Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to install irrigation pump
In today’s global market, B2B buyers face the critical challenge of efficiently installing irrigation pumps that meet their specific agricultural needs. Understanding how to install an irrigation pump can significantly enhance water management strategies, especially in regions where water scarcity is a pressing concern. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at various types of irrigation pumps, their applications across different agricultural sectors, and essential factors to consider when selecting the right equipment.
Throughout this guide, you will find valuable insights on supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and installation techniques tailored for diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. We address the unique challenges faced by international buyers, such as navigating local regulations and understanding regional water requirements. By empowering you with actionable knowledge, this guide aims to simplify your purchasing decisions and enhance your operational efficiency.
Whether you are looking to boost your current irrigation system or are starting from scratch, this resource serves as a reliable roadmap for selecting and installing irrigation pumps. With the right information at your fingertips, you can make informed choices that align with your business goals, ensuring sustainable and effective water usage for your agricultural endeavors.
Understanding how to install irrigation pump Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pumps | Utilizes rotational energy to move water | Agriculture, landscaping | Pros: Efficient for high flow rates. Cons: Less effective with high-viscosity fluids. |
| Submersible Pumps | Operates underwater, often in wells or reservoirs | Deep well irrigation, drainage | Pros: Space-saving and efficient. Cons: Requires professional installation and maintenance. |
| Booster Pumps | Increases water pressure for irrigation systems | Pressurized irrigation systems | Pros: Enhances performance of existing systems. Cons: Can lead to over-pumping if not sized correctly. |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Uses a diaphragm to create pressure and flow | Chemical application, wastewater | Pros: Handles viscous fluids well. Cons: Lower flow rates compared to centrifugal pumps. |
| Solar-Powered Pumps | Utilizes solar energy for operation | Remote areas, sustainable farming | Pros: Energy-efficient and eco-friendly. Cons: Initial costs can be high; dependent on sunlight. |
What Are the Characteristics of Centrifugal Pumps in Irrigation Systems?
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in irrigation due to their ability to handle large volumes of water effectively. These pumps work by converting rotational energy into hydrodynamic energy, making them suitable for applications that require high flow rates. When considering B2B purchases, buyers should evaluate the pump’s capacity, efficiency, and compatibility with existing systems, especially in agricultural settings where water demand can vary significantly.
How Do Submersible Pumps Function and Where Are They Best Suited?
Submersible pumps are designed to be submerged in water, making them ideal for deep well applications. Their compact design allows for easy installation in confined spaces, while their efficiency in lifting water from significant depths is a critical advantage. B2B buyers should focus on the pump’s material durability, energy consumption, and maintenance requirements, especially in regions with fluctuating water levels, such as those found in Africa and South America.
What Is the Role of Booster Pumps in Irrigation Systems?
Booster pumps are essential for enhancing water pressure in irrigation systems, ensuring that water reaches all areas of the landscape evenly. They are particularly useful in situations where the existing water supply is insufficient for the required flow rates. When purchasing a booster pump, businesses should consider the compatibility with their current system, the potential for over-pumping, and the pump’s capacity to handle peak demands.
What Advantages Do Diaphragm Pumps Offer in Irrigation Applications?
Diaphragm pumps are known for their ability to handle a variety of fluids, including those that are viscous or contain solids. This makes them suitable for applications in chemical irrigation and wastewater management. For B2B buyers, key considerations include the pump’s flow rate, maintenance needs, and the specific requirements of the fluids being transported, as these factors will impact overall system efficiency.
How Do Solar-Powered Pumps Contribute to Sustainable Irrigation?
Solar-powered pumps are an innovative solution for irrigation, particularly in remote areas where electricity may be unreliable or unavailable. These pumps harness solar energy, making them an eco-friendly option that can significantly reduce operational costs over time. Buyers should assess the initial investment versus long-term savings, as well as the pump’s performance in varying sunlight conditions, to ensure they meet their irrigation needs effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of how to install irrigation pump
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to install irrigation pump | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Installing irrigation pumps for crop cultivation | Enhanced crop yield and efficient water usage | Quality of pumps, compatibility with local water sources |
| Landscaping | Setting up irrigation systems for commercial landscaping projects | Improved aesthetic appeal and reduced labor costs | Durability, ease of installation, and maintenance support |
| Horticulture | Implementing irrigation systems for nurseries and greenhouses | Consistent watering leading to healthier plants | Pump capacity, energy efficiency, and local climate adaptation |
| Mining | Utilizing pumps for dust suppression and water supply in mining operations | Compliance with safety regulations and operational efficiency | Robustness, ability to handle abrasive materials, and reliability |
| Municipal Services | Installing pumps for public parks and recreational facilities | Enhanced community engagement and environmental sustainability | Regulatory compliance, energy consumption, and maintenance needs |
How is ‘how to install irrigation pump’ utilized in Agriculture?
