Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for how to prime an irrigation pump
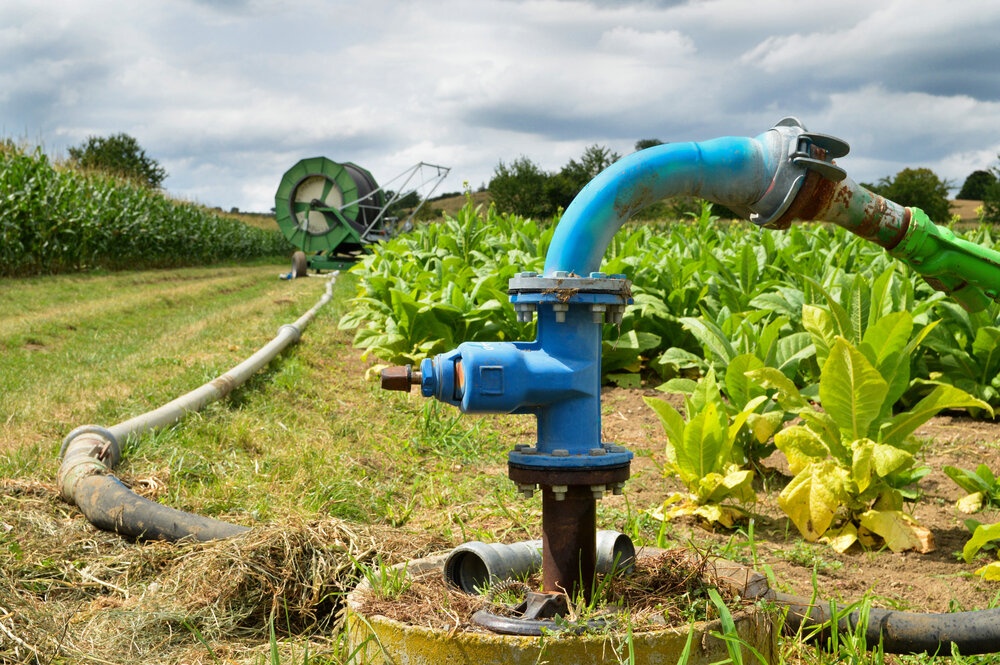
In the competitive landscape of global agriculture, one of the pivotal challenges faced by B2B buyers is understanding how to effectively prime an irrigation pump. Properly priming an irrigation pump is essential for ensuring the efficient delivery of water to crops, thus playing a critical role in agricultural productivity. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of irrigation pumps, including centrifugal and displacement models, and their specific applications across diverse agricultural settings.
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find valuable insights on how to select, maintain, and operate these pumps. We will explore the significance of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and best practices to ensure optimal performance.
By equipping decision-makers with actionable knowledge and practical steps for priming pumps, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. From understanding the nuances of different pump technologies to implementing effective maintenance strategies, we aim to enhance operational efficiency and drive success in irrigation practices globally. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your irrigation systems and secure a sustainable future for your agricultural endeavors.
Understanding how to prime an irrigation pump Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pumps | Utilize centrifugal force; common for irrigation; require priming. | Agricultural irrigation, landscaping | Pros: Efficient, widely available. Cons: Requires regular priming, can lose prime if not maintained. |
| Self-Priming Pumps | Designed to automatically remove air; no manual priming needed. | Residential and commercial irrigation systems | Pros: Saves time, reduces labor. Cons: Typically more expensive than standard pumps. |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Use a flexible diaphragm; can handle thick or viscous fluids. | Fertilizer application, chemical irrigation | Pros: Precise flow control, durable. Cons: Less common for standard water irrigation. |
| Submersible Pumps | Operate underwater; often used in deep wells; can be self-priming. | Well irrigation, deep-water applications | Pros: Efficient for deep water; no need for priming. Cons: Higher installation costs. |
| Positive Displacement Pumps | Move liquid by trapping a fixed amount and forcing it through. | Heavy-duty irrigation, industrial applications | Pros: High pressure and flow accuracy. Cons: More complex maintenance and higher costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Centrifugal Pumps for Irrigation?
Centrifugal pumps are the most commonly used type for irrigation systems due to their ability to efficiently move large volumes of water. They operate by converting rotational energy into kinetic energy, which propels water through the pump. These pumps typically require priming to eliminate air from the system, ensuring efficient operation. For B2B buyers, understanding the maintenance requirements and potential issues related to losing prime is crucial, particularly in regions with variable climates.
How Do Self-Priming Pumps Enhance Efficiency?
Self-priming pumps are designed to automatically expel air and maintain prime without manual intervention. This feature is particularly beneficial for B2B applications in residential and commercial irrigation, where time and labor savings are essential. While they may come at a higher initial cost, the reduced need for frequent maintenance and the convenience of automatic operation can justify the investment, especially for large-scale operations.
What Are the Advantages of Using Diaphragm Pumps?
