metal. Assess the environmental conditions in your region—such as temperature variations and exposure to chemicals—to select a material that will withstand the specific stresses of your application.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in providing quality irrigation components, as well as those who understand the unique challenges of your market.
- Supplier Certifications: Verify that suppliers meet international standards for quality and safety.
- Warranty and Support: Inquire about warranty terms and post-purchase support to ensure long-term satisfaction.
Step 4: Assess Additional Features
Consider any additional features that could enhance your master valve’s performance. For instance, options such as pressure regulation, debris tolerance, and reclaimed water compatibility can significantly improve efficiency and longevity. These features are particularly important in regions prone to sediment or contaminants in the water supply.
Step 5: Inquire About Integration Capabilities
Ensure that the master valve you choose is compatible with existing irrigation controllers and flow sensors. Compatibility is crucial for effective system automation and monitoring. Discuss integration options with suppliers to confirm that the master valve can work seamlessly within your current setup.
Step 6: Request Sample Testing
Before finalizing your purchase, request samples for testing in real-world conditions. This will allow you to evaluate the valve’s performance under your specific operational parameters. Ensure that the valve meets your expectations regarding functionality, durability, and ease of installation.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase Agreements
Once you have identified the right supplier and product, finalize your purchase agreement. Pay attention to terms related to delivery schedules, payment options, and after-sales service. Clear agreements help mitigate risks and set the stage for a successful partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions in sourcing irrigation system master valves, ensuring optimal performance and sustainability for their irrigation systems.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for irrigation system master valve Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Irrigation System Master Valves?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing irrigation system master valves, several components must be considered. The primary cost elements include:
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts pricing. Common materials such as glass-filled nylon, plastic, and metal each come with different cost implications. Metal valves, for example, tend to be more expensive due to their durability and longevity.
Labor: Labor costs encompass both the manufacturing process and installation. Skilled labor is necessary for precise installation, particularly in complex systems, which can elevate overall costs.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. The efficiency of the manufacturing process can help reduce these overhead costs.
Tooling: Specialized tools required for the production of master valves may involve significant upfront investments. The complexity of the valve design can increase tooling costs.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that master valves meet industry standards requires a robust quality control process. This is crucial for maintaining reliability, especially in regions prone to extreme weather conditions.
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary dramatically based on the origin and destination of the valves. This is particularly relevant for international buyers, as tariffs and customs duties may also apply.
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up the price to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the margin is essential for assessing the final price.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Master Valves?
Several factors can influence the pricing of irrigation system master valves:
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounted rates. Suppliers are more inclined to negotiate prices for larger orders, which can significantly reduce the per-unit cost.
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or unique specifications may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected expenses.
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or NSF) can increase costs but may also enhance performance and reliability, which is crucial for long-term usage.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their proven track record and quality assurance processes.
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can affect overall costs by determining who bears responsibility for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage their total costs effectively.
What Are the Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Master Valves?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of pricing can lead to significant savings:
Negotiation: Always be prepared to negotiate prices. Suppliers often have some flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with installation, maintenance, and potential replacements. A more expensive valve may offer greater durability and lower maintenance costs, leading to overall savings.
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Factor in additional costs such as shipping, customs duties, and potential tariffs. Understanding these can help you make more informed purchasing decisions.
Supplier Relationships: Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, exclusive offers, and priority service, which can be invaluable in urgent situations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for irrigation system master valves can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs. Always consider the total cost implications, including long-term operational costs, to achieve the best value.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing irrigation system master valve With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Irrigation System Master Valve
When considering irrigation solutions, it’s essential to evaluate various options available in the market. While an irrigation system master valve is a popular choice for controlling water flow and preventing leaks, alternative solutions may offer distinct advantages depending on specific needs and circumstances. This analysis will compare the irrigation system master valve with two viable alternatives: pressure-regulating valves and smart irrigation controllers.
