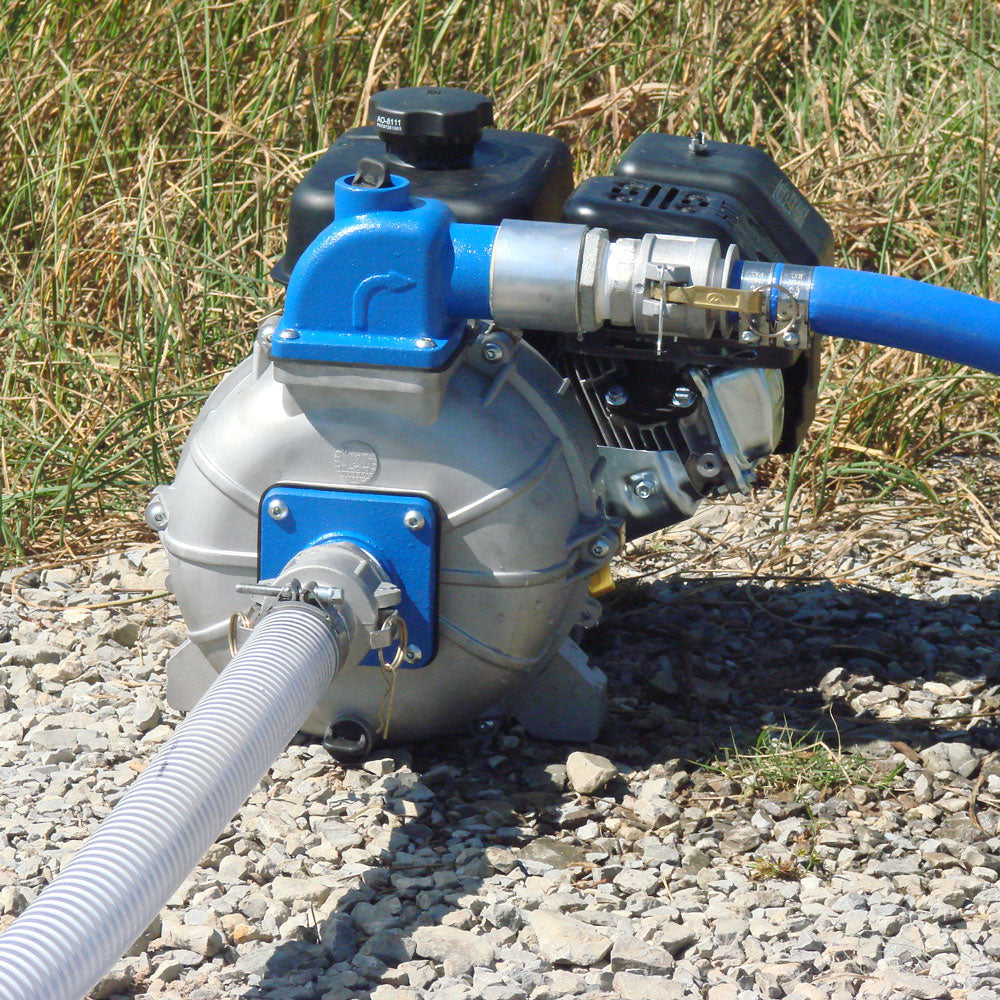
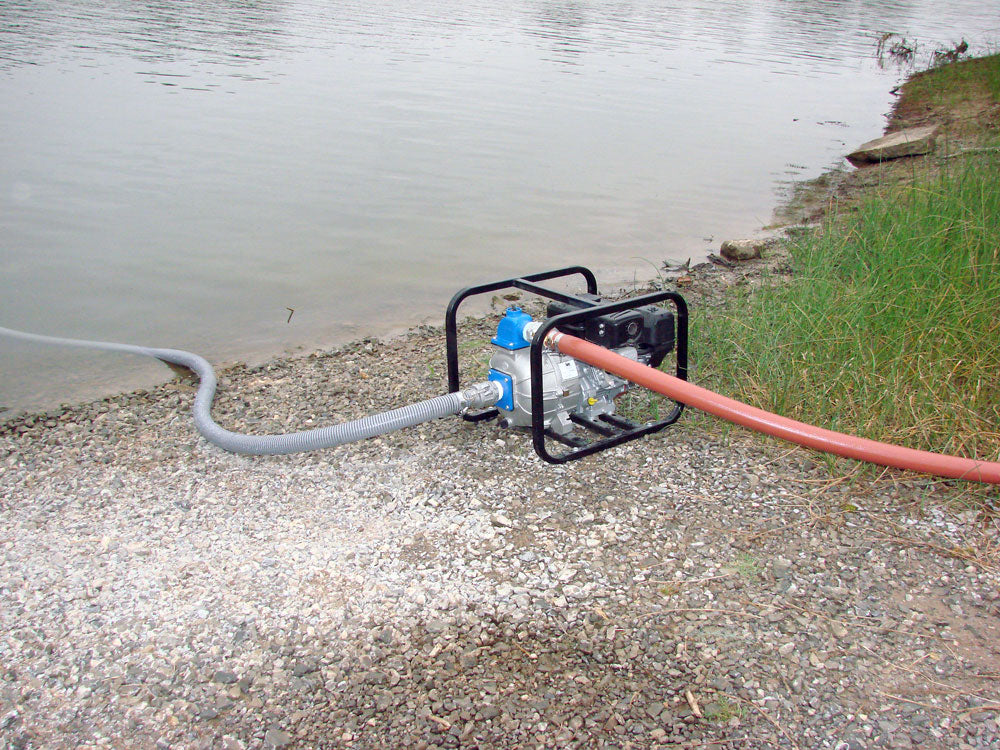
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for self priming irrigation pump
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing self-priming irrigation pumps poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Factors such as varying environmental conditions, fluctuating market prices, and diverse application requirements complicate the purchasing process. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of the global market for self-priming irrigation pumps, providing valuable insights into their types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
As irrigation plays a crucial role in agricultural productivity, understanding the nuances of self-priming pumps is essential for optimizing water management and achieving sustainable farming practices. This comprehensive resource empowers buyers by equipping them with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions. From identifying the right pump specifications for specific agricultural needs to evaluating supplier reliability and pricing strategies, the guide serves as a roadmap for successful procurement.