Diaphragm pumps are characterized by their ability to handle a variety of fluids, including those that are thick or contain solids. This makes them suitable for applications like fertilizer application in agriculture. Their design allows for precise flow control, making them ideal for specialized irrigation tasks. Buyers should consider the specific fluid types they will be handling, as diaphragm pumps excel in scenarios that require durability and accuracy but may not be the best choice for standard water irrigation.
Why Choose Submersible Pumps for Deep Water Applications?
Submersible pumps are designed to operate underwater, making them ideal for deep well applications. They can be self-priming, eliminating the need for manual priming, which is advantageous in agricultural settings where water sources are deep. While the installation costs may be higher, their efficiency in pumping from significant depths makes them a valuable investment for businesses that rely on groundwater for irrigation.
What Makes Positive Displacement Pumps Suitable for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Positive displacement pumps are engineered to move liquid by trapping a specific volume and forcing it through the system, which allows for high-pressure and flow accuracy. They are commonly used in heavy-duty irrigation and industrial applications where precise control over fluid delivery is required. While they offer significant advantages in terms of performance, buyers must be aware of the complexities involved in their maintenance and the higher costs associated with their operation, making them more suitable for specialized applications.
Key Industrial Applications of how to prime an irrigation pump
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of how to prime an irrigation pump | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Priming pumps for crop irrigation systems | Ensures efficient water delivery, promoting healthy crop yields | Quality of materials, compatibility with existing systems, local climate considerations |
| Horticulture | Priming pumps for greenhouse irrigation | Optimizes water usage and plant health, reducing waste and costs | Energy efficiency, ease of maintenance, availability of parts |
| Landscape Management | Priming pumps for commercial landscaping projects | Enhances the aesthetic appeal and health of landscapes, leading to customer satisfaction | Pump capacity, durability under varying conditions, support services |
| Mining and Quarrying | Priming dewatering pumps in mining operations | Prevents water accumulation, ensuring operational efficiency and safety | Robustness for harsh environments, flow rate capabilities, supplier reliability |
| Sports and Recreation | Priming pumps for irrigation of sports fields | Maintains optimal playing conditions, enhancing user experience | Speed of priming, water conservation features, local support availability |
How is Priming an Irrigation Pump Used in Agriculture?
In agriculture, properly priming irrigation pumps is crucial for effective crop irrigation. This process ensures that water is readily available to crops, significantly impacting growth and yield. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local water availability and pump compatibility with existing systems is vital. The efficiency gained through effective priming can lead to reduced operational costs and improved crop health, making it an essential practice for any agricultural operation.
What Role Does Pump Priming Play in Horticulture?
In horticulture, the priming of irrigation pumps is essential for greenhouses and nurseries. Efficient water delivery helps maintain optimal moisture levels for plants, which is critical for their growth and health. For international buyers, especially in Europe, sourcing pumps that are energy-efficient and easy to maintain can lead to long-term cost savings. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding water usage can inform the selection of suitable pump systems.
How is Pump Priming Essential for Landscape Management?
Landscape management professionals rely on effective irrigation systems to maintain the health of commercial properties. Priming pumps ensures that water is delivered consistently, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of landscapes. B2B buyers must consider the pump’s capacity and durability to withstand varying weather conditions. Moreover, having reliable support services in place can minimize downtime and ensure that landscapes remain vibrant and well-maintained.
Why is Pump Priming Important in Mining and Quarrying?
In the mining and quarrying sectors, priming dewatering pumps is critical to prevent water accumulation, which can disrupt operations and pose safety risks. Properly primed pumps facilitate continuous water removal, ensuring that mining activities can proceed without interruption. Buyers in these industries should prioritize robust pumps that can handle harsh environments and high flow rates. Supplier reliability is also essential, as any delays in pump operation can lead to significant operational losses.
How Does Pump Priming Benefit Sports and Recreation Facilities?
For sports and recreation facilities, maintaining optimal playing conditions is vital, and this is where priming irrigation pumps comes into play. Properly primed pumps ensure that sports fields receive adequate water, enhancing grass health and user experience. Buyers should focus on the speed of priming and water conservation features, as these can lead to more sustainable operations. Local availability of support services is also a key consideration to ensure prompt maintenance and repairs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘how to prime an irrigation pump’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Assessing Pump Condition Before Priming
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers face challenges in evaluating the condition of their irrigation pumps prior to the priming process. This often leads to inefficiencies or complete operational failures. For instance, a farmer in South America might discover that their pump has developed cracks or leaks over the winter, but they only notice these issues after attempting to prime it. The result is wasted time, resources, and potential crop damage due to improper watering.