In the agriculture sector, the installation of irrigation pumps is critical for optimizing water supply to crops. Farmers can enhance crop yields by ensuring consistent moisture levels, which is particularly important in regions with variable rainfall. Buyers in this sector must consider the pump’s compatibility with local water sources, as well as the quality and durability of the equipment to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Additionally, energy-efficient options are increasingly sought after to reduce operational costs.
What are the landscaping applications for irrigation pump installation?
For landscaping businesses, installing irrigation pumps facilitates efficient watering systems for commercial properties, parks, and residential areas. This not only helps maintain the aesthetic appeal of landscapes but also reduces labor costs associated with manual watering. Buyers should prioritize pumps that are durable and easy to install, as well as those that offer maintenance support. Understanding local water regulations and environmental impacts is also essential to ensure compliance and sustainability.
How does irrigation pump installation benefit horticulture?
In horticulture, particularly for nurseries and greenhouses, the installation of irrigation pumps ensures a consistent water supply tailored to the specific needs of various plants. This leads to healthier growth and higher quality produce. Buyers should focus on pump capacity and energy efficiency to match the scale of their operations. Additionally, adaptability to local climate conditions is crucial, as it influences the irrigation strategy and overall effectiveness of the system.
What role do irrigation pumps play in the mining industry?
In the mining sector, irrigation pumps are essential for dust suppression and providing water supply for various operational needs. Properly installed pumps help companies comply with safety regulations while enhancing operational efficiency. Buyers should consider the robustness of the pumps, especially their ability to handle abrasive materials and their reliability under challenging conditions. Ensuring that the equipment meets industry standards is critical for minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
How are irrigation pumps utilized in municipal services?
Municipal services benefit from the installation of irrigation pumps in public parks and recreational facilities, contributing to enhanced community engagement and environmental sustainability. These pumps support efficient water management practices, ensuring that green spaces remain vibrant and accessible. Buyers must focus on regulatory compliance and the energy consumption of the pumps to align with municipal budgets and sustainability goals. Maintenance needs and the availability of local service providers are also key considerations in the sourcing process.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to install irrigation pump’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Proper Pump Compatibility with Existing Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when selecting an irrigation pump that is compatible with their existing water supply systems. For instance, if a buyer operates a well with a specific flow rate, they may not know how to choose a pump that matches or exceeds this flow without overwhelming the system. This mismatch can lead to inadequate water supply, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to the pump or well system.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should start by calculating their irrigation needs based on the size of the area to be irrigated and the required gallons per minute (GPM). They should then assess their current water supply’s flow rate and pressure. If the well produces 10 GPM and the irrigation system requires 23 GPM, it may be necessary to either upgrade the existing well pump or install a booster pump. Buyers can consult with local well experts to understand the long-term sustainability of their water source, ensuring that any new installation won’t overdraw the aquifer. Additionally, sourcing pumps that offer variable speed options can help match output to demand, preventing excessive cycling and wear on the system.
Scenario 2: Navigating Complex Wiring and Electrical Requirements
The Problem: Electrical setup can be a daunting task for many buyers when installing an irrigation pump, especially if the existing infrastructure is outdated or incompatible. For instance, a buyer may have a low-voltage irrigation controller that needs to activate a high-voltage pump. This situation can lead to confusion about proper wiring and safety measures, which is critical to avoid electrical hazards or equipment failure.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize understanding the electrical requirements of their irrigation pump and controller before installation. This includes familiarizing themselves with the role of relays in controlling high-voltage devices through low-voltage signals. It’s advisable to engage a licensed electrician who specializes in irrigation systems to ensure that the electrical installation adheres to local codes and safety standards. Additionally, buyers should consider installing surge protection devices to safeguard their equipment against electrical spikes. Documenting the wiring scheme during installation can also facilitate future troubleshooting and maintenance.
Scenario 3: Managing Water Resource Constraints Effectively
The Problem: In regions facing water scarcity, B2B buyers may struggle with how to efficiently manage their irrigation needs while adhering to local regulations and sustainability practices. This is particularly relevant for buyers in areas like Africa and the Middle East, where water availability is limited and regulations around usage are becoming increasingly stringent.