| Comparison Aspect | Irrigation System Master Valve | Pressure-Regulating Valve | Smart Irrigation Controller |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High; prevents leaks, ensures efficient irrigation | Moderate; maintains constant pressure, but does not prevent leaks | High; optimizes water usage based on real-time data |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, potential long-term savings | Lower initial cost, but may require additional equipment | Higher initial cost, but can lead to significant water savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires proper installation and wiring | Easier to install; typically requires less technical knowledge | More complex; may need professional installation |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed to prevent sticking | Minimal; routine pressure checks recommended | Regular updates and checks required for optimal performance |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale systems needing robust control and leak prevention | Smaller systems where pressure control is paramount | Systems where water conservation and automation are prioritized |
In-Depth Look at Alternatives
Pressure-Regulating Valve (PRV)
Pressure-regulating valves are designed to maintain a consistent pressure level throughout the irrigation system. They are particularly beneficial in areas where fluctuations in water pressure can lead to inefficient irrigation or system damage. The primary advantage of PRVs is their lower initial cost and simpler installation compared to master valves. However, they do not prevent leaks; if a pipe fails or a valve sticks, water may continue to flow, leading to potential wastage. PRVs are best suited for smaller irrigation systems where pressure management is critical.
Smart Irrigation Controller
Smart irrigation controllers represent a high-tech alternative that optimizes water usage based on real-time data, such as weather conditions and soil moisture levels. These systems can significantly reduce water waste and improve overall irrigation efficiency. While the upfront cost of smart controllers can be higher than that of a master valve, they often provide substantial long-term savings through enhanced water management. However, they may require professional installation and regular software updates to function effectively. Smart controllers are ideal for environmentally conscious operations looking to maximize efficiency and sustainability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Irrigation Needs
When selecting the right irrigation solution, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the scale of the operation, budget constraints, and specific irrigation goals. The irrigation system master valve offers robust leak prevention and control, making it suitable for larger systems. In contrast, pressure-regulating valves may serve effectively in smaller setups, while smart irrigation controllers provide advanced water management capabilities for those prioritizing sustainability. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on the unique requirements and conditions of the irrigation project at hand. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for irrigation system master valve
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of an Irrigation System Master Valve?
Understanding the essential technical properties of a master valve is crucial for B2B buyers involved in irrigation system procurement. Here are some of the most critical specifications that impact performance and reliability:
1. Material Composition
Master valves are typically made from materials such as glass-filled nylon, plastic, or metal. The choice of material affects durability, resistance to corrosion, and overall lifespan. For instance, metal valves offer enhanced strength and longevity, making them suitable for high-pressure applications, while plastic options may be more cost-effective for smaller systems. Choosing the right material is vital for ensuring the valve can withstand environmental conditions and operational demands.
2. Size and Flow Rate Capacity
Master valves come in various sizes, typically ranging from 1 to 8 inches (25 to 200 mm). The size directly correlates with the flow rate capacity, which is essential for meeting the irrigation requirements of different agricultural or landscaping applications. When selecting a valve, it’s important to consider the expected flow rates to ensure efficient water management and prevent system overload.
3. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the valve can handle without failure. A higher pressure rating is essential for systems that operate under significant pressure, as it ensures reliability and safety. Understanding the pressure requirements of your irrigation system will help in selecting a master valve that can endure operational stresses, thus reducing the risk of leaks or ruptures.
4. Operational Type: Normally Open vs. Normally Closed
Master valves can be categorized into normally open (NOMV) and normally closed (NCMV) types. NOMVs remain open unless activated, allowing continuous access to pressurized water, which can be beneficial for mixed-use systems. Conversely, NCMVs isolate the mainline until irrigation is required, providing better protection against leaks and system failures. The choice between these types should align with the operational needs and safety considerations of the irrigation system.
5. Debris Tolerance and Maintenance Features
Valves with enhanced debris tolerance are designed to minimize clogging and operational issues, particularly in systems that utilize reclaimed water or are exposed to dirt and contaminants. Features such as easy access for maintenance and self-cleaning capabilities can significantly reduce downtime and operational costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Irrigation System Master Valves?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiations with suppliers. Here are some key terms relevant to the procurement of irrigation system master valves:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can be crucial for buyers seeking quality components that meet specific performance standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it can impact inventory management and purchasing strategies, particularly for international transactions.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. For irrigation system components like master valves, an RFQ can help buyers compare prices and features from various vendors, ensuring they get the best value.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and freight. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers engaging in international procurement, as they define who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk.