With a focus on the unique demands of international markets, this guide not only highlights the technical aspects of self-priming irrigation pumps but also addresses the broader implications of sourcing strategies. By leveraging this knowledge, B2B buyers can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately drive growth in their respective markets.
Understanding self priming irrigation pump Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Centrifugal Pumps | Powered by electricity; efficient for continuous use | Agricultural irrigation, landscape watering | Pros: High efficiency, low maintenance. Cons: Requires electrical infrastructure. |
| Cast Iron Self-Priming Pumps | Durable construction; ideal for high-pressure applications | Industrial irrigation, commercial landscapes | Pros: Robust and long-lasting. Cons: Heavier, may require more installation effort. |
| Thermoplastic Self-Priming Pumps | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant; suitable for various fluids | Residential gardening, light commercial use | Pros: Portable, resistant to chemicals. Cons: Lower pressure capabilities than metal pumps. |
| Multi-Stage Self-Priming Pumps | Multiple impellers for higher pressure and flow rates | Large-scale agricultural applications | Pros: High efficiency and performance. Cons: More complex, potentially higher maintenance costs. |
| Portable Self-Priming Pumps | Compact and easy to transport; suitable for temporary setups | Emergency irrigation, construction sites | Pros: Versatile and user-friendly. Cons: Limited capacity and durability compared to fixed installations. |
What Are Electric Centrifugal Pumps and Their B2B Suitability?
Electric centrifugal pumps are designed for efficiency and continuous operation. They are commonly used in agricultural irrigation systems and landscape watering, where consistent water supply is critical. B2B buyers should consider their energy source and electrical infrastructure, as these pumps require a stable power supply. Their low maintenance needs make them an attractive option for businesses looking to minimize operational costs.
How Do Cast Iron Self-Priming Pumps Stand Out?
Cast iron self-priming pumps are known for their durability and ability to handle high-pressure applications. They are particularly suitable for industrial irrigation and commercial landscape projects, where robust equipment is essential. While these pumps offer long-lasting performance, their heavier weight may increase installation complexity. Buyers should assess their specific pressure requirements and installation capabilities when considering these pumps.
What Advantages Do Thermoplastic Self-Priming Pumps Offer?
Thermoplastic self-priming pumps are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for various fluids, including water and chemicals. They are often used in residential gardening and light commercial applications due to their portability and ease of use. However, these pumps may not provide the same pressure capabilities as metal alternatives, so B2B buyers should evaluate their specific application needs before making a purchase.
Why Choose Multi-Stage Self-Priming Pumps for Large-Scale Applications?
Multi-stage self-priming pumps utilize multiple impellers to achieve higher pressure and flow rates, making them suitable for large-scale agricultural applications. Their high efficiency can lead to significant energy savings, but the complexity of these pumps may result in higher maintenance costs. Buyers should consider the scale of their irrigation needs and the potential for increased efficiency when selecting this type of pump.
What Makes Portable Self-Priming Pumps Ideal for Temporary Setups?
Portable self-priming pumps are compact and easy to transport, making them ideal for temporary irrigation setups, such as emergency situations or construction sites. While they offer versatility and user-friendliness, their capacity and durability may be limited compared to fixed installations. B2B buyers should weigh the need for portability against the required performance levels for their specific projects.