The Solution: To effectively manage water resources, buyers should consider integrating rainwater harvesting systems or constructing reservoirs to store excess water for irrigation use. This can help mitigate dependency on groundwater and reduce the risk of over-extraction. Additionally, implementing smart irrigation technologies, such as moisture sensors and weather-based controllers, can optimize water usage by adjusting irrigation schedules based on real-time data. Buyers should also engage with local agricultural extension services to understand best practices for sustainable irrigation and to ensure compliance with regulations. By adopting a holistic approach that includes both technology and water conservation strategies, buyers can enhance their irrigation system’s efficiency while promoting environmental stewardship.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to install irrigation pump
When selecting materials for the installation of irrigation pumps, it is crucial to consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compatibility with specific applications. Below are analyses of four commonly used materials in the irrigation pump industry, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of PVC in Irrigation Pump Installations?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used material in irrigation systems due to its favorable properties. PVC pipes typically have a temperature rating of up to 140°F (60°C) and can withstand pressures of around 300 psi, depending on the wall thickness. Its inherent corrosion resistance makes it ideal for transporting water without degrading over time.
Pros and Cons: PVC is lightweight and easy to install, which reduces labor costs. However, it can become brittle in extreme temperatures and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications without reinforcement.
Impact on Application: PVC is compatible with a variety of media, including potable water, making it a versatile choice for irrigation systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM is essential, and buyers should ensure that the PVC used meets local regulations, especially in regions like Africa and South America where environmental conditions can be harsh.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Irrigation Pump Applications?
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength and corrosion resistance, making it a premium choice for irrigation pumps, especially in areas with high salinity or chemical exposure. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, often rated for up to 250°F (121°C) and 1500 psi, depending on the grade.
Pros and Cons: The durability of stainless steel ensures a long lifespan, reducing replacement costs. However, it is significantly more expensive than other materials like PVC, and its installation can be more complex due to the need for specialized tools and fittings.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for a variety of media, including corrosive fluids, making it ideal for diverse irrigation applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific stainless steel grades (e.g., 304, 316) suitable for their application and ensure compliance with international standards like DIN and JIS.
What Are the Benefits of Using HDPE in Irrigation Systems?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is another popular material for irrigation installations, known for its flexibility and resistance to impact and corrosion. HDPE pipes can typically handle temperatures up to 140°F (60°C) and pressures of about 160 psi.
Pros and Cons: HDPE is highly durable and resistant to UV radiation, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, it can be more challenging to install due to its flexibility, which may require additional fittings and support.
Impact on Application: HDPE is compatible with various media, including wastewater, making it versatile for different irrigation needs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and local regulations is critical, especially in regions with varying environmental conditions.
Why Choose Copper for Irrigation Pump Installations?
Copper is often used in irrigation systems due to its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion. It can handle high temperatures (up to 400°F or 204°C) and pressures, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros and Cons: Copper’s durability and resistance to microbial growth are significant advantages. However, it is one of the more expensive options and can be prone to theft due to its value.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with potable water, making it a preferred choice for drinking water irrigation systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the copper used meets local standards and regulations, particularly in regions where water quality is a concern.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Irrigation Pump Installation
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to install irrigation pump | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | General irrigation systems | Lightweight and easy to install | Brittle in extreme temperatures | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure and corrosive environments | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | High cost and complex installation | High |
| HDPE | Flexible irrigation systems | UV resistant and durable | Challenging installation | Medium |
| Copper | Potable water systems | Superior thermal conductivity | Expensive and prone to theft | High |
This comprehensive analysis of materials used in irrigation pump installations provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, application suitability, and compliance with local standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to install irrigation pump
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Irrigation Pumps?
The manufacturing process for irrigation pumps typically consists of several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess the quality and reliability of the pumps they are considering for installation.
Material Preparation
The first step involves sourcing high-quality materials such as stainless steel, bronze, or thermoplastics, which are essential for durability and resistance to corrosion. Manufacturers often conduct thorough material inspections to ensure that raw materials meet industry specifications before they proceed to the next stage. This initial quality check is crucial as it sets the foundation for the entire manufacturing process.
Forming Techniques
Forming involves shaping the materials into the required components of the pump. Techniques such as casting, machining, and injection molding are commonly used, depending on the design specifications. For example, centrifugal pumps may require precision casting to form the impeller, while positive displacement pumps might be machined for tighter tolerances. Advanced technologies like CNC machining are often employed to enhance precision and reduce waste, thus improving overall efficiency.
Assembly Process
Once individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This step may involve manual assembly or automated processes, depending on the scale of production. Key components such as the motor, impeller, and housing must be meticulously fitted to ensure optimal performance. Quality control checkpoints during assembly are vital, as they verify that components fit correctly and function as intended.