5. Flow Sensor
A flow sensor is a device that monitors the flow of water through the irrigation system. Coupled with a master valve, it can detect issues such as leaks, allowing for immediate action to minimize water loss and damage. Familiarity with flow sensors and their integration can enhance the efficiency of irrigation systems.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when procuring irrigation system master valves, ensuring they select the right components for their specific needs and operational goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the irrigation system master valve Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Irrigation System Master Valve Sector?
The global irrigation system master valve market is witnessing a transformative shift driven by several key factors. The increasing demand for efficient water management solutions in agriculture, particularly in water-scarce regions such as Africa and the Middle East, is propelling the market forward. As urbanization accelerates and climate change exacerbates water scarcity, B2B buyers are prioritizing advanced irrigation technologies that ensure optimal water usage. This trend is particularly pronounced in emerging markets like Nigeria and Brazil, where agricultural productivity is critical to food security.
Technological advancements are also reshaping sourcing strategies. Smart irrigation systems, which integrate master valves with flow sensors and automated controllers, are becoming standard. These innovations not only enhance system efficiency but also enable real-time monitoring and diagnostics, reducing water waste significantly. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer these advanced features and demonstrate compatibility with existing systems.
Furthermore, the market is seeing a shift towards localized manufacturing and sourcing. International buyers are increasingly interested in suppliers who can provide timely deliveries and adapt products to regional needs. This trend is particularly beneficial for buyers in South America and Africa, where logistical challenges can impact the supply chain. Consequently, partnerships with local manufacturers or distributors can enhance reliability and reduce costs, making this an essential consideration for B2B buyers.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Irrigation System Master Valve Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount in the irrigation system master valve sector. The environmental impact of irrigation practices is under scrutiny, and stakeholders are increasingly focused on reducing water waste and promoting sustainable water management. Master valves, by design, minimize leaks and control water flow, contributing to water conservation efforts. B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through their product offerings and practices.
Ethical supply chains are also becoming essential. Buyers must ensure that the materials used in master valves are sourced responsibly. This includes looking for certifications that indicate adherence to environmental standards, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications for recycled materials. Utilizing eco-friendly materials not only supports sustainability goals but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible products.
Moreover, the integration of sustainable practices can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. Companies that transparently communicate their commitment to sustainability are more likely to attract and retain customers, particularly in regions where environmental awareness is rising. As such, B2B buyers should seek partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize ethical sourcing and sustainability in their operations.
What Is the Evolution of the Irrigation System Master Valve and Its Relevance Today?
The evolution of the irrigation system master valve reflects broader advancements in irrigation technology. Initially, master valves were rudimentary components with limited functionality, primarily serving to control water flow. However, with the advent of automation and smart technology, today’s master valves are sophisticated devices that integrate seamlessly with advanced irrigation systems.
Historically, the development of master valves has paralleled the growing understanding of water management and conservation. As agricultural practices evolved, so did the need for more efficient irrigation solutions. The introduction of automated controllers and flow sensors has transformed master valves into critical components for managing water resources intelligently.
Today, the relevance of master valves extends beyond mere flow control; they are essential for sustainable agricultural practices and effective water management. As global water challenges intensify, the role of master valves in preventing leaks, conserving resources, and ensuring system integrity will only become more vital. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial in making informed decisions about sourcing and investing in irrigation technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of irrigation system master valve
How do I solve leaks in my irrigation system due to valve failure?
To address leaks caused by valve failure, consider installing a master valve that automatically shuts off the water supply when the system isn’t in use. This prevents continuous water flow, significantly reducing the risk of leaks going unnoticed. Regular maintenance and inspections of your master valve and associated components, such as solenoids and seals, can help identify potential issues early. If leaks persist, a flow sensor can be integrated to detect anomalies, allowing for real-time responses to water loss and minimizing damage.What is the best type of master valve for commercial irrigation systems?
For commercial irrigation systems, a normally closed master valve (NCMV) is often the best choice. This type ensures that the mainline remains isolated until the irrigation controller activates it, providing enhanced safety and efficiency. An NCMV minimizes the risk of water waste from leaks and protects the system during emergencies, such as power outages. Additionally, consider valves made from durable materials like metal or glass-filled nylon for longevity and reliability in demanding environments.How can I ensure the quality of the master valves I purchase internationally?