The Solution:
To avoid this scenario, it’s crucial to implement a routine inspection protocol as part of the pre-priming process. Buyers should develop a checklist that includes inspecting all pump components—valves, fittings, hoses, and electrical connections—for any signs of wear or damage. Investing in a thermal imaging camera can also help identify hidden leaks or overheating components that are not visible to the naked eye. By ensuring that all parts are in optimal condition before beginning the priming process, buyers can save time and prevent costly repairs later on.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Knowledge of Priming Procedures
The Problem:
A common pain point for B2B buyers is the lack of clear, actionable knowledge regarding the correct priming procedures for various types of irrigation pumps. For instance, an agricultural manager in Africa might struggle with priming a non-self-priming centrifugal pump due to insufficient training or resources. This lack of understanding can lead to improper priming, resulting in air locks that can damage the pump or disrupt water supply to vital crops.
The Solution:
To address this knowledge gap, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs for their staff, covering the specific priming procedures for different pump types. Creating detailed instructional materials, such as step-by-step guides or instructional videos, can also be beneficial. Furthermore, establishing a mentorship program where experienced technicians guide newer employees through the priming process can enhance practical knowledge. Such measures will ensure that all personnel are equipped with the skills necessary to prime pumps efficiently and effectively, thus optimizing irrigation operations.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Water Supply During Priming
The Problem:
Buyers often encounter difficulties when attempting to ensure an adequate water supply during the priming process. For instance, a vineyard owner in Europe may have a limited water source, and any inefficiencies in the priming process can lead to inadequate watering, affecting crop yield. If water cannot be consistently supplied to the pump during priming, air may be trapped, leading to pump failure or inefficiency.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, buyers should consider installing a dedicated water supply line specifically for the priming process. This line should be designed to provide a continuous flow of water to the pump without interruption. Additionally, implementing a temporary reservoir or water tank can serve as a buffer to ensure a steady supply during priming. Utilizing pressure gauges and flow meters can help monitor water levels and flow rates, allowing operators to adjust as necessary. By ensuring an uninterrupted water supply during priming, buyers can enhance the reliability and efficiency of their irrigation systems, ultimately leading to better crop management and productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for how to prime an irrigation pump
What Are the Best Materials for Priming an Irrigation Pump?
When selecting materials for priming an irrigation pump, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. Here, we will analyze four common materials used in this context: PVC, stainless steel, rubber, and polyethylene. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the efficiency and longevity of the irrigation system.
How Does PVC Perform in Irrigation Pump Priming?
Key Properties: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is known for its lightweight nature and excellent resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for various water conditions. It can typically handle pressures up to 150 PSI and operates effectively within a temperature range of 32°F to 140°F.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantages of PVC include low cost and ease of installation, as it can be easily cut and joined with solvent cement. However, its rigidity can be a disadvantage in applications where flexibility is required. Additionally, prolonged exposure to UV light can degrade PVC, which may be a concern in sunny regions.
Impact on Application: PVC is compatible with most water types, including potable water, making it a versatile choice. However, it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications, which could limit its use in certain climates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM and ISO. In Europe, adherence to DIN standards is essential. PVC is widely accepted globally, but buyers should verify the quality of the PVC to avoid issues with durability.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Pump Priming?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It can withstand high pressures (up to 300 PSI) and operates effectively in a wide temperature range, from -40°F to 800°F.
Pros & Cons: The durability and longevity of stainless steel make it an ideal choice for applications requiring high performance. However, it comes at a higher cost compared to other materials. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for various media, including aggressive chemicals and high-temperature fluids. Its robustness makes it ideal for industrial applications, but it may be overkill for simpler irrigation systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe may prefer stainless steel due to its compliance with stringent quality standards. It is essential to ensure that the grade of stainless steel used meets the specific requirements of the application.
How Does Rubber Contribute to Pump Priming?
Key Properties: Rubber is flexible and has excellent sealing properties, making it ideal for gaskets and seals in irrigation systems. It can handle temperatures ranging from -40°F to 212°F and is resistant to various chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility of rubber allows it to conform to irregular surfaces, providing a tight seal. However, it may degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and extreme temperatures, leading to potential leaks.
Impact on Application: Rubber is best suited for sealing applications within the pump system. It is not typically used for the main body of pipes but is crucial for ensuring airtight connections.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific type of rubber used, as different formulations may be required for varying climates and applications. Compliance with local standards is also vital for ensuring product quality.
What Advantages Does Polyethylene Offer for Priming?
Key Properties: Polyethylene is lightweight, flexible, and resistant to impact and corrosion. It can handle pressures up to 100 PSI and operates effectively within a temperature range of -40°F to 140°F.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility and low cost of polyethylene make it an attractive option for irrigation systems. However, it is less durable than PVC or stainless steel and may not withstand high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: Polyethylene is suitable for transporting water and other non-aggressive fluids. Its flexibility allows for easy installation in various terrains, but its lower pressure rating may limit its use in high-demand applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions with varying climates, such as Africa and South America, polyethylene’s adaptability makes it a popular choice. Compliance with local standards is essential, and buyers should ensure the material’s quality to prevent premature failure.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Priming Irrigation Pumps
| Material | Typical Use Case for how to prime an irrigation pump | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Suction pipes and fittings | Low cost and easy installation | UV degradation over time | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure applications | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Rubber | Seals and gaskets | Flexible and excellent sealing | Degradation due to UV exposure | Medium |
| Polyethylene | Water transport pipes | Lightweight and flexible | Lower durability and pressure rating | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for priming irrigation pumps, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for how to prime an irrigation pump
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Irrigation Pumps?