Finishing Touches
The finishing stage includes surface treatment, painting, and any additional features such as wiring or installation of sensors. Surface treatments, such as powder coating or galvanization, enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. This stage may also involve rigorous testing to ensure that the pump meets operational standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of irrigation pumps, as it directly affects performance and reliability. Buyers should be familiar with relevant international standards, as well as industry-specific certifications.
International Standards
ISO 9001 is the most recognized quality management standard globally. It ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent quality of products and services. For B2B buyers, confirming that a supplier is ISO 9001 certified can provide assurance of their commitment to quality.
Industry-Specific Certifications
In addition to ISO standards, certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for pumps used in oil and gas applications may be relevant. These certifications indicate that the products have undergone rigorous testing and comply with specific safety and performance regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Pump Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process, with multiple checkpoints established to ensure product integrity.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
IQC involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This step ensures that all materials meet specified standards before production begins. B2B buyers should inquire about the supplier’s IQC process to understand how they manage material quality.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC involves ongoing inspections at various stages, such as after forming and assembly. This proactive approach helps identify and rectify defects early, minimizing waste and reducing the likelihood of failures in the final product.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
FQC is conducted after assembly and finishing, focusing on the overall functionality and safety of the pump. This includes performance testing under various conditions to ensure it meets the required flow rates and pressure specifications. Buyers should ask suppliers for documentation of FQC results to verify product reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to mitigate risks associated with product quality.
Supplier Audits
Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing practices and quality management systems. Audits can be performed by the buyer or outsourced to third-party firms specializing in supplier assessments. Key areas to evaluate include the effectiveness of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes.
Quality Reports and Certifications
Buyers should request quality reports that document the results of inspections and testing throughout the manufacturing process. Additionally, verifying certifications (such as ISO 9001, CE, and API) through official channels can confirm that the supplier adheres to recognized standards.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an additional layer of assurance. These independent entities can perform random checks at different stages of manufacturing, ensuring compliance with agreed specifications and standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various challenges when it comes to quality assurance. Understanding these nuances can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Cultural and Regulatory Differences
Different regions may have varying standards and expectations regarding quality. For example, European buyers might prioritize CE compliance, while buyers in Africa may focus more on durability and serviceability in harsh environments. It is essential for buyers to communicate their quality expectations clearly and understand the local regulations that may affect product performance.
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations
The logistics involved in international shipping can impact the quality of the product upon arrival. Ensuring that suppliers use appropriate packaging and handling procedures is vital to prevent damage during transit. Buyers should discuss logistics with suppliers to establish best practices for maintaining product integrity.
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards is crucial for B2B buyers looking to install irrigation pumps. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly processes, and finishing touches, buyers can assess the quality of the pumps. Furthermore, familiarity with international standards, quality control checkpoints, and verification methods will empower buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of their irrigation systems.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to install irrigation pump’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to install irrigation pumps effectively. Understanding the intricacies of pump installation is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your irrigation system. By following these steps, you can make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and regional conditions.
1. Assess Your Water Requirements
Before selecting an irrigation pump, clearly define the water needs of your agricultural or landscaping operations. Calculate the total flow rate (GPM) required based on the size of the area to be irrigated and the type of irrigation system in use, such as drip or sprinkler systems. This assessment helps in choosing a pump that meets your specific requirements without overloading the system.
2. Define Your Technical Specifications
Identify the technical specifications needed for your pump installation, including horsepower, voltage, and type (submersible vs. surface). Each specification affects the pump’s performance and compatibility with your existing system. Make sure to consider local power availability and water source characteristics (e.g., depth, salinity) to ensure proper functionality.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Look for suppliers with experience in your geographical area, as they will be more familiar with local regulations and environmental conditions.
- Check for certifications: Ensure that suppliers have relevant certifications, such as ISO or local quality standards, which indicate compliance with industry norms.
4. Understand Installation Requirements
Familiarize yourself with the installation requirements of the chosen pump. This includes understanding the necessary piping, electrical connections, and any permits that may be required. Proper installation is vital to avoid operational issues and ensure the pump functions efficiently.
- Consider zoning: If your water requirements exceed the pump’s capacity, plan for a multi-zone system to manage flow effectively without overwhelming the pump.
5. Plan for Maintenance and Support
Choose a supplier that offers robust post-installation support and maintenance services. Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity of your pump, and having access to technical support can prevent downtime during critical irrigation periods.
- Inquire about warranties: Ensure that the pump comes with a warranty and understand the terms for maintenance services.