Key Industrial Applications of self priming irrigation pump
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Self Priming Irrigation Pump | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Crop irrigation systems for large-scale farms | Efficient water delivery leads to higher crop yields | Assess pump capacity, energy efficiency, and durability |
| Horticulture | Greenhouse irrigation and misting systems | Optimizes plant growth and reduces water waste | Consider pump size, material compatibility, and maintenance needs |
| Landscaping | Landscape irrigation for commercial properties | Enhances property aesthetics and increases property value | Evaluate flow rates, pressure requirements, and installation ease |
| Mining and Construction | Dust suppression and water supply for mining operations | Reduces dust-related health risks and operational downtime | Ensure pump reliability, ruggedness, and adaptability to terrain |
| Municipal Water Supply | Water supply augmentation in urban areas | Supports water distribution efficiency and sustainability | Look for compliance with local regulations and energy consumption |
How Are Self Priming Irrigation Pumps Used in Agriculture?
In agriculture, self priming irrigation pumps are crucial for crop irrigation systems on large-scale farms. These pumps draw water from wells or reservoirs, ensuring a steady flow to irrigation lines. By providing efficient water delivery, they significantly enhance crop yields, especially in regions with variable rainfall, such as parts of Africa and South America. Buyers in this sector should focus on assessing pump capacity, energy efficiency, and durability to ensure long-term operational success.
What Role Do Self Priming Pumps Play in Horticulture?
In horticulture, self priming irrigation pumps facilitate the irrigation and misting systems essential for greenhouse operations. These pumps ensure consistent water delivery, optimizing plant growth while minimizing water waste. This is particularly important in areas like the Middle East, where water scarcity is a pressing issue. Buyers should consider pump size, material compatibility, and maintenance needs to guarantee the system’s efficiency and longevity.
How Are Self Priming Pumps Beneficial for Landscaping?
For landscaping projects, self priming irrigation pumps are used to supply water for irrigation systems in commercial properties. These pumps enhance the aesthetics of the landscape while increasing property value through consistent and efficient watering. In Europe, where urban landscaping is increasingly emphasized, businesses must evaluate flow rates, pressure requirements, and ease of installation when sourcing these pumps to meet specific landscape needs.
Why Are Self Priming Pumps Important in Mining and Construction?
In the mining and construction sectors, self priming irrigation pumps serve dual purposes: dust suppression and water supply. These pumps help mitigate dust-related health risks and minimize operational downtime by ensuring a reliable water source. In rugged terrains, especially prevalent in regions like Brazil, buyers should ensure that the pumps are reliable, rugged, and adaptable to various environmental conditions.
How Do Self Priming Pumps Support Municipal Water Supply Systems?
Municipal water supply systems utilize self priming irrigation pumps to augment water supply in urban areas, particularly during peak demand periods. These pumps enhance water distribution efficiency and support sustainability initiatives in cities across Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should prioritize compliance with local regulations and energy consumption efficiency when sourcing pumps for municipal applications, ensuring they meet both operational and regulatory requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘self priming irrigation pump’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Consistent Priming
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in regions with variable water table levels face the challenge of inconsistent priming with self-priming irrigation pumps. This can lead to significant downtime, crop damage, and increased operational costs. For instance, a buyer in Brazil may find that during the dry season, the pump fails to prime correctly, resulting in inadequate water supply for irrigation and jeopardizing crop yields.
The Solution: To address this issue, it’s essential to choose a self-priming pump with a proven capability to handle varying water levels. When sourcing pumps, look for models specifically designed for high suction lift capabilities, ideally with adjustable priming settings. Additionally, consider investing in a pump with a robust impeller design that can handle debris or sediment, which is often an issue in agricultural settings. Regular maintenance checks are also crucial; ensure that the pump’s priming chamber is clean and free of air leaks, which can affect performance. Implementing a scheduled maintenance plan can help in maintaining optimal performance throughout different seasons.
Scenario 2: Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs
The Problem: Buyers are increasingly concerned about the operational costs associated with self-priming irrigation pumps, particularly regarding energy consumption. In regions such as the Middle East, where energy costs can be substantial, the inefficiency of pumps can lead to significant financial strain. A pump that consumes too much energy can quickly erode profit margins, making it vital to find energy-efficient solutions.
The Solution: To mitigate these costs, B2B buyers should prioritize the selection of energy-efficient self-priming pumps, ideally those that meet international energy efficiency standards. When evaluating options, consider pumps with variable speed drives (VSDs) that adjust the motor speed based on demand, which can significantly reduce energy consumption. Additionally, sourcing pumps from reputable manufacturers who provide detailed energy performance data and operational cost analyses can help in making informed decisions. Implementing smart irrigation systems that optimize water use can also complement energy-efficient pumps, resulting in reduced operational costs.
Scenario 3: Integration with Existing Irrigation Systems
The Problem: Buyers often struggle with integrating new self-priming irrigation pumps into existing systems. For example, a buyer in South America may find that their current irrigation setup, which includes various pump types and control systems, is incompatible with a new self-priming pump. This can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs due to system modifications or replacements.