To ensure quality when sourcing master valves internationally, start by vetting suppliers through thorough research. Look for manufacturers with industry certifications and a history of compliance with international quality standards. Request product samples and detailed specifications to assess the materials and performance. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can also clarify their manufacturing processes, quality assurance protocols, and customer service support, helping you make an informed decision.What customization options are available for irrigation master valves?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for irrigation master valves to meet specific project needs. Customization can include valve sizes, materials, pressure ratings, and additional features like built-in flow sensors or pressure regulation. When discussing customization with suppliers, be clear about your requirements and project conditions. This dialogue can lead to tailored solutions that enhance system efficiency and longevity, ultimately resulting in better performance in diverse environmental conditions.What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for irrigation master valves?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for irrigation master valves can vary significantly by supplier and region. Typically, MOQs range from a few units to several hundred, depending on the manufacturer’s production capabilities and inventory policies. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about MOQs and explore options for smaller initial orders or trial purchases. This flexibility can facilitate risk management, especially for businesses looking to test product performance before committing to larger orders.What payment terms are common for international purchases of master valves?
Common payment terms for international purchases of master valves include options such as letters of credit, advance payments, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers prefer a 30% deposit upfront, with the remaining balance due upon shipment or receipt. It is essential to discuss and agree on payment terms in advance to ensure clarity and avoid potential disputes. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods to protect your financial interests during international transactions.How can I manage logistics for shipping master valves internationally?
Effective logistics management for shipping master valves internationally involves several key steps. First, collaborate closely with your supplier to understand packaging requirements and shipping timelines. Utilize reliable freight forwarders experienced in handling industrial equipment to navigate customs regulations and shipping documentation. Additionally, consider insurance options to protect your investment during transit. Establishing a clear communication line with all parties involved will help address any potential issues swiftly and ensure timely delivery.What are the best practices for maintaining irrigation master valves?
Maintaining irrigation master valves is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Regular inspections should include checking for leaks, ensuring the solenoid operates correctly, and testing the valve’s responsiveness to the controller. Cleaning the valve and its components can prevent debris buildup that may hinder operation. Additionally, seasonal maintenance, especially before high-demand periods, will help identify any potential issues early. Keeping a maintenance log can also assist in tracking performance and scheduling necessary repairs or replacements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
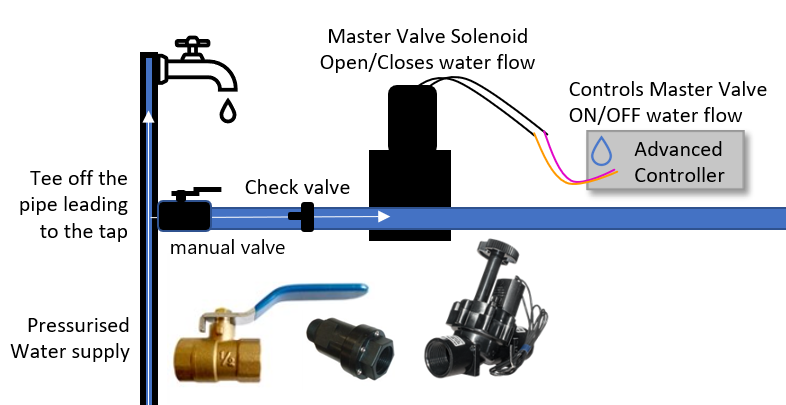
Top 10 Irrigation System Master Valve Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sprinkler Warehouse – Irrigation Master Valve
Domain: school.sprinklerwarehouse.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: An irrigation master valve is an electric valve installed at the supply point that controls water flow into the main piping system. It prevents water supply to the irrigation system when closed, reducing water loss from leaky station valves and allowing for mainline repairs without shutting off the water supply. Typically, it is the same type of valve used for station valves but is installed upstr…
2. Reddit – Master Valves in Irrigation Systems
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Master valves are debated in terms of their utility in irrigation systems. Some users suggest that while master valves can prevent prolonged leaks and damage from mainline breaks, they can also mask smaller leaks that go unnoticed for extended periods. They are recommended in systems that irrigate slopes or areas prone to washouts, but may not be necessary if a monitoring system is in place. High-…
3. Seattle Landscapes – Master Valve