6. Evaluate Financial Implications
Assess the total cost of ownership, including purchase price, installation, maintenance, and operational costs. A cheaper initial investment may lead to higher long-term costs due to inefficiencies or frequent repairs.
- Consider energy efficiency: Look for energy-efficient models that can reduce operational costs and comply with local energy regulations.
7. Seek Local Expertise
Engage local irrigation professionals for insights on best practices in installation and operation. Their expertise can help you avoid common pitfalls and optimize your irrigation system for local conditions.
- Network with industry peers: Attend local agricultural fairs or industry seminars to connect with experts and gather additional insights on effective irrigation practices.
By following this checklist, you can streamline the process of procuring and installing an irrigation pump that meets your specific needs, ultimately enhancing the efficiency and productivity of your operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to install irrigation pump Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Installing an Irrigation Pump?
When considering the installation of an irrigation pump, several cost components come into play. The primary categories include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: This encompasses the pump itself, piping, fittings, valves, and any additional components necessary for installation. The choice of materials significantly impacts costs, with high-quality, durable options generally commanding higher prices. For instance, PVC piping is a common choice due to its affordability and ease of installation, while stainless steel components may be preferred for their longevity in harsh environments.
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and complexity of the installation. In developing markets, such as parts of Africa or South America, labor may be less expensive compared to Europe or the Middle East. However, skilled labor is crucial for ensuring proper installation and compliance with local regulations.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep overhead low, which is beneficial for pricing strategies.
Tooling: Specialized tools may be required for installation, especially in cases where custom solutions are needed. The cost of these tools should be factored into the overall installation budget.
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that all components meet safety and performance standards is essential. Costs associated with QC processes can vary based on the supplier and the certifications required, particularly for international buyers.
Logistics: Transportation costs can affect the overall price, especially for international buyers. Factors such as shipping methods, distance, and customs duties should be considered.
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on market competition and demand.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Irrigation Pump Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing when sourcing irrigation pumps:
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often result in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQ) to maximize cost-efficiency.
Specifications and Customization: Custom pumps designed for specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly outline their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO or local standards) can lead to increased costs but may reduce maintenance and operational expenses in the long run.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and guarantees.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions as they define responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting overall costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Irrigation Pump Costs?
International B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to optimize their purchasing process:
Negotiate for Better Terms: Leverage volume purchases to negotiate discounts, favorable payment terms, or free shipping. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also yield better pricing in the future.
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than just the initial purchase price, consider ongoing maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime when evaluating costs. This holistic view can reveal the true value of a pump.
Understand Pricing Nuances in Different Markets: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional price variations due to local demand, economic conditions, and currency fluctuations.
Conduct Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and competitor pricing. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help them identify the best sourcing opportunities.
Conclusion
While the initial costs associated with installing an irrigation pump may seem daunting, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components and pricing influencers can lead to more informed purchasing decisions. By utilizing effective negotiation strategies and focusing on long-term value, international B2B buyers can optimize their investment in irrigation systems. Always remember to request indicative pricing from suppliers to ensure a realistic budget framework.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to install irrigation pump With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Installing an Irrigation Pump
In the world of irrigation, installing a pump is a common solution for ensuring adequate water supply for agricultural needs. However, there are alternative methods that can also achieve effective irrigation management. This section compares the traditional method of installing an irrigation pump against two viable alternatives: using a gravity-fed irrigation system and utilizing a rainwater harvesting system. Each method has unique benefits and drawbacks that B2B buyers should consider based on their specific operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | How To Install Irrigation Pump | Gravity-Fed Irrigation System | Rainwater Harvesting System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency; consistent water pressure. | Depends on elevation; may vary with terrain. | Variable; relies on rainfall patterns. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment (pump, installation, maintenance). | Lower setup costs; minimal ongoing expenses. | Moderate setup costs; dependent on storage capacity. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires technical expertise for installation. | Relatively easy to implement; minimal infrastructure needed. | Requires planning for collection and storage. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for pump functionality. | Low maintenance; mainly involves checking water sources. | Moderate; needs regular cleaning of catchment and storage systems. |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale operations with high water demand. | Suitable for sloped terrains with reliable water sources. | Ideal for regions with seasonal rainfall and water scarcity. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of a Gravity-Fed Irrigation System?
A gravity-fed irrigation system relies on the natural slope of the land to move water from a higher elevation to the plants below. This method is often less expensive to implement, as it does not require the installation of pumps. However, its performance is highly dependent on the terrain and can lead to uneven water distribution, especially on flat lands. Maintenance needs are minimal, but users must ensure that the water source remains reliable and that sediment does not clog the system. This solution is best suited for agricultural operations located in hilly or mountainous regions where gravity can be effectively utilized.