The Solution: To ensure seamless integration, it is crucial to assess the compatibility of the new self-priming pump with existing irrigation infrastructure before purchase. Conduct a thorough analysis of the system’s hydraulic requirements, including flow rate and pressure needs, and choose a pump that aligns with these specifications. Consulting with irrigation specialists or engineers can provide valuable insights into the necessary adjustments or additional components needed for integration. Additionally, opting for pumps with flexible installation options and adjustable settings can facilitate easier integration. Training for operational staff on the new system can also enhance efficiency and reduce the risk of errors during the transition period.
By addressing these pain points proactively, B2B buyers can optimize their irrigation systems, ensuring reliability and efficiency in water management.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for self priming irrigation pump
What Are the Key Materials Used in Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
When selecting materials for self-priming irrigation pumps, several factors come into play, including performance characteristics, durability, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these pumps: cast iron, thermoplastic, stainless steel, and fiberglass-reinforced thermoplastic. Each material has distinct properties and implications for performance and suitability in various applications.
How Does Cast Iron Perform in Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
Cast iron is a traditional choice for many irrigation pumps due to its excellent strength and durability. It can withstand high pressure and temperature ratings, making it suitable for various irrigation applications. Cast iron also offers good corrosion resistance when properly coated, which is essential in environments where water quality may vary.
Pros: Cast iron pumps are highly durable and can handle significant wear and tear, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. They are also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials, especially in large-scale operations.
Cons: The weight of cast iron can complicate installation and transportation, especially in remote areas. Additionally, if not properly maintained, cast iron can corrode over time, leading to potential failure.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with a wide range of media, including clean water and some chemical solutions. However, it may not be suitable for highly corrosive substances without appropriate coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, particularly regarding corrosion resistance.
What Advantages Do Thermoplastics Offer for Self-Priming Pumps?
Thermoplastic materials, such as polypropylene and PVC, are increasingly popular in self-priming irrigation pumps. These materials are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for applications involving aggressive chemicals or saline water.
Pros: Thermoplastics are generally less expensive than metals and are easier to mold into complex shapes, reducing manufacturing complexity. They also offer excellent chemical resistance and are lightweight, facilitating easier handling and installation.
Cons: While thermoplastics are resistant to corrosion, they may not withstand high temperatures or pressures as effectively as metals. This can limit their use in certain high-demand applications.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are suitable for applications involving non-potable water and mild chemicals. However, they may not be appropriate for high-temperature or high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that thermoplastic materials meet relevant international standards, particularly in regions with strict regulations on material safety and environmental impact.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and strength, making it a premium choice for self-priming irrigation pumps. It is particularly effective in environments where the pump may be exposed to corrosive substances or extreme conditions.
Pros: Stainless steel offers exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, significantly extending the lifespan of the pump. It also maintains structural integrity under high pressure and temperature.
Cons: The cost of stainless steel is generally higher than that of cast iron or thermoplastics, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, it can be more challenging to machine and fabricate.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel pumps are ideal for applications involving saline water, chemicals, or high-pressure systems. They are often used in agricultural and industrial settings where reliability is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards for food safety and environmental regulations, especially in regions like the Middle East where such standards are strictly enforced.
What Role Does Fiberglass-Reinforced Thermoplastic Play in Pump Design?
Fiberglass-reinforced thermoplastic combines the lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties of thermoplastics with the added strength of fiberglass. This material is particularly useful in applications requiring both durability and resistance to harsh environments.
Pros: This composite material provides excellent strength-to-weight ratios and is resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various irrigation applications. It also allows for more complex designs due to its molding capabilities.
Cons: Fiberglass-reinforced thermoplastic can be more expensive than standard thermoplastics and may require specialized manufacturing processes. Its performance under extreme temperatures may vary based on the specific formulation.
Impact on Application: This material is well-suited for applications involving non-potable water and certain chemicals. However, like other thermoplastics, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the material’s compliance with regional standards and certifications, particularly in Europe, where environmental regulations may dictate material use.
Summary Table of Material Properties
| Material | Typical Use Case for Self-Priming Irrigation Pump | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty agricultural applications | High durability and pressure resistance | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Thermoplastic | Chemical and saline water applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited temperature and pressure tolerance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial and saline water applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Fiberglass-Reinforced Thermoplastic | Various irrigation applications | Strong and lightweight | More expensive and variable performance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for self priming irrigation pump
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
The manufacturing of self-priming irrigation pumps involves several critical stages, ensuring that each component meets rigorous performance standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, such as cast iron, thermoplastic, or stainless steel, chosen for their durability and resistance to corrosion. These materials undergo quality checks upon arrival to ensure they meet the specified standards. Documentation of material certifications is essential for B2B buyers, as it provides insights into the material properties and compliance with relevant standards.
Forming: The selected materials are then shaped into components through various techniques such as casting, machining, and injection molding. For example, cast iron components are typically produced using sand casting, while thermoplastic parts may be manufactured using injection molding processes. This stage requires precision to ensure that components fit together correctly and operate efficiently.