Understanding the manufacturing processes of irrigation pumps is essential for B2B buyers looking to invest in high-quality equipment. The manufacturing journey of these pumps typically encompasses several main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Irrigation Pumps?
The initial stage in the manufacturing process involves sourcing and preparing materials. Common materials used in irrigation pumps include cast iron, stainless steel, and thermoplastics. Each material is selected based on its properties, such as corrosion resistance and strength.
Once the materials are chosen, they undergo a series of inspections to ensure they meet industry standards. This may include checking for impurities, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties. Suppliers often utilize techniques like spectrochemical analysis to assess the composition of metals.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Irrigation Pumps?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into components of the pump. Techniques employed in this phase include casting, machining, and molding.
- Casting: For components like pump casings, casting is widely used. The molten metal is poured into molds and allowed to cool, forming the desired shape.
- Machining: After casting, components often require precision machining to meet exact specifications. This could include turning, milling, and drilling operations that enhance the accuracy of fit and function.
- Molding: For non-metal components, such as impellers made from thermoplastics, injection molding is a common technique. This method allows for complex shapes and high-volume production.
How Are Irrigation Pumps Assembled?
Once individual components are formed, they proceed to the assembly stage. This process typically involves:
- Component Inspection: Each part is inspected for quality and conformity to specifications.
- Sub-Assembly: Components are often pre-assembled into sub-units, such as the motor assembly or the impeller housing.
- Final Assembly: All sub-assemblies are then combined into the final product. This stage may involve the use of torque wrenches to ensure that fasteners are tightened to specified levels, preventing future operational issues.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Irrigation Pumps?
The finishing stage enhances both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the irrigation pumps. This may include:
- Surface Treatments: Techniques such as powder coating or galvanization protect against corrosion and wear.
- Quality Checks: Final inspections assess the overall appearance and functionality of the pumps. This may involve checking for leaks and verifying that all moving parts operate smoothly.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are In Place for Irrigation Pumps?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring the reliability and performance of irrigation pumps. Various international standards and industry-specific guidelines dictate the QA processes that manufacturers must follow.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding relevant international standards is crucial. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This globally recognized standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries, including pump manufacturing. Compliance ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates that a product meets health, safety, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly important for B2B buyers in the European market.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards that may be relevant for pumps used in oil and gas applications, ensuring safety and performance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is often segmented into different checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, checks are conducted to monitor the quality of the components being produced. This includes dimensional checks and functional testing.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the finished pumps undergo a series of tests to confirm they operate as intended. This may include pressure testing and performance evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent QC processes, B2B buyers can take several steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing practices, quality systems, and adherence to international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC processes, including defect rates and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
B2B buyers operating in diverse regions must navigate various quality control and certification nuances. For instance:
- Regional Regulations: Understanding local regulations and standards is vital, as they can vary significantly between regions like Africa and Europe. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local certifications required for irrigation pumps.
- Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and service. Engaging with local suppliers who understand these nuances can facilitate smoother transactions and ensure compliance with regional standards.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for irrigation pumps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable suppliers who meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘how to prime an irrigation pump’
Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Proper Pump Priming
Priming an irrigation pump is essential for optimal performance and longevity. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed for B2B buyers seeking to ensure that their irrigation systems operate efficiently. By following these steps, you can prevent costly downtime and ensure that your agricultural operations run smoothly.
Step 1: Assess Your Pump Type and Specifications
Understanding the type of irrigation pump you are working with is crucial. Different pumps, such as centrifugal or displacement pumps, have varying priming requirements. Knowing the specifications will help you choose the correct priming method and tools needed for the task.
- Sub-bullet: Ensure you have the manufacturer’s manual for precise guidance tailored to your pump model.
- Sub-bullet: Consider the pump’s capacity and the source of water to determine the volume of water needed for priming.
Step 2: Prioritize Safety Measures
Safety should always come first when working with irrigation pumps. Disconnect the power supply before starting any maintenance or priming process to prevent accidents.
- Sub-bullet: Use personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and goggles during the procedure.
- Sub-bullet: Ensure the area around the pump is dry and free from obstructions to minimize risks.
Step 3: Inspect Pump Components for Damage
Before attempting to prime, conduct a thorough inspection of the pump and associated piping. Look for any visible damage, such as cracks or leaks, which can hinder the priming process.