How Does a Rainwater Harvesting System Compare?
A rainwater harvesting system collects and stores rainwater for irrigation use. It can be a cost-effective solution, particularly in areas with significant rainfall. The initial investment includes the cost of storage tanks and filtration systems, but ongoing costs are low. Maintenance mainly involves ensuring that the collection and storage systems are clean and functioning well. The primary drawback is that it is highly variable; during dry spells, the water supply can diminish, making it less reliable for large-scale operations. This system is best for regions with fluctuating water availability, allowing for sustainable water use while reducing dependency on external sources.
Choosing the Right Irrigation Solution for Your Needs
When determining the best irrigation solution, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific operational needs, including the scale of their agricultural activities, local climate conditions, and budget constraints. While installing an irrigation pump offers high efficiency and reliability, alternatives like gravity-fed systems and rainwater harvesting can provide viable, cost-effective solutions depending on the geographic and economic context. By carefully considering these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their water management goals and sustainability initiatives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to install irrigation pump
What Are the Essential Technical Properties for Installing an Irrigation Pump?
When installing an irrigation pump, understanding key technical specifications is crucial for ensuring the system operates efficiently and effectively. Here are several critical properties to consider:
Flow Rate (GPM)
The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM), indicates how much water the pump can deliver within a specific timeframe. This is vital for ensuring that the pump can meet the irrigation demands of the area being serviced. For example, if your irrigation system requires 23 GPM, selecting a pump that can deliver that volume consistently is essential to avoid underperformance.Pressure Rating (PSI)
The pressure rating, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), reflects the pump’s ability to generate sufficient pressure to distribute water effectively through the irrigation system. Understanding the required pressure for your irrigation design is important to avoid system failures and ensure optimal water distribution, especially in systems with varying elevation.Power Source and Voltage
The power source for the pump (electric, diesel, solar) and its voltage requirements are crucial for compatibility with existing infrastructure. Ensuring the right voltage is available can prevent operational issues and reduce the risk of damage to the pump. For instance, a 230V pump may require different wiring compared to a 115V model.Material Grade
The material of the pump (such as stainless steel, cast iron, or thermoplastic) affects durability, resistance to corrosion, and overall lifespan. For B2B buyers operating in diverse climates, selecting a pump made from appropriate materials is key to minimizing maintenance costs and ensuring longevity.Suction Lift Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum vertical distance from which the pump can draw water. Understanding suction lift is particularly important for installations where the water source is below the pump level, such as in well or pond applications. Insufficient suction lift can lead to pump failure or inadequate water supply.Motor Size (HP)
The horsepower (HP) of the pump’s motor determines its efficiency and ability to handle the required flow rate and pressure. Selecting the appropriate motor size is critical to avoid energy waste and ensure the pump can perform adequately under varying conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Irrigation Pump Installation?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several common terms related to irrigation pump installation:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products. When sourcing pumps or components, buyers may prefer OEM parts for quality assurance and compatibility with existing systems.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term denotes the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers looking to manage inventory costs and ensure that they are purchasing in economically viable quantities.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. Submitting an RFQ is a crucial step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms from different suppliers effectively.Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs associated with the procurement of irrigation pumps.Backflow Preventer
A backflow preventer is a device that prevents contaminated water from flowing back into the potable water supply. This is critical for irrigation systems to ensure compliance with health regulations and protect water quality.Pressure Switch
A pressure switch is an electrical device that automatically turns the pump on or off based on the water pressure in the system. Understanding how pressure switches operate is important for ensuring the pump operates efficiently and to avoid potential cycling issues that could lead to equipment damage.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of their irrigation systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to install irrigation pump Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers Influencing the Irrigation Pump Sector?
The irrigation pump sector is experiencing dynamic growth driven by several global factors. As agriculture becomes increasingly reliant on technology, the demand for efficient irrigation systems is surging, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where water scarcity is a pressing issue. The adoption of precision agriculture techniques is another significant trend, allowing farmers to optimize water use and enhance crop yields. Additionally, advancements in pump technology—such as solar-powered pumps—are gaining traction, providing sustainable and cost-effective solutions for irrigation.