Assembly: After forming, the components are assembled into the final product. This stage often involves the installation of the impeller, motor, and seals. Automated assembly lines may be utilized for high-volume production, while manual assembly may be preferred for custom or low-volume orders. Each assembly line should have designated quality checkpoints to catch any issues early in the process.
Finishing: The last stage includes surface treatments, painting, and final inspections. The finishing process not only enhances aesthetics but also adds protective coatings to prevent corrosion and wear. This is particularly important for pumps that may be exposed to harsh environmental conditions, common in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Self-Priming Irrigation Pump Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that every pump meets international and industry-specific standards. Several key components define an effective quality assurance strategy.
International Standards Compliance: Manufacturers often adhere to ISO 9001 standards, which outline the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards is crucial for B2B buyers, as it indicates a commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, certifications such as CE mark in Europe and API standards for pumps used in oil and gas applications are essential for ensuring that products meet specific safety and performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints: The manufacturing process includes multiple quality control (QC) checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Incoming materials are tested for quality before being used in production. This ensures that only compliant materials enter the manufacturing process.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, samples are regularly taken to verify that components meet specified tolerances and quality standards.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the pumps are assembled, they undergo a final inspection where performance tests, such as pressure tests and flow rate measurements, are conducted to ensure they function as intended.Testing Methods for Quality Assurance: Common testing methods include hydrostatic testing, where pumps are tested for leaks under pressure, and performance testing to ensure they meet flow and pressure specifications. Vibration analysis may also be employed to detect potential mechanical issues before pumps are shipped.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with local regulations.
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing and quality control processes. Buyers should consider both on-site audits and remote assessments, especially for suppliers located in different regions.
Quality Reports and Documentation: Requesting detailed quality reports, including inspection and testing records, can help buyers understand the supplier’s adherence to quality standards. Documentation should include results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing processes and product quality. This is particularly beneficial for buyers who may not have the capacity to perform extensive due diligence themselves.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances that can impact their purchasing decisions.
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulations regarding product safety and performance. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local and international standards applicable to their markets. For instance, pumps exported to Europe must meet CE marking requirements, while those sold in the United States may require compliance with ANSI or UL standards.
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is crucial in establishing trust and ensuring that quality expectations are met. Buyers should be aware of cultural differences that may influence negotiations and quality assurance practices.
Logistical Challenges: Transporting pumps across international borders can introduce challenges such as customs inspections and delays. Buyers should factor in these potential issues when planning their supply chain logistics and ensure that suppliers are prepared to address them.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in self-priming irrigation pump production is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing, implementing robust quality assurance practices, and verifying supplier capabilities, buyers can ensure they source reliable, high-quality pumps that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘self priming irrigation pump’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring self-priming irrigation pumps effectively. Given the diverse applications and the critical role these pumps play in agricultural and landscaping operations, following a structured approach will ensure you make informed decisions that align with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Consider factors such as flow rate (GPM), horsepower (HP), and maximum pressure (PSI) required for your irrigation system. Understanding these parameters will help you identify pumps that meet your operational needs and avoid overspending on unnecessary features.
Step 2: Research Market Options
Conduct thorough market research to identify available models and manufacturers. Utilize online resources, industry publications, and trade shows to gather information about the latest innovations and best practices in self-priming irrigation pumps. Pay attention to the reputation of different brands and their product offerings to ensure you are considering reliable options.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This step helps you assess the supplier’s credibility, reliability, and the quality of their customer service, ensuring they can support your needs beyond the initial purchase.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the self-priming pumps comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. Look for certifications such as ISO, CE, or local regulatory compliance that demonstrate the product’s quality and safety. This verification is essential to mitigate risks associated with substandard products and to ensure that the pumps will function efficiently in your specific environment.
Step 5: Assess Warranty and After-Sales Support
Investigate the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by the supplier. A solid warranty indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in their product, while responsive customer service can be invaluable for troubleshooting and maintenance. Make sure to clarify the terms of service, including parts replacement, repair services, and the availability of technical support.
Step 6: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline the pricing, shipping costs, and payment terms. Comparing these quotes will not only give you a clear understanding of the market pricing but also highlight the value-added services each supplier may offer. Look for transparency in their pricing structures to avoid hidden costs.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Arrange Logistics
After selecting a supplier, finalize your purchase agreement and arrange for logistics. Discuss delivery timelines, installation support, and any specific shipping requirements based on your location. Proper logistics planning ensures that your self-priming irrigation pump arrives on time and is ready for immediate deployment in your operations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for self-priming irrigation pumps, ensuring they make informed and strategic procurement decisions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for self priming irrigation pump Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Self-Priming Irrigation Pump Production?