- Sub-bullet: Check drain plugs, fittings, and valves to ensure they are secure and functioning properly.
- Sub-bullet: Inspect belts and pulleys for wear, as these can affect pump performance.
Step 4: Prepare the Hose and Water Source
The hose and water source must be ready for priming to ensure a smooth operation. Ensure that the hose is clear of blockages and contaminants.
- Sub-bullet: Flush the hose with clean water before connecting it to the pump to remove any debris.
- Sub-bullet: Make sure the water source is adequate and accessible for the volume required for priming.
Step 5: Open Relief Valves and Attach Hose
To prevent pressure buildup during the priming process, open the relief valves before attaching the hose to the water source.
- Sub-bullet: Monitor the pressure gauge during this step to avoid any sudden pressure spikes.
- Sub-bullet: Ensure a secure connection to prevent leaks during the priming process.
Step 6: Fill the Pump and Check for Air Bubbles
Begin filling the pump with water slowly, allowing any trapped air to escape. This step is crucial for establishing the necessary pressure.
- Sub-bullet: Observe the water flow and gauge readings; a steady increase indicates successful filling.
- Sub-bullet: If air bubbles persist, you may need to repeat the filling process until the pump is fully primed.
Step 7: Restore Power and Monitor Performance
Once you have confirmed that the pump is filled and free of air, restore power and start the pump. Monitor its operation closely to ensure it runs smoothly.
- Sub-bullet: If the pump fails to start or stops shortly after, you may need to repeat the priming process.
- Sub-bullet: Regularly check for leaks and overall performance to maintain efficiency in your irrigation system.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure that their irrigation pumps are primed correctly, minimizing the risk of damage and optimizing operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for how to prime an irrigation pump Sourcing
When sourcing solutions for priming an irrigation pump, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for B2B buyers. This analysis provides insights into various cost components, price influencers, and strategic buyer tips, particularly relevant for international buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Priming an Irrigation Pump?
Materials: The primary materials involved include hoses, fittings, valves, and the pump itself. Quality materials can influence both initial costs and long-term durability. For instance, using corrosion-resistant materials may incur higher upfront costs but can reduce maintenance expenses over time.
Labor: Labor costs encompass the time required for installation and priming, which can vary significantly based on local labor rates. In regions with high labor costs, like parts of Europe, hiring skilled technicians may be necessary, whereas, in other regions, local labor might be more cost-effective.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and salaries of support staff. Understanding the manufacturing location can help buyers gauge the overhead costs that contribute to the final price.
Tooling: Specific tools may be required for priming, including wrenches and gauges. While these costs might seem negligible, they can add up, especially for larger operations requiring multiple pumps.
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the pumps function correctly and meet international standards. While this can increase costs, it also minimizes the risk of failures that could lead to costly downtime.
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the distance, mode of transport, and whether the supplier offers inclusive shipping terms. Buyers should be aware of the logistics costs associated with importing pumps, particularly when sourcing from overseas.
Margin: Suppliers often have different profit margins based on their market positioning, brand reputation, and the level of service they provide. Understanding these margins can assist buyers in negotiating better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Priming Equipment?
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically attract discounts. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers optimize their orders for cost savings.
Specifications and Customization: Custom pumps or specific configurations can significantly impact pricing. Buyers should assess whether they need customized solutions or if standard models suffice, as customization usually leads to higher costs.
Material Quality and Certifications: Pumps made from high-quality, certified materials tend to have a higher price tag. However, these can offer improved performance and longevity, which may justify the investment.
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and service quality can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and support services, but they often provide better long-term value.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms can clarify shipping responsibilities and costs. For international buyers, terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect total landed costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Buyers to Ensure Cost Efficiency?
Negotiate Terms and Pricing: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate prices and terms. Highlighting potential long-term relationships can often lead to better pricing structures.
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Factors such as maintenance, energy consumption, and lifespan play crucial roles in the total cost over time. Investing in higher-quality pumps may yield savings in the long run.
Research Local Market Conditions: Understanding local pricing dynamics and labor costs can provide leverage when negotiating with suppliers. Buyers should also be aware of currency fluctuations that might affect pricing.
Leverage Group Purchasing: Collaborating with other buyers to place bulk orders can lead to significant discounts. This approach is especially effective in regions where irrigation needs are shared among multiple farmers or businesses.
Stay Informed About Industry Trends: Keeping abreast of technological advancements and market trends can help buyers make informed decisions about equipment that offers the best value and efficiency.