International B2B buyers must also be aware of emerging sourcing trends, such as the increased use of digital platforms for procurement. Online marketplaces and e-commerce solutions are transforming how buyers source irrigation pumps, making it easier to compare products, prices, and suppliers across borders. Furthermore, the shift towards automated irrigation systems is prompting manufacturers to innovate, leading to the development of smart irrigation controllers that can integrate with existing pump systems. These innovations not only improve efficiency but also align with the growing emphasis on sustainability in agricultural practices.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Irrigation Pumps?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the irrigation pump sector. The environmental impact of traditional irrigation practices has led to a growing demand for sustainable solutions that minimize water waste and energy consumption. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing practices and can demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated; consumers are now prioritizing products that are produced responsibly. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and WaterSense for water-efficient products are becoming essential for suppliers to secure contracts with environmentally conscious buyers. Additionally, the use of recycled materials in pump manufacturing and packaging is gaining traction, appealing to buyers focused on sustainability.
As international buyers navigate these trends, they should prioritize partnerships with suppliers that emphasize green practices and transparency in their supply chains. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with global sustainability goals, ultimately contributing to a more resilient agricultural sector.
What Is the Historical Context of Irrigation Pump Technology?
The evolution of irrigation pump technology has been instrumental in shaping modern agricultural practices. Initially, farmers relied on manual methods and gravity-fed systems, which often proved inefficient and limited in scope. The introduction of mechanical pumps in the 19th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for greater control over water distribution and enabling farmers to irrigate larger areas.
Over the decades, advancements in pump design and materials have led to the development of more efficient and durable systems. The integration of electrical and solar-powered pumps in the late 20th century further revolutionized irrigation, particularly in remote areas lacking reliable electricity. Today, the focus is shifting towards smart irrigation systems that utilize IoT technology, allowing for real-time monitoring and management of water resources.
Understanding this historical context equips B2B buyers with insights into the capabilities and limitations of current irrigation pump technologies, guiding them in making informed decisions that align with their agricultural needs and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to install irrigation pump
How do I solve low water pressure issues when installing an irrigation pump?
To address low water pressure, first, assess the flow rate of your water source. If the source cannot meet the required gallons per minute (GPM) for your irrigation system, consider installing a booster pump. This pump enhances the existing pressure and can be set up after the main pump. However, ensure that the booster pump’s capacity does not exceed the main pump’s output to avoid overworking the system. Additionally, check for any leaks or blockages in the piping that could be affecting water pressure.What is the best type of irrigation pump for large agricultural fields?
For large agricultural fields, centrifugal pumps are typically the best choice due to their efficiency in moving large volumes of water. These pumps can handle varying flow rates and are suitable for both surface and groundwater applications. When selecting a pump, consider factors such as the required flow rate, total dynamic head, and the specific crop irrigation needs. It’s advisable to consult with local suppliers who can recommend pumps tailored to the regional conditions and regulations.How can I ensure the quality of the irrigation pump I am purchasing?
To ensure the quality of an irrigation pump, conduct thorough supplier vetting. Request certifications, product specifications, and customer testimonials. It’s also beneficial to ask for product samples or visit their manufacturing facility if possible. Inquire about warranties and after-sales support to gauge the supplier’s commitment to quality. Additionally, consider sourcing from suppliers who comply with international standards, which can provide further assurance of product quality.What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for irrigation pumps?
Minimum order quantities for irrigation pumps can vary significantly among suppliers, often depending on the pump type and manufacturer. Typically, MOQs can range from a single unit for smaller suppliers to hundreds for larger manufacturers. When negotiating, discuss your specific needs and explore whether the supplier can accommodate lower MOQs, especially if you are a new buyer. Establishing a good relationship with the supplier can lead to more flexible terms in the future.What payment terms should I expect when sourcing irrigation pumps internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50%) with the balance due before shipping or upon delivery. For larger orders, some suppliers may offer more favorable terms, such as letter of credit or installment payments. Always clarify payment methods and terms in the contract to avoid misunderstandings, and consider using escrow services for additional security in international transactions.How do I assess the logistics involved in importing irrigation pumps?
Assessing logistics involves understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery times. Collaborate with a freight forwarder experienced in international trade to navigate these complexities. They can provide insights on shipping costs, insurance, and duty fees. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the importing country’s regulations regarding agricultural equipment to ensure compliance. Planning for potential delays and having contingency plans can also help streamline the logistics process.What customization options are available for irrigation pumps?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific agricultural needs. Customizations can include variations in size, material, pump capacity, and additional features such as automated controls or energy-efficient designs. When discussing options with suppliers, clearly outline your requirements and ask for design flexibility. This not only ensures that the pump fits your irrigation system but can also enhance efficiency and effectiveness in your operations.How can I ensure proper installation of the irrigation pump?