When sourcing self-priming irrigation pumps, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
Materials: The quality and type of materials used, such as cast iron or thermoplastic, significantly influence costs. High-grade materials that enhance durability and performance typically lead to higher prices.
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the location of the manufacturer and the complexity of the pump design. Regions with lower labor costs may provide a more cost-effective solution, but this can sometimes compromise quality.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
Tooling: Specialized tools and equipment are often necessary for producing self-priming pumps. The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom designs, impacting the overall pricing.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality involves additional processes and inspections, which contribute to the overall cost. Certifications and compliance with international standards can also affect pricing.
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary significantly based on the destination and the Incoterms agreed upon. International shipping, particularly to regions like Africa and South America, can lead to increased costs due to customs duties and tariffs.
Margin: The supplier’s desired profit margin will influence the final price. This margin can vary based on market competition and demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
Several factors can influence the pricing of self-priming irrigation pumps:
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Manufacturers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their purchasing.
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as specific flow rates or enhanced materials, can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against their budget constraints.
Quality and Certifications: Pumps with certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may come at a premium but can ensure compliance with international standards, which is crucial for certain markets.
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capacity can affect pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their track record and service quality.
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms is vital, as they dictate responsibility for shipping costs and risks. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly impact the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Prices on Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
To maximize value when sourcing self-priming irrigation pumps, consider the following strategies:
Negotiate Volume Discounts: If your purchasing needs are significant, leverage this to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts for larger orders.
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront cost but also the long-term expenses associated with maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial cost may yield better efficiency and lower operational costs over time.
Research Market Prices: Familiarize yourself with current market pricing for similar pumps. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations and help you identify fair pricing.
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and lead times, providing a competitive edge.
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Understand the economic conditions and currency fluctuations in your region, as these factors can influence pricing and availability.
Conclusion
Navigating the costs and pricing of self-priming irrigation pumps requires a comprehensive understanding of various components and influencers. By employing strategic negotiation tactics and being aware of the total cost of ownership, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remember that indicative prices may vary based on market conditions, so thorough research and supplier communication are key to successful sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing self priming irrigation pump With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Alternatives Exist for Self Priming Irrigation Pumps?
In the realm of agricultural irrigation, selecting the right pumping system is crucial for efficiency and productivity. While self-priming irrigation pumps are popular for their ability to draw water without manual priming, there are several alternative solutions available. Each option offers unique advantages and disadvantages, making it essential for B2B buyers to evaluate these alternatives based on their specific needs, budget, and operational requirements.
Comparison Table of Irrigation Pump Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Self Priming Irrigation Pump | Submersible Pump | Centrifugal Pump |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High suction capability; can handle varying water levels | Excellent for deep water; constant flow rates | Good for high flow rates; less effective with air exposure |
| Cost | Moderate upfront cost; low operating costs | Higher initial investment; energy-efficient | Generally lower cost; maintenance can add up |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires minimal setup | Requires deeper installation; more complex | Straightforward installation; less versatile |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional checks needed | Moderate maintenance; requires regular checks | High maintenance; needs frequent servicing |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for irregular water sources; varied terrains | Best for deep wells or lakes; consistent water levels | Suitable for flat terrains; high-volume irrigation |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Submersible Pump
Submersible pumps are designed to be submerged in water, making them ideal for deep wells or lakes. They excel in providing consistent flow rates and can handle varying water levels without losing efficiency. However, their installation can be more complex and may require additional infrastructure, which can lead to higher upfront costs. Maintenance is moderate, as regular checks are necessary to ensure functionality and efficiency. They are particularly effective in scenarios where a steady water supply is essential, such as in deep agricultural wells.
2. Centrifugal Pump
Centrifugal pumps utilize rotational energy to move water, making them suitable for high-flow applications. They are generally less expensive to purchase compared to self-priming pumps and are easy to install. However, they are less effective at handling air exposure and require a consistent water source to operate efficiently. Maintenance can be a significant factor, as these pumps often need more frequent servicing to ensure optimal performance. Centrifugal pumps are best suited for flat terrains where water is readily available, and high flow rates are needed.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Irrigation Pump Solution?
Selecting the right irrigation pump solution requires a thorough understanding of your specific operational requirements. Self-priming irrigation pumps offer versatility and ease of use, making them a solid choice for varied terrains and irregular water sources. In contrast, submersible pumps provide efficiency for deep water sources, while centrifugal pumps are ideal for high-flow needs in flat areas. B2B buyers should assess factors such as cost, maintenance, and the specific water source characteristics to make an informed decision that aligns with their agricultural needs and budget constraints. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, businesses can optimize their irrigation systems for better performance and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for self priming irrigation pump
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
When considering self-priming irrigation pumps for agricultural or landscaping applications, several technical properties are critical for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Understanding these specifications can significantly impact purchasing decisions.