In conclusion, B2B buyers looking to prime irrigation pumps should consider these multifaceted cost structures and pricing strategies. By understanding the key components, price influencers, and best practices, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing how to prime an irrigation pump With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Priming an Irrigation Pump
In the realm of agricultural irrigation, priming an irrigation pump is a critical process that ensures efficient water delivery. However, several alternative methods and technologies can achieve similar outcomes without the traditional priming steps. Understanding these alternatives can help international B2B buyers select the most suitable solution for their specific irrigation needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | How To Prime An Irrigation Pump | Self-Priming Pumps | Suction Pumps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Requires manual effort; effective with proper technique | Automatically primes; consistent performance | Effective for shallow water sources; limited depth capability |
| Cost | Generally low upfront cost; potential for labor costs | Higher initial investment; reduced labor costs over time | Moderate cost; maintenance can add to expenses |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward, but requires knowledge and physical effort | Simple installation; no manual priming needed | Requires specific installation; may need professional setup |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed; prone to wear and tear | Low maintenance; designed for durability | Moderate maintenance; susceptible to debris |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for seasonal use; small to medium-scale operations | Best for consistent and frequent use; larger operations | Suitable for shallow wells or ponds; limited irrigation needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Self-Priming Pumps
Self-priming pumps offer a significant advantage over traditional priming methods as they automatically remove air from the system and create a vacuum to draw water without manual intervention. This feature not only saves time but also reduces labor costs, making it an appealing choice for larger agricultural operations that require consistent water supply. However, the initial investment is higher compared to non-self-priming pumps, and while maintenance is generally low, any mechanical failure can lead to downtime.
Suction Pumps
Suction pumps are another alternative, particularly effective for shallow water sources such as ponds and wells. They operate by creating a vacuum that pulls water into the pump. While suction pumps are typically less expensive and simpler to maintain, their effectiveness diminishes with increased depth. This limitation makes them less suitable for areas where water sources are deeper than the pump’s capacity. Additionally, they may require regular maintenance to ensure that debris does not clog the system.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Irrigation Needs
When selecting the right irrigation solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, including the depth of water sources, the scale of irrigation needed, and budget constraints. Self-priming pumps are ideal for operations requiring consistent water flow without manual priming, while suction pumps are suitable for shallow applications. Understanding these alternatives and their respective advantages and disadvantages will empower buyers to make informed decisions that enhance their irrigation efficiency and ultimately support their agricultural productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for how to prime an irrigation pump
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Irrigation Pumps?
Understanding the technical properties of irrigation pumps is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
Material Grade
– Definition: The material grade of the pump components (such as casing, impeller, and seals) indicates their resistance to corrosion, wear, and pressure.
– B2B Importance: High-grade materials, such as stainless steel or high-density polyethylene, enhance durability and reduce maintenance costs, making them essential for buyers focused on long-term investment.Flow Rate
– Definition: The flow rate measures the volume of water the pump can move per unit time, typically expressed in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per second (L/s).
– B2B Importance: Knowing the required flow rate is vital for selecting the right pump for specific irrigation needs, ensuring efficient water distribution and minimizing energy consumption.Pressure Rating
– Definition: This specification indicates the maximum pressure the pump can handle, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bars.
– B2B Importance: A pump with an appropriate pressure rating is essential for overcoming elevation changes in irrigation systems, ensuring water reaches the desired areas without loss of efficiency.Power Requirements
– Definition: This refers to the electrical or mechanical energy needed to operate the pump, typically measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW).
– B2B Importance: Understanding power requirements helps in selecting compatible energy sources and managing operational costs, particularly in regions with varying electricity costs.Self-Priming Capability
– Definition: This property indicates whether the pump can automatically remove air from the system to start water flow without manual priming.
– B2B Importance: Self-priming pumps reduce labor and operational downtime, appealing to buyers looking for efficiency and ease of use in their irrigation systems.Efficiency Rating
– Definition: This rating measures how effectively the pump converts electrical energy into hydraulic energy, often expressed as a percentage.
– B2B Importance: Higher efficiency ratings lead to lower operating costs and energy consumption, making such pumps more attractive to cost-conscious buyers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Priming Irrigation Pumps?
Navigating the B2B landscape requires familiarity with specific jargon and trade terms. Here are some key terms related to irrigation pumps:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Buyers often prefer OEM parts for reliability and compatibility, ensuring that their irrigation systems function optimally.MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is critical for budgeting and inventory planning, particularly for larger B2B purchases.RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs can help buyers compare costs and negotiate better deals, ensuring they get the best value for their investment.Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: These are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers for the delivery of goods.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international buyers to understand shipping costs, risk, and insurance responsibilities.Lead Time
– Definition: This refers to the amount of time from placing an order until the product is delivered.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time helps buyers plan their irrigation projects and manage expectations around delivery schedules.Warranty Period
– Definition: This term indicates the duration during which a manufacturer guarantees the performance of their product against defects.
– Importance: A robust warranty period can provide buyers with peace of mind and reduce long-term costs associated with repairs or replacements.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions when selecting and priming irrigation pumps.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the how to prime an irrigation pump Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing the Irrigation Pump Sector?