Proper installation is crucial for optimal pump performance. Follow the manufacturer’s installation guidelines meticulously, which typically include site preparation, plumbing connections, and electrical wiring. Hiring a qualified technician familiar with irrigation systems can enhance installation quality. Additionally, conduct pressure tests post-installation to identify leaks or performance issues early on. Regular maintenance checks can also prolong the pump’s lifespan and ensure it operates efficiently throughout its service life.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 How To Install Irrigation Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
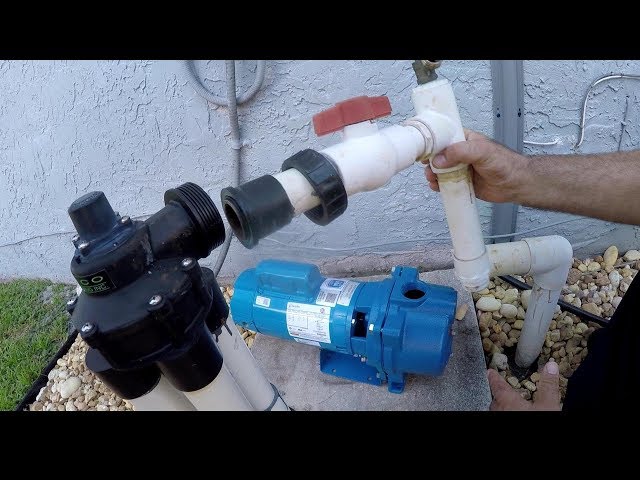
1. Irrigation Pump – Above Ground Installation Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Irrigation pump installation details: 1. Pump type: Above ground pump, recommended 1/2 to 3/4 HP. 2. Pump performance: Temporary installation of a 3/4 HP pump producing 13 GPM. 3. Irrigation zones: Two zones, each requiring 10 GPM for lawn irrigation. 4. Pressure tank: Not necessary unless a constant pressure system is needed. 5. Components: Inquiry about sched40 flexible components, advised again…
2. The Lawn Forum – Booster Pump
Domain: thelawnforum.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Booster pump that pumps 30GPM; Drip irrigation requires 23GPM; Well pump capacity is 10GPM; Drip tube GPM/100′ is 0.9; Total drip tube length is 2550′.
3. Sprinkler Warehouse – Irrigation Controllers with Pump Start Relay
Domain: school.sprinklerwarehouse.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Irrigation controllers with a built-in pump start relay are essential for systems using a pump to supply water. The pump start relay allows the irrigation timer to communicate with the pump, converting the irrigation timer’s signal to normal household voltage. Key steps for installation include choosing the right controller, mounting it in a sheltered location, installing the pump start relay near…
4. Pinterest – DIY Portable Sprinkler System Guide
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Pinterest – DIY Portable Sprinkler System Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Terry Love – Irrigation System Components
Domain: terrylove.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Pump with pressure switch, Hunter relay, PVC pipe for irrigation system, flexible PVC tubing for pump suction line (minimum size 1.5 inches), inline sand separator filter, well screen or lake strainer for intake line, flexible poly pipe, hard PVC, or suction rated hose (minimum size 1.25 inches), Rainbird Maxi Paw heads.
6. Myers – HJ100S Irrigation Pump
Domain: diy.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Myers HJ100S irrigation pump; 20A/250V three-prong plug; wire colors: white (neutral), red (hot), black (hot), bare copper (grounding); terminals labeled L1 and L2.
7. Do It Yourself – Irrigation System Solutions
Domain: doityourself.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Irrigation system on a well pump, 12 zone sprinkler system, pressure settings at 30psi low end and 50psi high end, issues with pump cycling on and off, potential solutions include using a dedicated irrigation pump, ensuring proper sizing of pressure tank, and splitting system into multiple zones.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to install irrigation pump
To ensure a successful irrigation pump installation, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in optimizing resources and achieving operational efficiency. By carefully selecting reliable suppliers and manufacturers, businesses can secure high-quality pumps, necessary components, and support services that align with their specific irrigation needs. Understanding the technical requirements, such as pump capacity and system compatibility, is crucial for maximizing water efficiency and minimizing energy costs.
Moreover, international buyers should consider local market conditions and environmental factors that could influence the selection of irrigation systems. Collaborating with local experts can provide valuable insights into the best practices for installation and maintenance tailored to diverse geographical challenges, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As we look toward the future, the demand for efficient irrigation solutions will only grow, driven by the need for sustainable agriculture and resource conservation. We encourage B2B buyers to take proactive steps in sourcing the right irrigation pumps and systems. By investing in strategic partnerships and leveraging local expertise, you can enhance your operational capabilities and contribute to the resilience of agricultural practices in your region. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your irrigation projects and drive sustainable growth.