1. Material Grade
The construction material of a self-priming pump is paramount. Common materials include cast iron, thermoplastic, and stainless steel. Cast iron is favored for its durability and resistance to corrosion, while thermoplastic options are lightweight and often more affordable. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material can influence not only the pump’s longevity but also its suitability for various environmental conditions.
2. Flow Rate (GPM)
The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM), indicates how much water the pump can move. This specification is vital for determining whether the pump meets the operational requirements of a specific irrigation system. For instance, a pump with a higher GPM is necessary for larger agricultural fields, while smaller gardens may suffice with lower flow rates. Understanding this metric helps buyers match pump capabilities to their irrigation needs.
3. Horsepower (HP)
Horsepower determines the pump’s power output and is directly correlated to its ability to handle larger volumes of water or overcome higher pressure conditions. Pumps typically range from 0.5 HP to over 10 HP, depending on application demands. Buyers should carefully consider the horsepower necessary for their specific use case, as insufficient horsepower can lead to operational inefficiencies.
4. Maximum Pressure (PSI)
The maximum pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates how much pressure the pump can generate. This is particularly important for systems that require a specific pressure to function effectively, such as sprinkler systems or drip irrigation setups. Buyers need to ensure that the pump’s maximum pressure aligns with their irrigation system’s specifications to avoid damage or underperformance.
5. Self-Priming Capability
The self-priming feature allows the pump to draw water without manual intervention, which is essential for systems that may not have a steady water source. This capability is crucial in remote or variable water supply scenarios, making it a key consideration for buyers in diverse geographical regions.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies Relevant to Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B environment. Here are some commonly used terms in the context of self-priming irrigation pumps:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of pumps, knowing the OEM can help buyers assess product quality and reliability, as well as their options for replacement parts.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to determine budget and inventory management. It can also impact purchasing decisions, particularly for smaller companies that may not need large quantities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. For B2B buyers, submitting an RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and better terms, as suppliers often provide customized offers based on detailed specifications.
4. Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping, risk, and cost obligations, which is crucial for international procurement, especially in regions like Africa and South America.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management, as delays can impact agricultural cycles and project timelines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals in the irrigation market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the self priming irrigation pump Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
The global self-priming irrigation pump market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing agricultural productivity demands and the need for efficient water management solutions. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, farmers and agricultural enterprises are increasingly adopting self-priming pumps to enhance irrigation efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve crop yields. Key trends include the integration of smart technology, such as IoT-enabled pumps that allow for remote monitoring and control, which is particularly valuable for large-scale agricultural operations.
Another emerging trend is the shift towards energy-efficient models that consume less power while maintaining high performance. As energy costs rise, this trend is expected to gain momentum, especially in energy-sensitive markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainability is pushing manufacturers to innovate and offer eco-friendly products, including those made from recyclable materials and featuring energy-efficient designs.
International B2B buyers are also increasingly focused on sourcing from suppliers who demonstrate reliability, transparency, and a strong track record of product quality. This has led to a more competitive landscape, where companies that can offer robust after-sales support, including maintenance and spare parts availability, are more likely to secure long-term contracts with buyers.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Self-Priming Pump Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the self-priming irrigation pump sector. Environmental impact assessments are increasingly required during the sourcing process, reflecting a growing awareness of the need to minimize ecological footprints. Buyers are looking for manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials in production and adopting energy-efficient technologies.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance, with businesses keen to ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and responsible manufacturing processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) are becoming essential criteria for supplier evaluation. Additionally, ‘green’ certifications for pumps that meet specific energy efficiency and environmental standards are increasingly being demanded by buyers, facilitating their commitment to sustainable agricultural practices.
By prioritizing suppliers who embrace sustainable and ethical sourcing, international buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute to the global effort of promoting responsible resource management and environmental conservation.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
The evolution of self-priming irrigation pumps dates back to the early 20th century when the need for efficient water lifting and irrigation solutions became apparent in agriculture. Initially, these pumps were mechanically driven and required significant manual effort. Over the decades, technological advancements led to the introduction of electric self-priming pumps, which significantly improved efficiency and ease of use.
Today, self-priming pumps are equipped with advanced features such as variable speed drives, digital monitoring systems, and energy-efficient motors, making them indispensable in modern irrigation practices. The transition from basic mechanical designs to sophisticated, automated systems reflects the industry’s response to the growing demands for efficiency, sustainability, and productivity in agriculture, particularly in regions facing water scarcity challenges.
As international B2B buyers seek reliable and innovative solutions, understanding this evolution provides context for the current capabilities and future potential of self-priming irrigation pumps in the agricultural sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of self priming irrigation pump
1. How do I select the right self-priming irrigation pump for my needs?
Choosing the right self-priming irrigation pump involves assessing your specific requirements, including flow rate, pressure, and the type of application (e.g., agricultural, landscaping). Consider factors such as the pump’s horsepower, inlet and outlet diameter, and the material (cast iron vs. thermoplastic) based on your environment. Consulting with manufacturers or distributors can provide valuable insights tailored to your operational conditions. Additionally, reviewing product specifications and performance curves can help ensure the pump meets your needs effectively.2. What is the best self-priming irrigation pump for low water sources?