The irrigation pump market is experiencing significant growth driven by a combination of global agricultural demands and technological advancements. As water scarcity becomes a pressing issue, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, efficient irrigation solutions are increasingly sought after. The rise of precision agriculture is leading to the adoption of advanced pumping technologies that enhance water management, thereby maximizing crop yields and minimizing waste. Additionally, the trend towards automation in farming practices is pushing B2B buyers to seek irrigation pumps that can integrate with smart irrigation systems, offering real-time monitoring and control capabilities.
Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled pumps are becoming more prevalent, allowing for remote management and diagnostics. This is particularly appealing to international buyers in South America and Europe, where operational efficiency and resource management are critical. Moreover, the global push for sustainability is prompting manufacturers to innovate, focusing on energy-efficient designs and self-priming capabilities that reduce manual intervention. As these dynamics unfold, B2B buyers must stay informed about product specifications and supplier capabilities to ensure they select the right systems for their specific agricultural needs.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Irrigation Pumps?
Sustainability is a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the irrigation pump sector. With increasing awareness of environmental impacts, businesses are prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing practices and environmental stewardship. The use of ‘green’ certifications, such as Energy Star or ISO 14001, is becoming a standard requirement for procurement, ensuring that products not only meet performance expectations but also contribute to reducing carbon footprints.
Moreover, buyers are increasingly interested in materials that are recyclable or have minimal environmental impact during their lifecycle. This trend is particularly significant in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent regarding environmental compliance. In Africa and South America, where agricultural practices are evolving, there is a growing demand for sustainable solutions that can enhance resilience to climate change while also being economically viable.
By aligning purchasing decisions with sustainability goals, businesses can not only improve their corporate social responsibility profiles but also benefit from cost savings associated with energy-efficient technologies. B2B buyers must evaluate their supply chains and consider the sustainability credentials of their suppliers to enhance their competitive advantage in the market.
What Is the Historical Context of Irrigation Pump Technology?
The evolution of irrigation pump technology can be traced back to ancient civilizations that relied on rudimentary systems for water distribution. Over the centuries, advancements in engineering led to the development of more sophisticated pumps, such as centrifugal and displacement pumps, which are now prevalent in modern agriculture. The introduction of electric and diesel-powered pumps in the 20th century revolutionized irrigation practices, allowing for greater efficiency and scalability.
In recent years, the integration of digital technologies has marked a significant turning point in the sector. The rise of smart irrigation systems, driven by IoT and data analytics, is transforming how irrigation pumps are utilized, enabling farmers to optimize water usage based on real-time data. This historical progression highlights the importance of continuous innovation in meeting the evolving needs of agricultural markets worldwide, particularly as they face challenges related to climate change and resource management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of how to prime an irrigation pump
How do I prime a non-self-priming irrigation pump?
To prime a non-self-priming irrigation pump, start by ensuring the pump is powered off. Access the pump system, typically through a valve near the water source. Inspect for any damage or leaks in the pump and piping. Open the relief valves to prevent pressure buildup, then connect a hose to your water source and turn on the water. Fill the pump and suction pipe until water flows freely from the hose, indicating it is full. Finally, restore power and allow the pump to run for about a minute while monitoring for proper operation.What is the best irrigation pump type for my agricultural needs?
The best type of irrigation pump for your agricultural needs depends on various factors, including the size of your operation, the water source, and the types of crops. Centrifugal pumps are typically preferred for their efficiency in moving large volumes of water, while displacement pumps may be suitable for specific applications involving thicker liquids. Evaluate your water source’s depth, required pressure, and flow rate to determine the most effective pump type for optimal irrigation results.How can I ensure the quality of irrigation pumps from international suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing irrigation pumps from international suppliers, conduct thorough research on potential vendors. Look for certifications such as ISO standards, which indicate compliance with quality management practices. Request product samples and performance documentation, and verify references from previous clients. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer warranties and robust customer service, as these factors can indicate reliability and commitment to quality.What are the common payment terms for purchasing irrigation pumps internationally?
Common payment terms for international purchases of irrigation pumps may include options such as letters of credit, advance payment, or payment upon delivery. Terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your buyer-seller relationship. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that protect both parties, ensuring that payments are contingent upon meeting quality and delivery timelines. Always clarify the currency and method of payment to avoid misunderstandings.What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for irrigation pumps from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for irrigation pumps can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the pump type. Generally, larger suppliers may have higher MOQs to offset production costs, while smaller manufacturers might offer lower MOQs to attract diverse buyers. When negotiating, consider your actual needs and the supplier’s flexibility. In some cases, it may be beneficial to consolidate orders with other buyers to meet MOQ requirements while reducing overall costs.How can I assess the logistics involved in importing irrigation pumps?