Domain: seattlelandscapes.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: A Master Valve is an automatic valve installed on the main line of an irrigation system, usually just after the backflow preventer. It opens only when an irrigation zone is actively running and closes when the system is off, minimizing the risk of leaks and water waste. Key benefits include preventing water waste, protecting property from unnoticed irrigation leaks, adding system control and autom…
4. Superior – Master Valve 3200 Brass
Domain: sprinklersupplystore.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: {‘product_name’: ‘Superior Master Valve 3200 Brass Normally Closed FIPT x FIPT’, ‘brand’: ‘Superior’, ‘original_price’: ‘$217.15’, ‘current_price’: ‘$162.86’, ‘sku’: ‘3200100’, ‘sizes’: [{‘size’: ‘1 in’, ‘type’: ‘Standard Valve’, ‘price’: ‘$162.86’}, {‘size’: ‘1 in’, ‘type’: ‘Non-Potable (Purple Handle)’, ‘price’: ‘$169.95’}, {‘size’: ‘1-1/2 in’, ‘type’: ‘Standard Valve’, ‘price’: ‘$538.62’}, {‘si…
5. Hunter – Master Valve
Domain: thelawnforum.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Master Valve: An electric valve used in irrigation systems to control water flow. Benefits include preventing massive water leaks by keeping lines uncharged when not in use. Installation costs vary, with mentions of $90 for the Hunter master valve and additional costs for flow meters and wiring. Flow meters can provide leak detection alerts when water usage exceeds normal levels.
6. U.S. Solid – Motorized Ball Valve 1 Brass
Domain: community.rachio.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Motorized Ball Valve- 1″ Brass Ball Valve with Standard Port, 9-24V DC and 2 Wire Reverse Polarity by U.S. Solid
7. Irrigation Tutorials – Master Valve Guide
Domain: irrigationtutorials.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: A master valve is an automatic electric solenoid valve installed at the connection point of the irrigation system to the water supply. It is wired to a master valve circuit on the irrigation controller, which turns the valve on and off. The master valve acts as a fail-safe, shutting off water to the irrigation system when no zone valves are operating. Benefits include minimizing water loss from le…
8. Lawnsite – Master Control Valve
Domain: lawnsite.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Master Control Valve; Purpose: Shuts down the entire sprinkler system and conserves water; Types: Automatic valve and gate valve; Compatibility: Can be wired into a controller (e.g., Hunter Pro-C); Functionality: Opens each time a zone valve is activated; Installation: Recommended to be placed where the main line is tapped; Example Products: 1″ Rain Bird PEB as a master valve, 1″ Hunter PGV valves…
9. OpenSprinkler – OpenSprinkler Pi
Domain: opensprinkler.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: OpenSprinkler Pi (OSPi) allows for the use of multiple master valves, enabling users to manage different water sources (e.g., city water and pump water) for irrigation zones. Users can configure master valves to operate independently or in conjunction with specific zones, enhancing automation and flexibility in irrigation management. The firmware supports features like parallel stations, allowing …
10. Hunter – X2 Master Valve
Domain: hunterirrigation.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: The X2 master valve is a normally closed valve installed at the supply point of the main line in an irrigation system. It opens only when the controller initiates a watering program and shuts off water to the irrigation system when none of the zone valves are operating. To connect the master valve, attach the common wire to either of the two solenoid wires (red wires) of the valve, and a separate …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for irrigation system master valve
As the global demand for efficient irrigation systems continues to rise, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the strategic sourcing of master valves has become increasingly vital. These components not only enhance water conservation efforts by minimizing leaks and waste but also protect property from potential damage caused by irrigation failures. By investing in high-quality master valves, businesses can ensure reliable performance and long-term sustainability in their irrigation practices.
International buyers should prioritize sourcing valves that meet specific operational needs, including size, material durability, and compatibility with existing systems. Features like flow sensors and pressure regulation can further optimize water management and promote eco-friendly practices.
Looking ahead, the integration of smart technology within irrigation systems presents a significant opportunity for enhanced control and efficiency. By leveraging these advancements, businesses can not only improve their operational effectiveness but also align with global sustainability goals. Now is the time to engage with trusted suppliers and invest in master valves that will support your irrigation strategy for years to come. Take the next step towards a more efficient irrigation system today.