For low water sources, a self-priming irrigation pump with a strong suction lift capability is essential. Pumps designed with a higher GPM (gallons per minute) rating and robust impeller systems can efficiently handle low water levels. Brands like Franklin Electric and Red Lion offer models specifically engineered for such scenarios. It’s important to evaluate the pump’s total dynamic head (TDH) to ensure it can lift water from your specific source without compromising performance.3. What are the typical lead times for ordering self-priming irrigation pumps internationally?
Lead times for international orders of self-priming irrigation pumps can vary significantly based on the manufacturer, shipping method, and destination. Generally, expect lead times of 4 to 12 weeks, which includes production, quality assurance, and shipping. To minimize delays, confirm production timelines with your supplier and consider utilizing expedited shipping options if urgent delivery is necessary. It’s also wise to account for potential customs clearance times in your planning.4. What should I consider when vetting suppliers for self-priming irrigation pumps?
When vetting suppliers, assess their experience and reputation in the industry, including customer reviews and case studies. Verify their manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and compliance with international quality standards. Request samples or product demonstrations to evaluate performance firsthand. Additionally, inquire about their warranty policies, after-sales support, and responsiveness to inquiries, as these factors are crucial for establishing a reliable long-term partnership.5. Can I customize a self-priming irrigation pump to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for self-priming irrigation pumps. Customizations can include modifications to size, materials, and motor specifications to better suit your operational needs. When discussing customization, clearly outline your requirements and any specific challenges you face. Be prepared to discuss lead times and potential costs associated with these modifications to ensure they fit within your budget and timeline.6. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for self-priming irrigation pumps?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for self-priming irrigation pumps can vary by manufacturer and product line. Typically, MOQs can range from a single unit for standard models to larger quantities for customized or specialized pumps. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their MOQ policies and consider discussing flexible options, especially if you are a new buyer or require a trial order before committing to larger purchases.7. What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of irrigation pumps?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upon order confirmation (often 30-50%) with the balance due before shipping. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms (e.g., Net 30 or Net 60) for established customers. It’s crucial to discuss payment options upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow needs. Consider exploring trade finance options if you require additional flexibility in managing payments.8. How can I ensure quality assurance for my self-priming irrigation pump order?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and certifications from your supplier, such as ISO or CE markings. Conduct factory visits if feasible, or consider third-party inspections before shipping. Establish clear quality control standards and communicate them with your supplier, including criteria for performance testing. Additionally, consider negotiating warranty terms and post-purchase support to address any quality concerns that may arise after delivery.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 3 Self Priming Irrigation Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Big Sprinkler – 9 HP Honda High Pressure Self-Priming Irrigation IPT Pump
Domain: bigsprinkler.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “9 HP Honda High Pressure Self-Priming Irrigation IPT Pump”, “SKU”: “IPT-9H-PO”, “Price”: “$2,912.00”, “Engine”: “9 HP Honda Commercial Series Recoil Start Engine”, “Pump Type”: “High Pressure Self-Priming”, “Pump Case Material”: “Heavy Duty American Made Cast Aluminum”, “Suction and Discharge Ports Material”: “Cast Iron”, “Impeller”: “High Pressure Enclosed Aluminum Impeller”, “C…
2. Grainger – Self-Priming Sprinkler Pumps
Domain: grainger.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, Grainger – Self-Priming Sprinkler Pumps, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Pentair – Self-Priming Pumps
Domain: pentair.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Self-Priming Pumps from Pentair are designed for efficient water disposal without the need for manual priming. Key features include:
– Automatic operation: Built-in mechanism evacuates air and fills the pump casing with liquid, allowing for immediate use.
– Convenience: No time-consuming manual priming required, and maintenance can be performed above ground.
– Versatility: Capable of handling liqu…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for self priming irrigation pump
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement of Self-Priming Irrigation Pumps?
In the evolving landscape of agricultural technology, strategic sourcing of self-priming irrigation pumps is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring sustainable water management. Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize suppliers that offer high-quality, reliable pumps that meet local environmental conditions and agricultural demands. Understanding the specifications, including flow rate, horsepower, and material durability, is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Moreover, leveraging digital platforms for procurement can streamline the sourcing process, allowing for comparative analysis of prices and features. This not only enhances transparency but also fosters competitive pricing, ensuring that buyers receive the best value. Collaborating with manufacturers who understand regional challenges can lead to tailored solutions that enhance productivity and sustainability.
As you look toward the future, consider establishing long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers. This will not only secure a consistent supply chain but also enable you to stay ahead of market trends and technological advancements. Engage proactively with suppliers to explore innovations in pump technology that can further enhance your irrigation efficiency. Your strategic sourcing decisions today will pave the way for a more productive and sustainable agricultural future.