To assess logistics for importing irrigation pumps, start by evaluating shipping options based on your location and supplier’s capabilities. Consider factors like freight costs, delivery times, and customs regulations in your country. Collaborate with a logistics provider experienced in handling agricultural equipment to streamline the process. Additionally, ensure that you account for potential delays due to customs clearance, especially when importing from regions with strict regulations.What quality assurance measures should I consider when sourcing irrigation pumps?
When sourcing irrigation pumps, implement quality assurance measures such as pre-shipment inspections and third-party testing. Verify that the pumps meet industry standards and specifications relevant to your region. Establish communication with the supplier to understand their quality control processes, including material sourcing and manufacturing practices. It’s also beneficial to review warranty policies and after-sales support, as these can indicate the supplier’s commitment to product quality.How do I troubleshoot common issues with irrigation pumps?
Common issues with irrigation pumps include insufficient pressure, unusual noises, or failure to start. Begin troubleshooting by checking the power supply and ensuring the pump is properly primed. Inspect for leaks or blockages in the intake hose and filter. For centrifugal pumps, ensure that the relief valves are functioning correctly. If problems persist, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or engage a qualified technician to diagnose and resolve more complex mechanical issues.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 How To Prime An Irrigation Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Water Pumping Guide
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – Water Pumping Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. TWL – Smart Irrigation Solutions
Domain: twl-irrigation.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Featured Products: Weather Station IOT-S300WS7, Power Gulp 18 Volt Pump w/MudGuard & Battery Plate, TW/NG-1 2 Wire Irrigation Decoder, Internet Controller RM-2 Rainmaker 4G (available in 1, 2, 3, and 4 Zones).
3. Do It Yourself – Lawn Irrigation Pump
Domain: doityourself.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Lawn irrigation pump, water source from pond, requires priming, process involves unscrewing the top part of the pump, filling with clean water until hose is filled, ensuring output valve is open, and plugging the unit in. Rainbird controller located in basement.
4. NewAgTalk – Air-Powered Pump Primer
Domain: talk.newagtalk.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Air-powered pump primer developed for the manure industry; requires a larger CFM compressor to create a vacuum; commonly used with a 185 CFM compressor; designed to help prime irrigation pumps by sucking water up from the well; can be used with a pitcher pump style primer; includes a video demonstration on the manufacturer’s website.
5. DIY Chatroom – Irrigation Pump Solutions
Domain: diychatroom.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Irrigation pump, shallow well, one line suction, check valve installed about 1 foot from pump on suction side, potential crack in suction line, pressure fluctuations, self-priming capability, two well points.
6. AN PUMP – Centrifugal Irrigation Pumps
Domain: angroupcn.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: AN PUMP supplies a variety of centrifugal irrigation pumps, including: end suction pump, split case pump, multistage pump, mixed flow pump, and self-priming pump. These pumps can be equipped with either diesel engines or electric motors and can be directly connected with couplings or pulleys. The company offers many options for customers to choose from.
7. The Farming Forum – Electric Pump Solutions
Domain: thefarmingforum.co.uk
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Electric pump for priming main pump, exhaust powered primer (£2500), hand suction pump, foot valve, Caprari pump.
8. JustAnswer – Lawn Sprinkler Pump Priming Guide
Domain: justanswer.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: How to Prime a Lawn Sprinkler Pump: Step-by-Step Guide. Lawn sprinkler pumps often face airlocks and failure to build proper suction. To prime a lawn sprinkler pump, first ensure the pump housing is filled with water. Open the priming port or cap and pour water in until full. Close the port securely to prevent air entry. Check all suction hoses for leaks or cracks that can introduce air. Turn on t…
9. Terry Love – Irrigation Well Pump & PVC Piping
Domain: terrylove.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Irrigation well pump, 2″ PVC piping, 1 1/2″ PVC coupling, check valve.
10. ABI – Electric Irrigation Pump Primer
Domain: abi-irrigation.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Irrigation Pump Primer – Electric Primer Pump | ABI Irrigation
Key Features:
– Available in DC, AC, and Hand Pump Priming units for various applications.
– Ideal for irrigation and slurry pumps, pivots, and more.
– ABI Perfect Primers designed for fast, reliable priming in installations with high suction lifts or long suction lines.
– AC or DC units suitable for propane, natural gas, PTO, and die…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for how to prime an irrigation pump
In conclusion, successfully priming an irrigation pump is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring efficient water distribution. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of pump types—such as centrifugal versus displacement—and the priming process can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Strategic sourcing of high-quality irrigation pumps and accessories plays a vital role in optimizing your irrigation systems. By investing in reliable, self-priming pumps or ensuring proper maintenance of existing equipment, businesses can mitigate risks associated with water scarcity and maximize agricultural productivity.
As you move forward, consider the long-term benefits of investing in durable irrigation solutions tailored to your specific environmental and operational needs. Engage with trusted suppliers who can offer not only products but also expert guidance on best practices for pump maintenance and priming. Take proactive steps today to secure a sustainable and efficient irrigation future for your agricultural endeavors.